Credit life insurance provides coverage specifically designed to pay off a borrower's outstanding loan balance in the event of death, ensuring debt protection for both the insured and the lender. Universal life insurance offers flexible premiums and a cash value component, serving as a long-term financial planning tool that combines death benefits with potential investment growth. Explore the differences between these insurance types to determine which best suits your financial goals and protection needs.
Why it is important
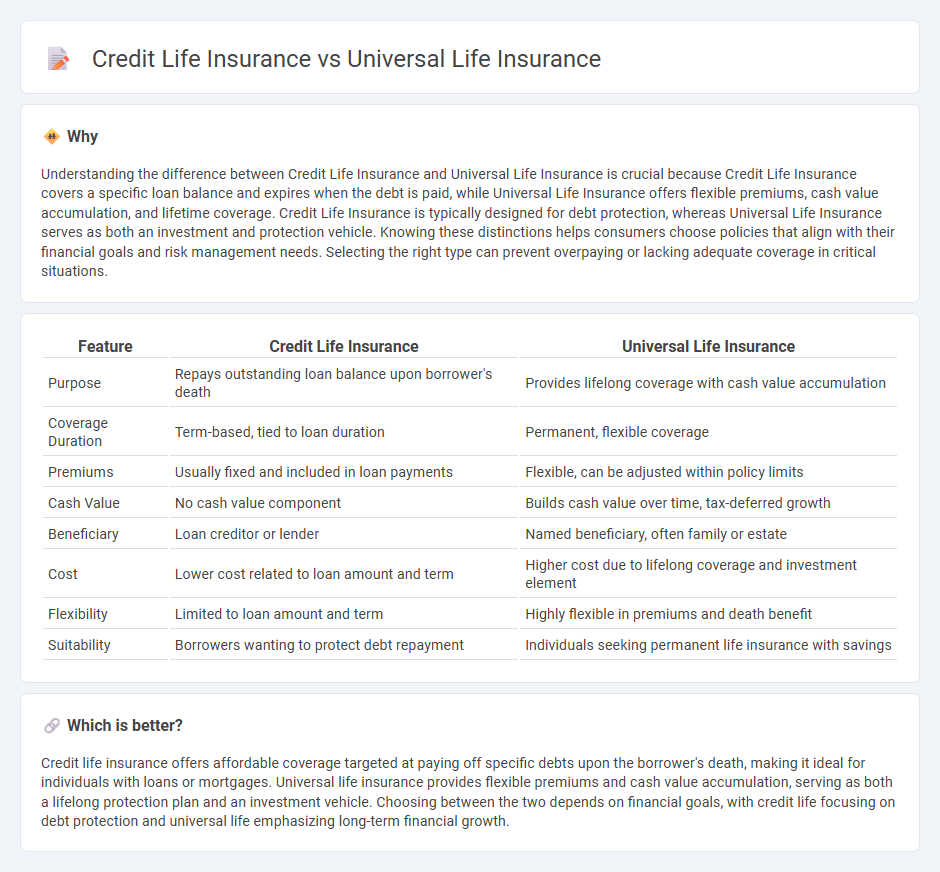
Understanding the difference between Credit Life Insurance and Universal Life Insurance is crucial because Credit Life Insurance covers a specific loan balance and expires when the debt is paid, while Universal Life Insurance offers flexible premiums, cash value accumulation, and lifetime coverage. Credit Life Insurance is typically designed for debt protection, whereas Universal Life Insurance serves as both an investment and protection vehicle. Knowing these distinctions helps consumers choose policies that align with their financial goals and risk management needs. Selecting the right type can prevent overpaying or lacking adequate coverage in critical situations.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Credit Life Insurance | Universal Life Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Repays outstanding loan balance upon borrower's death | Provides lifelong coverage with cash value accumulation |
| Coverage Duration | Term-based, tied to loan duration | Permanent, flexible coverage |
| Premiums | Usually fixed and included in loan payments | Flexible, can be adjusted within policy limits |
| Cash Value | No cash value component | Builds cash value over time, tax-deferred growth |
| Beneficiary | Loan creditor or lender | Named beneficiary, often family or estate |
| Cost | Lower cost related to loan amount and term | Higher cost due to lifelong coverage and investment element |
| Flexibility | Limited to loan amount and term | Highly flexible in premiums and death benefit |
| Suitability | Borrowers wanting to protect debt repayment | Individuals seeking permanent life insurance with savings |
Which is better?
Credit life insurance offers affordable coverage targeted at paying off specific debts upon the borrower's death, making it ideal for individuals with loans or mortgages. Universal life insurance provides flexible premiums and cash value accumulation, serving as both a lifelong protection plan and an investment vehicle. Choosing between the two depends on financial goals, with credit life focusing on debt protection and universal life emphasizing long-term financial growth.
Connection
Credit life insurance and universal life insurance are connected through their shared objective of providing financial protection and life coverage, yet they serve different purposes; credit life insurance specifically pays off outstanding debts in case of the insured's death, while universal life insurance combines lifelong protection with a cash value component that grows over time. Both types leverage actuarial principles and risk assessments to determine premiums, and policyholders can potentially benefit from the flexible premium payments characteristic of universal life products. Insurers offering these products manage risk portfolios that balance guaranteed death benefits with varying investment returns to optimize policyholder benefits and profitability.
Key Terms
Cash Value
Universal life insurance builds cash value over time through flexible premiums and interest credits, allowing policyholders to access funds or adjust coverage. Credit life insurance offers coverage tied to a loan balance but does not accumulate cash value, serving primarily as debt protection. Explore comprehensive differences in cash value benefits and policy features to determine the most suitable option for your financial needs.
Beneficiary
Universal life insurance allows policyholders to name any beneficiary, offering flexibility in designating individuals or entities to receive death benefits, and the proceeds typically pass outside probate. Credit life insurance usually names the lender as beneficiary, ensuring the loan balance is paid off upon the borrower's death, often limiting benefits solely to debt repayment. Explore how these beneficiary designations affect financial planning and protection strategies.
Debt Coverage
Universal life insurance offers flexible premiums and cash value accumulation, providing long-term debt coverage that can adapt to changing financial needs. Credit life insurance specifically covers outstanding loans, ensuring debt repayment upon the policyholder's death but often lacks cash value and broader financial benefits. Explore detailed comparisons to understand which insurance best protects your debt and financial future.
Source and External Links
Universal Life Insurance: What it is, How it works - Provides information on universal life insurance, highlighting its flexibility in premiums and cash value growth over time.
Universal life insurance - Explains the mechanics of universal life insurance, including how it accumulates cash value and offers flexible premium payments.
What is Universal Life? - Details the customizable aspects of universal life insurance, including coverage adjustment and cash value utilization.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com