Insurance as a service offers personalized coverage plans through digital platforms, enabling flexible policies and real-time risk management for individuals and businesses. Mutual insurance operates on a cooperative model where policyholders are also owners, sharing profits and losses, often resulting in lower premiums and a focus on member benefits. Explore more to understand which insurance model best fits your needs.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between insurance as a service and mutual insurance is crucial for selecting the right coverage model that aligns with individual or business needs. Insurance as a service typically offers standardized policies through centralized providers, emphasizing convenience and a wide range of products. Mutual insurance is owned by policyholders, focusing on shared risks and dividends, which can lead to lower costs and more personalized service. Choosing the appropriate type affects financial security, customer rights, and the overall value derived from the insurance contract.
Comparison Table
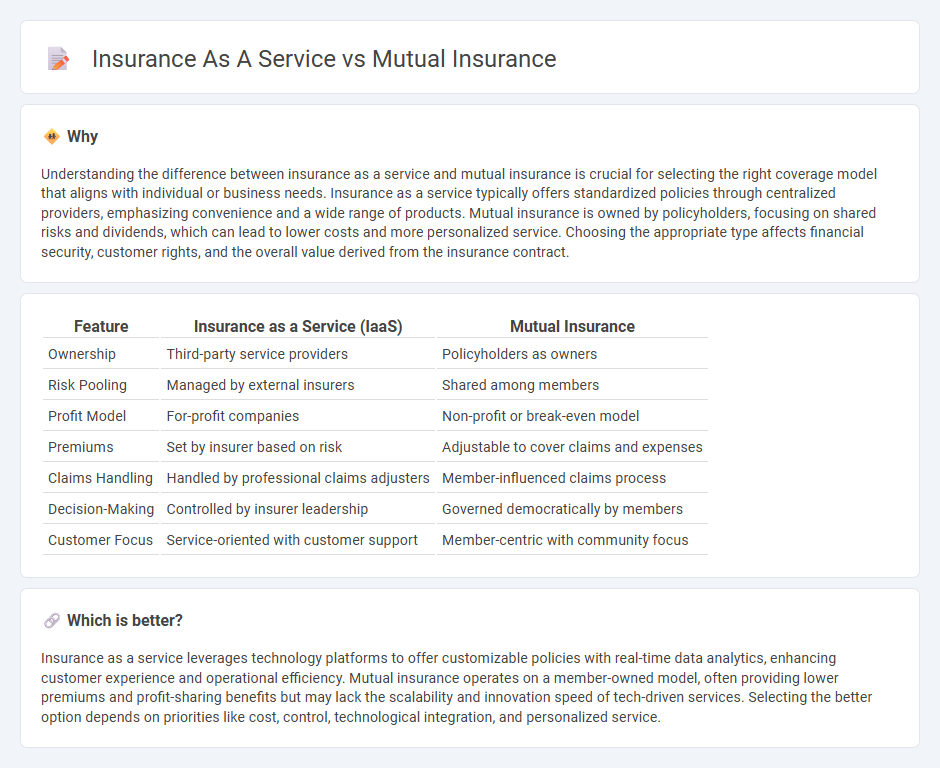
| Feature | Insurance as a Service (IaaS) | Mutual Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Ownership | Third-party service providers | Policyholders as owners |
| Risk Pooling | Managed by external insurers | Shared among members |
| Profit Model | For-profit companies | Non-profit or break-even model |
| Premiums | Set by insurer based on risk | Adjustable to cover claims and expenses |
| Claims Handling | Handled by professional claims adjusters | Member-influenced claims process |
| Decision-Making | Controlled by insurer leadership | Governed democratically by members |
| Customer Focus | Service-oriented with customer support | Member-centric with community focus |
Which is better?
Insurance as a service leverages technology platforms to offer customizable policies with real-time data analytics, enhancing customer experience and operational efficiency. Mutual insurance operates on a member-owned model, often providing lower premiums and profit-sharing benefits but may lack the scalability and innovation speed of tech-driven services. Selecting the better option depends on priorities like cost, control, technological integration, and personalized service.
Connection
Insurance as a service leverages digital platforms to provide personalized policies, seamlessly integrating customer data for real-time risk assessment and claims processing. Mutual insurance operates on a model where policyholders collectively share risk, profits, and governance, fostering trust and community-driven decision-making. The connection lies in how digital insurance services enhance the efficiency, transparency, and member engagement of mutual insurance, driving innovation in cooperative risk management.
Key Terms
Ownership structure
Mutual insurance companies are owned by their policyholders, giving members voting rights and a stake in the company's profits, while insurance-as-a-service providers are typically shareholder-owned entities focused on delivering insurance products through digital platforms. The ownership structure in mutual insurance fosters a customer-centric approach with profits often reinvested or returned to policyholders, contrasting with the profit-driven motives of insurance-as-a-service businesses. Explore the distinctive features of both models to understand how ownership impacts policyholder benefits and service delivery.
Profit distribution
Mutual insurance companies distribute profits directly to policyholders as dividends or reduced premiums, reflecting their ownership stake in the company. In contrast, Insurance as a Service (IaaS) models prioritize reinvestment of profits to enhance technological platforms and user experience, with profits typically accruing to service providers or shareholders. Explore more about how profit distribution impacts policyholder value and company growth in each model.
Technology/platform model
Mutual insurance leverages member-driven platforms emphasizing transparency and shared risk management, while insurance as a service utilizes cloud-based architectures for scalable, on-demand policy underwriting and claims processing. Technology in mutual insurance integrates blockchain for trust and decentralized data, whereas insurance as a service prioritizes API-centric models enabling seamless integration with third-party services. Explore how these platform models transform insurance delivery and customer engagement.
Source and External Links
Mutual Insurance - A mutual insurance company is an insurance company owned entirely by its policyholders, providing benefits such as dividend distributions or reduced premiums from profits.
Amica Mutual Insurance - Amica Mutual Insurance offers auto, home, and life insurance with a focus on customer service and empathy.
Nationwide Mutual Insurance Company - Nationwide started as a mutual auto insurance company and now offers a wide range of insurance and financial services across the U.S.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com