Crowdlending platforms offer direct peer-to-peer loans, often providing higher returns with increased risk compared to traditional bonds issued by governments or corporations. Bonds typically guarantee fixed periodic interest payments and principal repayment at maturity, making them a more stable investment choice. Explore the differences between crowdlending and bonds to optimize your investment strategy.
Why it is important
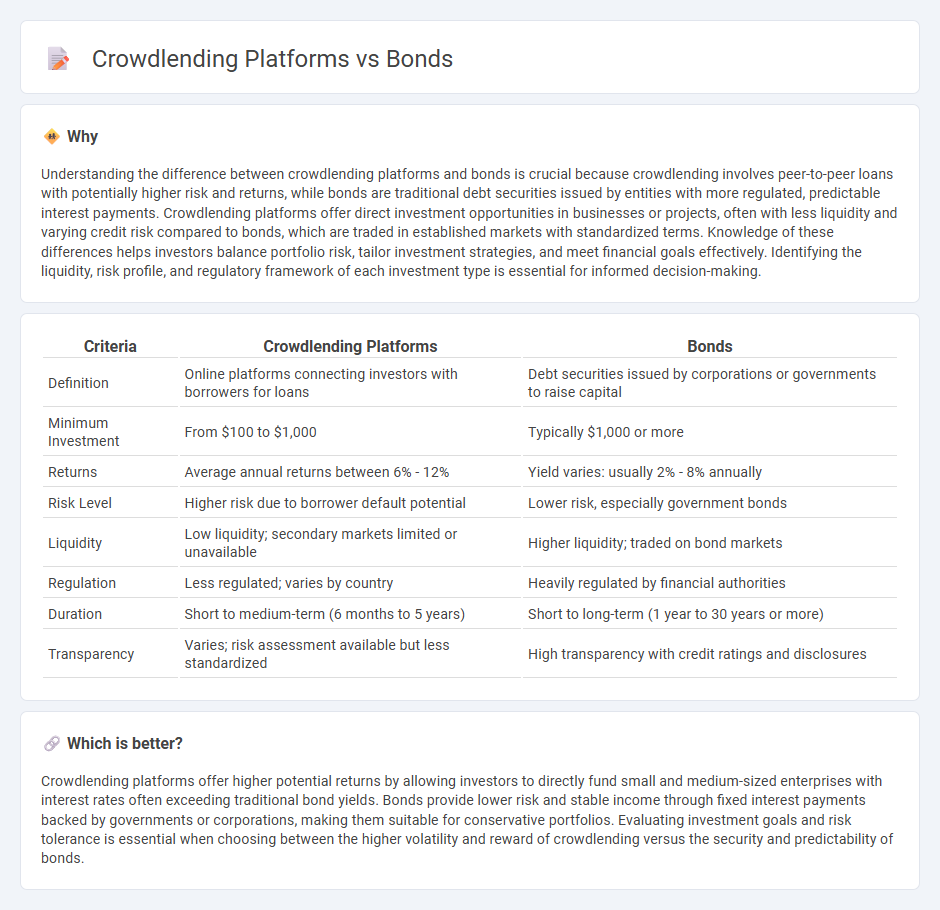
Understanding the difference between crowdlending platforms and bonds is crucial because crowdlending involves peer-to-peer loans with potentially higher risk and returns, while bonds are traditional debt securities issued by entities with more regulated, predictable interest payments. Crowdlending platforms offer direct investment opportunities in businesses or projects, often with less liquidity and varying credit risk compared to bonds, which are traded in established markets with standardized terms. Knowledge of these differences helps investors balance portfolio risk, tailor investment strategies, and meet financial goals effectively. Identifying the liquidity, risk profile, and regulatory framework of each investment type is essential for informed decision-making.
Comparison Table
| Criteria | Crowdlending Platforms | Bonds |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Online platforms connecting investors with borrowers for loans | Debt securities issued by corporations or governments to raise capital |
| Minimum Investment | From $100 to $1,000 | Typically $1,000 or more |
| Returns | Average annual returns between 6% - 12% | Yield varies: usually 2% - 8% annually |
| Risk Level | Higher risk due to borrower default potential | Lower risk, especially government bonds |
| Liquidity | Low liquidity; secondary markets limited or unavailable | Higher liquidity; traded on bond markets |
| Regulation | Less regulated; varies by country | Heavily regulated by financial authorities |
| Duration | Short to medium-term (6 months to 5 years) | Short to long-term (1 year to 30 years or more) |
| Transparency | Varies; risk assessment available but less standardized | High transparency with credit ratings and disclosures |
Which is better?
Crowdlending platforms offer higher potential returns by allowing investors to directly fund small and medium-sized enterprises with interest rates often exceeding traditional bond yields. Bonds provide lower risk and stable income through fixed interest payments backed by governments or corporations, making them suitable for conservative portfolios. Evaluating investment goals and risk tolerance is essential when choosing between the higher volatility and reward of crowdlending versus the security and predictability of bonds.
Connection
Crowdlending platforms and bonds both serve as fixed-income investment vehicles that allow investors to earn interest by lending capital to borrowers. Crowdlending offers peer-to-peer loans typically to small businesses or individuals, while bonds represent debt securities issued by corporations or governments. Both provide predictable cash flows through periodic interest payments and principal repayment, making them integral components of diversified investment portfolios.
Key Terms
Yield
Bonds typically offer fixed yields determined by credit ratings and market interest rates, providing predictable income for investors seeking stability. Crowdlending platforms often present higher yields by funding diverse SMEs and startups, albeit with increased risk due to borrower default potential and platform reliability. Explore our in-depth analysis to understand which investment aligns with your yield expectations and risk tolerance.
Risk Profile
Bonds typically offer lower risk due to issuer credit ratings and regulatory oversight, with predictable interest payments and principal repayment at maturity. Crowdlending platforms present higher risk through borrower defaults and platform solvency but often provide higher yields and portfolio diversification across multiple loans. Explore detailed risk comparisons and investment strategies to optimize your portfolio allocation.
Liquidity
Bonds typically offer higher liquidity with established secondary markets allowing investors to buy and sell easily, whereas crowdlending platforms often involve longer lock-in periods with limited or no secondary trading options. The liquidity of bonds is supported by regulatory frameworks and wide investor bases, contrasting with the nascent and less liquid nature of most crowdlending markets. Explore further to understand how liquidity impacts investment strategies in bonds and crowdlending.
Source and External Links
Bonds | Investor.gov - Bonds are debt securities where investors lend money to issuers such as governments or corporations, receiving fixed interest payments and the return of principal at maturity, providing a predictable income and capital preservation option.
Bond (finance) - Wikipedia - Bonds function as loans to issuers, are typically less volatile than stocks, are widely held by institutions for liability matching, and offer bondholders legal protections in case of issuer bankruptcy.
What is a Bond and How do they Work? - Vanguard - Bonds provide income through periodic interest payments, do not grant ownership rights unlike stocks, and serve to reduce portfolio volatility while offering a return of principal on a set maturity date.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com