Pay-as-you-drive insurance charges premiums based on the actual miles driven, offering cost savings for low-mileage drivers by using odometer readings or GPS data. Usage-based insurance utilizes telematics technology to monitor driving behaviors such as speed, acceleration, and braking patterns, allowing insurers to tailor rates based on risk factors. Explore the differences between these models to determine which pay-as-you-go option aligns best with your driving habits.
Why it is important
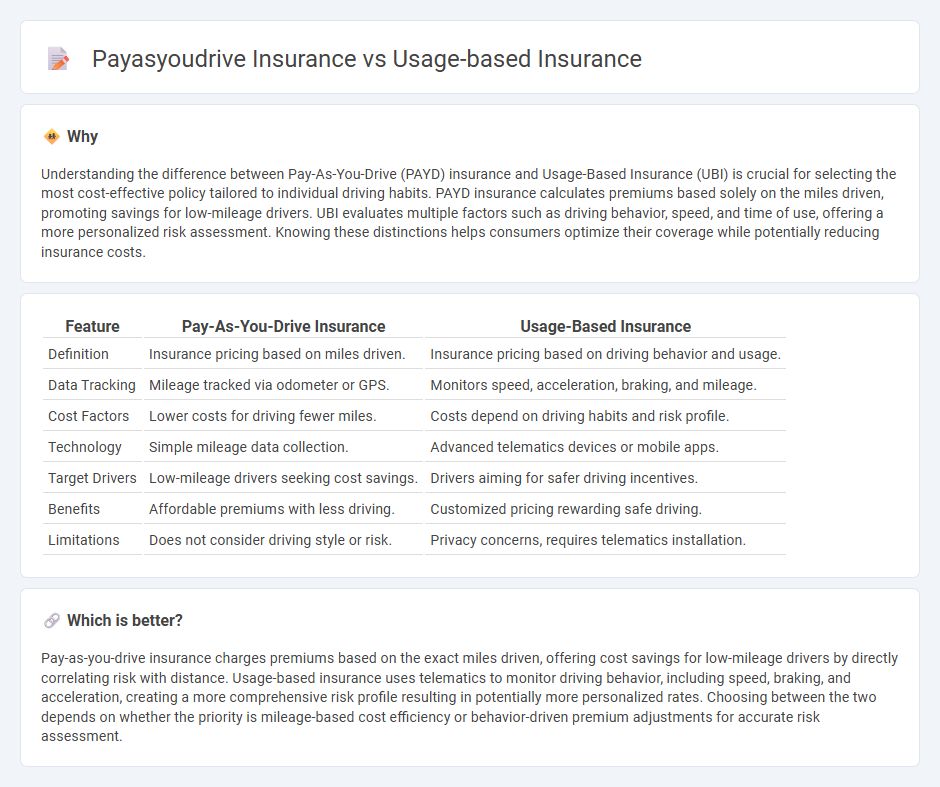
Understanding the difference between Pay-As-You-Drive (PAYD) insurance and Usage-Based Insurance (UBI) is crucial for selecting the most cost-effective policy tailored to individual driving habits. PAYD insurance calculates premiums based solely on the miles driven, promoting savings for low-mileage drivers. UBI evaluates multiple factors such as driving behavior, speed, and time of use, offering a more personalized risk assessment. Knowing these distinctions helps consumers optimize their coverage while potentially reducing insurance costs.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Pay-As-You-Drive Insurance | Usage-Based Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Insurance pricing based on miles driven. | Insurance pricing based on driving behavior and usage. |
| Data Tracking | Mileage tracked via odometer or GPS. | Monitors speed, acceleration, braking, and mileage. |
| Cost Factors | Lower costs for driving fewer miles. | Costs depend on driving habits and risk profile. |
| Technology | Simple mileage data collection. | Advanced telematics devices or mobile apps. |
| Target Drivers | Low-mileage drivers seeking cost savings. | Drivers aiming for safer driving incentives. |
| Benefits | Affordable premiums with less driving. | Customized pricing rewarding safe driving. |
| Limitations | Does not consider driving style or risk. | Privacy concerns, requires telematics installation. |
Which is better?
Pay-as-you-drive insurance charges premiums based on the exact miles driven, offering cost savings for low-mileage drivers by directly correlating risk with distance. Usage-based insurance uses telematics to monitor driving behavior, including speed, braking, and acceleration, creating a more comprehensive risk profile resulting in potentially more personalized rates. Choosing between the two depends on whether the priority is mileage-based cost efficiency or behavior-driven premium adjustments for accurate risk assessment.
Connection
Pay-as-you-drive (PAYD) insurance is a type of usage-based insurance (UBI) where premiums are calculated based on the actual miles driven, promoting safer and reduced driving habits. Usage-based insurance leverages telematics technology to monitor driving behavior, including speed, acceleration, and braking patterns, to personalize risk assessment and pricing. Both PAYD and UBI aim to align insurance costs with individual driving patterns, enhancing fairness while encouraging responsible driving.
Key Terms
Telematics
Usage-based insurance (UBI) and pay-as-you-drive (PAYD) insurance both rely on telematics technology to monitor driving behavior, but UBI incorporates a broader range of data points such as speed, acceleration, and braking patterns, while PAYD primarily focuses on the distance driven. Telematics devices collect real-time information through GPS and onboard diagnostics, enabling insurers to tailor premiums based on actual driving habits, enhancing risk assessment and cost savings. Explore how telematics transforms insurance models and benefits both drivers and providers by learning more about UBI and PAYD.
Premium calculation
Usage-based insurance calculates premiums based on real-time driving data such as distance traveled, driving behavior, and frequency of trips monitored through telematics devices. Pay-as-you-drive insurance specifically focuses on mileage, with premiums directly proportional to the miles driven, incentivizing lower vehicle use. Explore how these models optimize premium accuracy and cost efficiency for personalized coverage.
Mileage tracking
Usage-based insurance (UBI) relies on comprehensive driving behavior data including mileage, speed, and braking patterns, whereas pay-as-you-drive (PAYD) insurance primarily focuses on tracking mileage to calculate premiums. Mileage tracking in PAYD offers straightforward pricing based solely on miles driven, providing cost savings for low-mileage drivers, while UBI delivers more personalized rates by analyzing a broader range of driving habits. Discover how these mileage tracking methods can impact your insurance costs and coverage options.
Source and External Links
Usage-Based Car Insurance | Progressive - Usage-based insurance helps calculate auto insurance rates by analyzing driving habits, offering potential discounts based on safe driving behaviors.
Usage-based insurance | Office of the Insurance Commissioner - Usage-based insurance involves tracking driving behavior to determine premiums, often using devices or apps to monitor factors like speed and acceleration.
Want Your Auto Insurer to Track Your Driving? Understanding Usage-Based Insurance - Usage-based insurance (UBI) uses data on driving behavior to personalize auto policy premiums, potentially offering discounts for safe and efficient driving habits.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com