Decoupled insurance separates coverage components into distinct policies tailored to specific risks, enhancing flexibility and customization for policyholders. Standalone insurance offers comprehensive protection within a single policy, simplifying claims handling and ensuring consolidated coverage. Explore how these approaches impact risk management and premium structures to determine the best fit for your insurance needs.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between decoupled insurance and standalone insurance is crucial for optimizing risk management and cost-efficiency in coverage. Decoupled insurance separates risk components, allowing tailored policies for specific exposures, while standalone insurance provides complete coverage under one policy. Knowing these distinctions helps businesses and individuals choose more precise protection strategies aligned with their unique needs. This knowledge can lead to significant savings by avoiding unnecessary coverage overlap or gaps in protection.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Decoupled Insurance | Standalone Insurance |
|---|---|---|
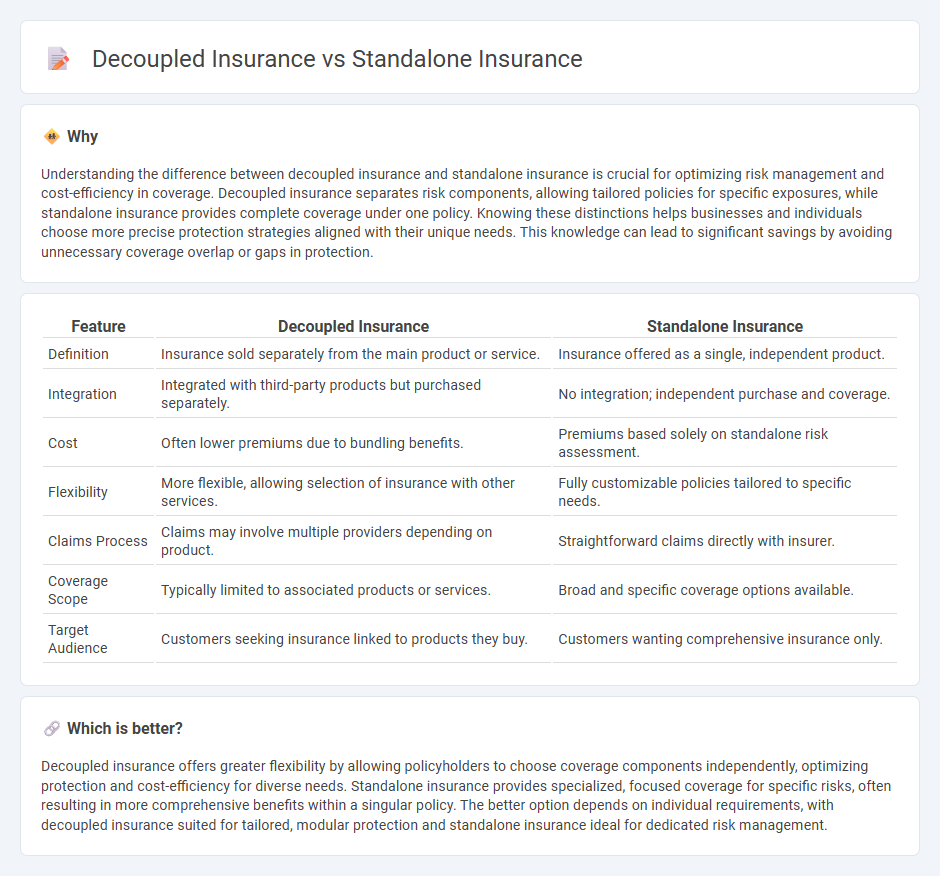
| Definition | Insurance sold separately from the main product or service. | Insurance offered as a single, independent product. |
| Integration | Integrated with third-party products but purchased separately. | No integration; independent purchase and coverage. |
| Cost | Often lower premiums due to bundling benefits. | Premiums based solely on standalone risk assessment. |
| Flexibility | More flexible, allowing selection of insurance with other services. | Fully customizable policies tailored to specific needs. |
| Claims Process | Claims may involve multiple providers depending on product. | Straightforward claims directly with insurer. |
| Coverage Scope | Typically limited to associated products or services. | Broad and specific coverage options available. |
| Target Audience | Customers seeking insurance linked to products they buy. | Customers wanting comprehensive insurance only. |
Which is better?
Decoupled insurance offers greater flexibility by allowing policyholders to choose coverage components independently, optimizing protection and cost-efficiency for diverse needs. Standalone insurance provides specialized, focused coverage for specific risks, often resulting in more comprehensive benefits within a singular policy. The better option depends on individual requirements, with decoupled insurance suited for tailored, modular protection and standalone insurance ideal for dedicated risk management.
Connection
Decoupled insurance and standalone insurance are connected through their approach to risk coverage, with decoupled insurance separating policy components such as underwriting and claims management, while standalone insurance offers a single, comprehensive policy for specific risks. Both models provide tailored solutions that enhance flexibility and customization in insurance products. Insurers leverage these frameworks to optimize operational efficiency and address diverse customer needs effectively.
Key Terms
Coverage Scope
Standalone insurance policies offer protection against specific risks, providing coverage tailored to unique needs without integration with other services. Decoupled insurance separates the insurance component from the primary product or service, enabling customized coverage that can be adjusted independently. Explore detailed comparisons to understand which coverage scope best fits your insurance requirements.
Policy Integration
Standalone insurance policies provide coverage independently without reliance on other contracts, ensuring straightforward claims and billing processes. Decoupled insurance involves separate but interrelated policies that require integration for cohesive risk management, often leveraging technology platforms for seamless policy synchronization. Explore the advantages and challenges of policy integration in these insurance types to optimize your risk strategy.
Premium Structure
Standalone insurance policies feature a single premium reflecting the total coverage cost, simplifying payment and budgeting for policyholders. Decoupled insurance separates premiums into distinct components, often dividing coverage and administrative fees, allowing for more flexible financial planning and potentially lower initial costs. Explore how these premium structures impact your insurance strategy and savings potential.
Source and External Links
What Is Standalone Insurance? - Standalone insurance is a policy that covers a specialized risk or cost not covered by your existing policies, such as flood insurance, earthquake insurance, or umbrella liability insurance that supplements your other coverage.
General Liability Stand alone - Pollution Liability Insurance - Standalone insurance can also refer to general liability coverage provided independently, protecting third parties from bodily injury or property damage claims for which you are legally liable, often used by businesses needing specific liability coverage without additional bundled policies.
Long-Term Care Insurance: Rider or Stand-Alone Policy? - Standalone insurance can apply to long-term care insurance as well, where purchasing a separate policy may be more affordable for covering future long-term care expenses than adding a rider to another policy.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com