Mental health insurance specifically covers therapies, counseling, and psychiatric treatments essential for managing mental illnesses, while supplemental health insurance provides additional financial support for out-of-pocket medical costs not covered by primary health plans. Mental health coverage often includes services like inpatient care and prescription medications, whereas supplemental policies may assist with expenses such as deductibles, copayments, or specialized treatments. Explore detailed comparisons to understand which insurance aligns best with your healthcare needs.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between mental health insurance and supplemental health insurance is crucial for selecting appropriate coverage that meets specific needs. Mental health insurance specifically covers therapy, counseling, and psychiatric services, whereas supplemental health insurance provides additional financial support for out-of-pocket medical expenses. Knowing these distinctions helps individuals avoid unexpected costs and ensures access to necessary care for mental health conditions. Clear comprehension of policy benefits optimizes health outcomes and financial protection.
Comparison Table
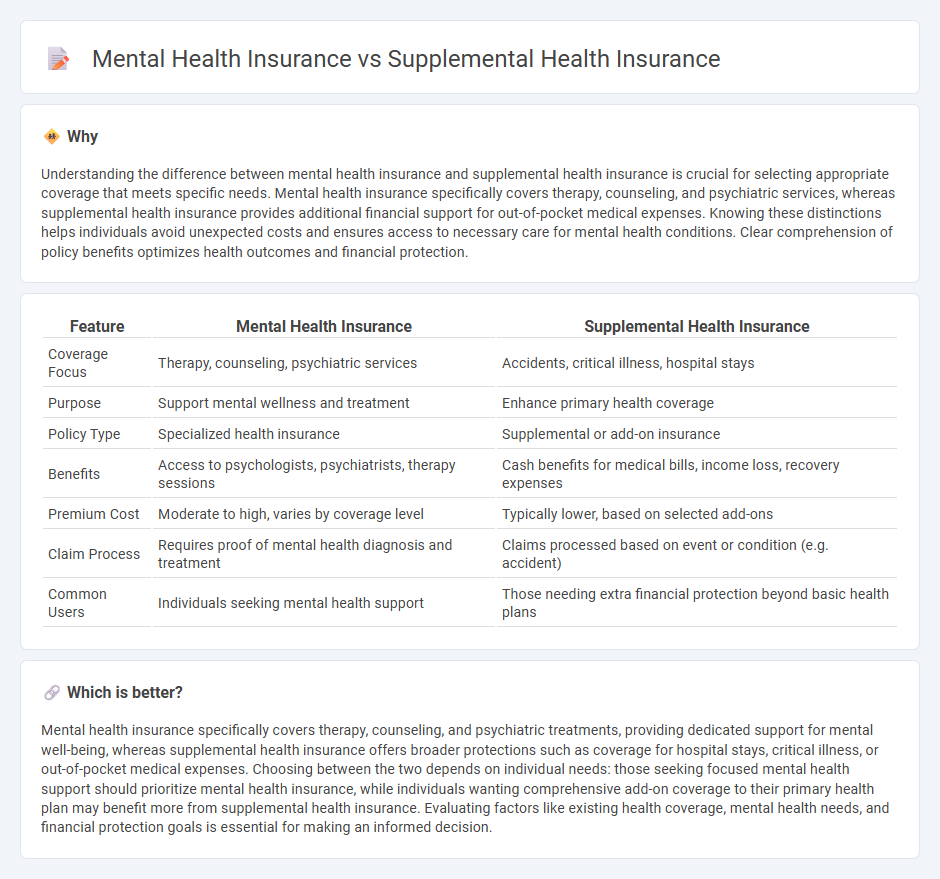
| Feature | Mental Health Insurance | Supplemental Health Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Coverage Focus | Therapy, counseling, psychiatric services | Accidents, critical illness, hospital stays |
| Purpose | Support mental wellness and treatment | Enhance primary health coverage |
| Policy Type | Specialized health insurance | Supplemental or add-on insurance |
| Benefits | Access to psychologists, psychiatrists, therapy sessions | Cash benefits for medical bills, income loss, recovery expenses |
| Premium Cost | Moderate to high, varies by coverage level | Typically lower, based on selected add-ons |
| Claim Process | Requires proof of mental health diagnosis and treatment | Claims processed based on event or condition (e.g. accident) |
| Common Users | Individuals seeking mental health support | Those needing extra financial protection beyond basic health plans |
Which is better?
Mental health insurance specifically covers therapy, counseling, and psychiatric treatments, providing dedicated support for mental well-being, whereas supplemental health insurance offers broader protections such as coverage for hospital stays, critical illness, or out-of-pocket medical expenses. Choosing between the two depends on individual needs: those seeking focused mental health support should prioritize mental health insurance, while individuals wanting comprehensive add-on coverage to their primary health plan may benefit more from supplemental health insurance. Evaluating factors like existing health coverage, mental health needs, and financial protection goals is essential for making an informed decision.
Connection
Mental health insurance often forms a critical part of supplemental health insurance, expanding coverage beyond basic medical needs to include therapy, counseling, and psychiatric services. Supplemental health insurance enhances mental health benefits by covering gaps such as copayments, deductibles, and treatments not included in primary health plans. This integrated approach ensures comprehensive care and financial protection for individuals managing mental health conditions.
Key Terms
Coverage Scope
Supplemental health insurance generally offers broader coverage for medical services like hospital stays, surgeries, and prescription drugs, whereas mental health insurance specifically targets psychological treatments such as therapy sessions, counseling, and psychiatric medications. Mental health coverage often includes benefits for substance abuse treatment, crisis intervention, and ongoing mental wellness programs that may not be fully covered by supplemental plans. Explore detailed comparisons to understand which insurance aligns better with your healthcare needs.
Benefit Limits
Supplemental health insurance typically offers broader coverage for various medical services but often has strict benefit limits that cap reimbursement amounts, potentially excluding extensive mental health treatments. Mental health insurance specifically targets psychiatric services, therapy sessions, and medication coverage, with benefit limits tailored to mental health care needs, often allowing higher reimbursements for counseling and inpatient psychiatric care. Explore detailed comparisons to understand which insurance type best supports your health goals and financial planning.
Eligible Expenses
Supplemental health insurance covers a broad range of additional medical costs like copayments, deductibles, and specialized treatments not fully covered by primary insurance, whereas mental health insurance specifically targets expenses related to psychiatric services, therapy sessions, and prescription medications for mental health conditions. Eligible expenses under supplemental health plans often include outpatient care, hospitalization surcharges, and alternative therapies, while mental health insurance focuses on expenses directly tied to diagnosis, counseling, and inpatient psychiatric care. Explore our detailed guide to understand eligibility nuances and coverage benefits for both insurance types.
Source and External Links
Supplemental Health Insurance: What Is It & Do You Need it? - Supplemental health insurance helps pay for treatments and services that standard health insurance may not cover by providing direct lump sum or percentage payments for specific conditions like accidents, critical illness, or cancer.
Explore supplemental insurance options - Supplemental insurance offers limited-benefit coverage designed to complement your main health insurance by paying cash benefits directly to you for covered medical conditions, unlike secondary insurance that pays providers.
Dental, vision & more supplemental plans - Supplemental plans add extra coverage for areas like dental, vision, accidents, critical illness, and hospital stays to help cover costs not paid by your primary health insurance.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com