Climate risk insurance specifically covers losses from climate-related events like floods, hurricanes, and droughts, providing targeted protection against increasingly frequent and severe natural disasters. Traditional indemnity insurance generally compensates policyholders for verified financial losses across a broader range of risks, relying on detailed claims assessments to determine payout amounts. Explore how climate risk insurance uniquely addresses environmental challenges compared to conventional coverage models.
Why it is important
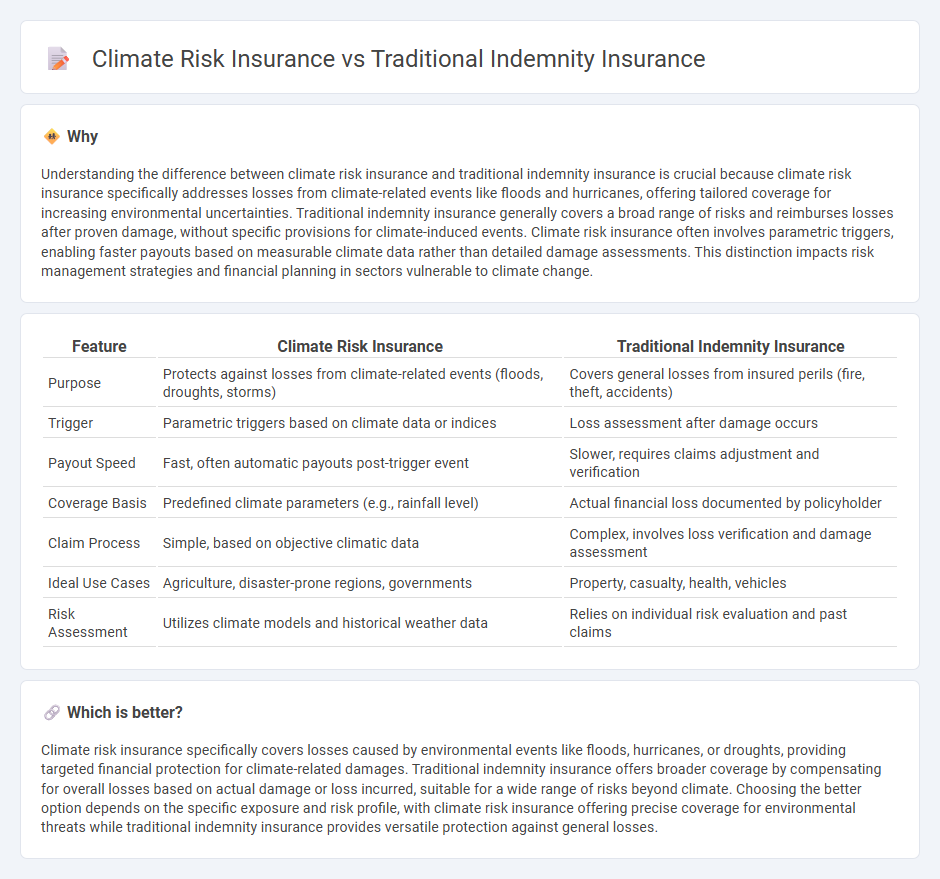
Understanding the difference between climate risk insurance and traditional indemnity insurance is crucial because climate risk insurance specifically addresses losses from climate-related events like floods and hurricanes, offering tailored coverage for increasing environmental uncertainties. Traditional indemnity insurance generally covers a broad range of risks and reimburses losses after proven damage, without specific provisions for climate-induced events. Climate risk insurance often involves parametric triggers, enabling faster payouts based on measurable climate data rather than detailed damage assessments. This distinction impacts risk management strategies and financial planning in sectors vulnerable to climate change.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Climate Risk Insurance | Traditional Indemnity Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Protects against losses from climate-related events (floods, droughts, storms) | Covers general losses from insured perils (fire, theft, accidents) |
| Trigger | Parametric triggers based on climate data or indices | Loss assessment after damage occurs |
| Payout Speed | Fast, often automatic payouts post-trigger event | Slower, requires claims adjustment and verification |
| Coverage Basis | Predefined climate parameters (e.g., rainfall level) | Actual financial loss documented by policyholder |
| Claim Process | Simple, based on objective climatic data | Complex, involves loss verification and damage assessment |
| Ideal Use Cases | Agriculture, disaster-prone regions, governments | Property, casualty, health, vehicles |
| Risk Assessment | Utilizes climate models and historical weather data | Relies on individual risk evaluation and past claims |
Which is better?
Climate risk insurance specifically covers losses caused by environmental events like floods, hurricanes, or droughts, providing targeted financial protection for climate-related damages. Traditional indemnity insurance offers broader coverage by compensating for overall losses based on actual damage or loss incurred, suitable for a wide range of risks beyond climate. Choosing the better option depends on the specific exposure and risk profile, with climate risk insurance offering precise coverage for environmental threats while traditional indemnity insurance provides versatile protection against general losses.
Connection
Climate risk insurance and traditional indemnity insurance are connected through their shared objective of mitigating financial losses from unforeseen events, with climate risk insurance specifically addressing hazards related to climate change such as floods, hurricanes, and droughts. Both types of insurance employ risk assessment models and indemnity principles to compensate policyholders based on verified damages or losses incurred. The integration of climate risk data into traditional indemnity insurance frameworks enhances resilience by tailoring coverage to evolving environmental risks.
Key Terms
Traditional Indemnity Insurance:
Traditional indemnity insurance provides compensation based on the actual financial loss incurred by the insured party, covering risks such as property damage, liability, or business interruption. It operates on a claim-by-claim basis, requiring proof of loss and detailed assessments to determine the payout amount, often limiting coverage to documented damages. Explore the differences and benefits of climate risk insurance to understand how emerging solutions address environmental uncertainties beyond traditional indemnity models.
Deductible
Traditional indemnity insurance typically features a fixed deductible amount that policyholders must pay before coverage begins, which remains constant regardless of claim size. Climate risk insurance often incorporates parametric deductibles based on specific climate events' severity or measurable triggers, enabling faster payouts and reduced administrative costs. Explore more about how deductible structures influence claim processes and risk management in different insurance models.
Premium
Traditional indemnity insurance premiums are calculated based on historical loss data, insured value, and risk factors specific to the policyholder's assets, providing compensation after actual losses occur. Climate risk insurance premiums, however, incorporate advanced climate models, catastrophe simulations, and probabilistic risk assessments that account for increasing frequency and severity of climate-related events. Explore deeper insights on premium structures and risk evaluation methodologies in both insurance types.
Source and External Links
Traditional Indemnity Insurance Plans - Virginia Health Information - Traditional indemnity insurance reimburses patients based on usual, customary, and reasonable fees after they pay medical bills upfront, offering flexibility without restrictions on provider choice and typically involves fee-for-service plans.
Indemnity Insurance - CT.gov - Indemnity insurance is the most traditional form of health coverage, giving insured individuals freedom to choose any doctor or hospital and reimbursing costs after receiving a bill, although it is now less common in today's market.
Indemnity Health Insurance Plans | eHealth - Indemnity plans require policyholders to pay for healthcare services upfront and then submit claims for reimbursement from insurance, providing flexibility to select any providers but demanding active management of claims by the insured.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com