Regenerative agriculture investing focuses on restoring soil health, increasing biodiversity, and enhancing carbon sequestration through sustainable farming practices, while climate tech investing targets innovations that reduce greenhouse gas emissions via renewable energy, energy storage, and carbon capture technologies. Both sectors aim to combat climate change but differ in approach, timescale, and impact metrics. Discover how these investment strategies compare and contribute to a sustainable future.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between regenerative agriculture investing and climate tech investing is crucial because each targets distinct environmental outcomes and sectors. Regenerative agriculture investing focuses on enhancing soil health, biodiversity, and carbon sequestration through sustainable farming practices that restore ecosystems. Climate tech investing prioritizes innovations like renewable energy, carbon capture, and emission reduction technologies to combat climate change on a technological front. This knowledge helps investors align portfolios with specific impact goals, risk profiles, and market opportunities within the rapidly evolving green economy.
Comparison Table
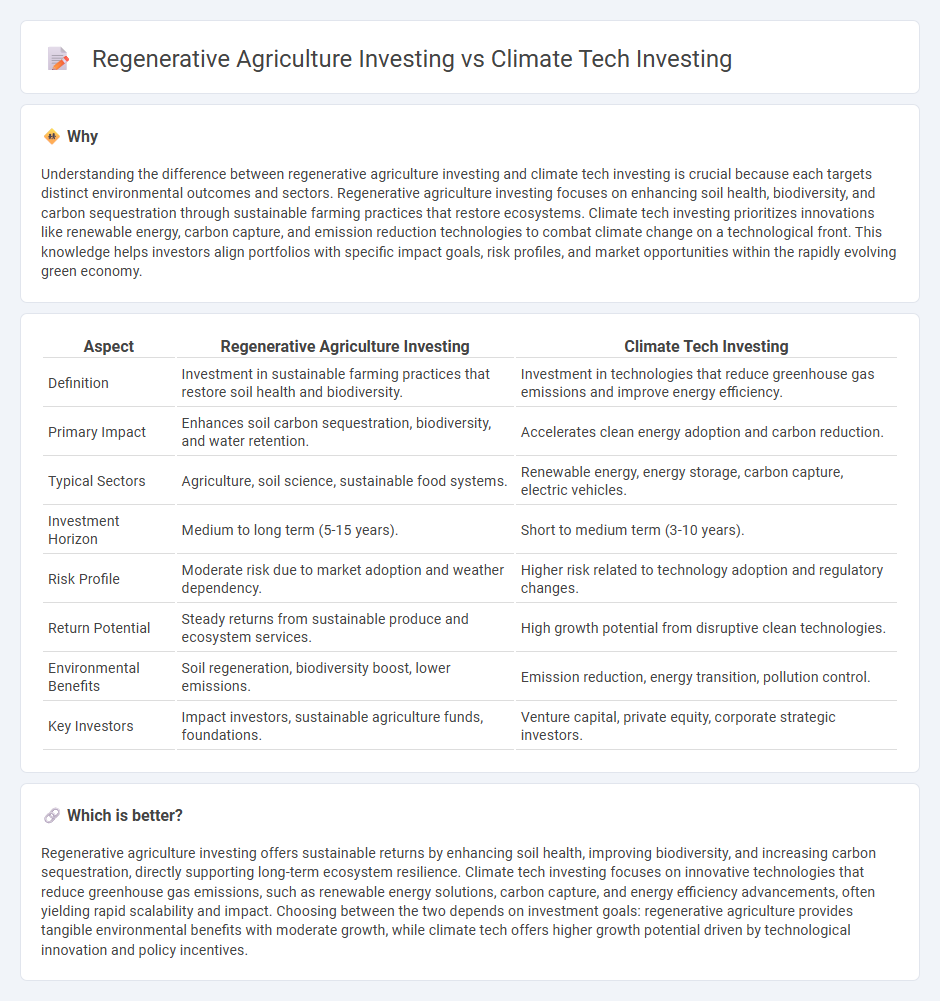
| Aspect | Regenerative Agriculture Investing | Climate Tech Investing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Investment in sustainable farming practices that restore soil health and biodiversity. | Investment in technologies that reduce greenhouse gas emissions and improve energy efficiency. |
| Primary Impact | Enhances soil carbon sequestration, biodiversity, and water retention. | Accelerates clean energy adoption and carbon reduction. |
| Typical Sectors | Agriculture, soil science, sustainable food systems. | Renewable energy, energy storage, carbon capture, electric vehicles. |
| Investment Horizon | Medium to long term (5-15 years). | Short to medium term (3-10 years). |
| Risk Profile | Moderate risk due to market adoption and weather dependency. | Higher risk related to technology adoption and regulatory changes. |
| Return Potential | Steady returns from sustainable produce and ecosystem services. | High growth potential from disruptive clean technologies. |
| Environmental Benefits | Soil regeneration, biodiversity boost, lower emissions. | Emission reduction, energy transition, pollution control. |
| Key Investors | Impact investors, sustainable agriculture funds, foundations. | Venture capital, private equity, corporate strategic investors. |
Which is better?
Regenerative agriculture investing offers sustainable returns by enhancing soil health, improving biodiversity, and increasing carbon sequestration, directly supporting long-term ecosystem resilience. Climate tech investing focuses on innovative technologies that reduce greenhouse gas emissions, such as renewable energy solutions, carbon capture, and energy efficiency advancements, often yielding rapid scalability and impact. Choosing between the two depends on investment goals: regenerative agriculture provides tangible environmental benefits with moderate growth, while climate tech offers higher growth potential driven by technological innovation and policy incentives.
Connection
Regenerative agriculture investing enhances soil health and carbon sequestration, directly supporting climate tech advancements focused on reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Climate tech investing develops innovative technologies such as carbon capture and renewable energy systems that amplify the environmental benefits of regenerative farming practices. Together, these investment avenues create synergistic effects driving sustainable agriculture and climate resilience.
Key Terms
**Climate Tech Investing:**
Climate tech investing targets advanced technologies that reduce greenhouse gas emissions and enhance environmental sustainability, including renewable energy, carbon capture, and energy-efficient solutions. This sector attracts significant venture capital due to its potential for scalable impact on global climate change mitigation. Explore how these innovations drive economic growth while addressing urgent environmental challenges.
Carbon Capture
Investing in climate tech, particularly carbon capture technologies, targets innovative solutions that extract and store CO2 directly from the atmosphere or industrial emissions, playing a critical role in reducing global greenhouse gas levels. In contrast, regenerative agriculture investing emphasizes soil health improvement and carbon sequestration through natural processes like cover cropping and reduced tillage, thus enhancing ecosystem resilience while lowering atmospheric CO2. Explore the comparative benefits and growth opportunities of carbon capture within these sectors to understand their impact on climate mitigation strategies.
Clean Energy
Clean energy investments in climate tech emphasize innovations such as solar, wind, and battery storage technologies that reduce carbon emissions and foster sustainable power generation. Regenerative agriculture investing integrates clean energy by promoting bioenergy solutions and enhancing carbon sequestration through advanced farming practices. Explore how clean energy drives transformative impacts in both sectors and discover strategic opportunities for sustainable investing.
Source and External Links
US Climate Tech Investment Achieves Six Straight Months of Growth - Venture capital investment in US climate tech is recovering with growth sustained for six months, driven by energy, manufacturing, and carbon tech sectors, and early-stage funding remains resilient despite fundraising challenges.
State of Climate Tech 2024 - Climate tech investment has declined overall since its peak but remains strong in the US, particularly boosted by the Inflation Reduction Act and AI-related climate ventures, while large corporations play a crucial role in later-stage funding and scaling innovations.
The Future of Climate Tech 2025 - In 2024, $7.6 billion VC was invested into US clean energy and power companies with early-stage startups comprising 75% of deals, reflecting a strong pipeline for future climate innovation despite increasing needs for capital raises.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com