NFT insurance provides specialized protection for digital assets by covering risks such as hacking, fraud, and loss, offering a safety net that self-insurance cannot easily replicate. Self-insurance requires individuals or entities to set aside capital to absorb potential losses, demanding significant financial reserves and risk management expertise. Explore the advantages and limitations of NFT insurance versus self-insurance to determine the best strategy for safeguarding your digital investments.
Why it is important
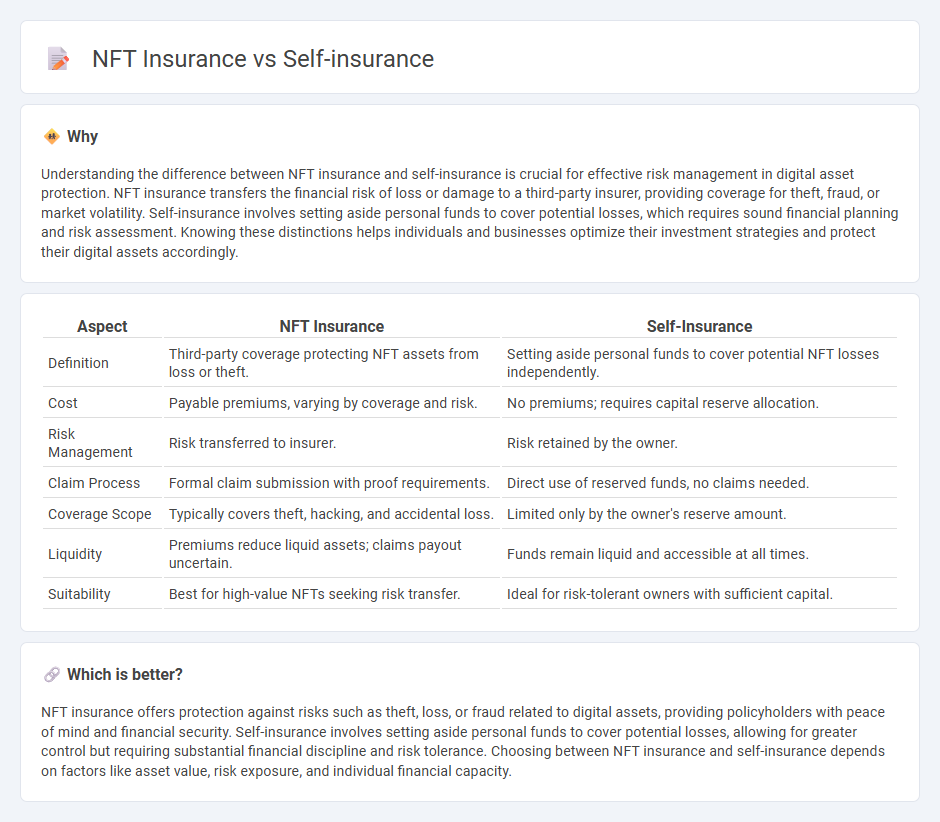
Understanding the difference between NFT insurance and self-insurance is crucial for effective risk management in digital asset protection. NFT insurance transfers the financial risk of loss or damage to a third-party insurer, providing coverage for theft, fraud, or market volatility. Self-insurance involves setting aside personal funds to cover potential losses, which requires sound financial planning and risk assessment. Knowing these distinctions helps individuals and businesses optimize their investment strategies and protect their digital assets accordingly.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | NFT Insurance | Self-Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Third-party coverage protecting NFT assets from loss or theft. | Setting aside personal funds to cover potential NFT losses independently. |
| Cost | Payable premiums, varying by coverage and risk. | No premiums; requires capital reserve allocation. |
| Risk Management | Risk transferred to insurer. | Risk retained by the owner. |
| Claim Process | Formal claim submission with proof requirements. | Direct use of reserved funds, no claims needed. |
| Coverage Scope | Typically covers theft, hacking, and accidental loss. | Limited only by the owner's reserve amount. |
| Liquidity | Premiums reduce liquid assets; claims payout uncertain. | Funds remain liquid and accessible at all times. |
| Suitability | Best for high-value NFTs seeking risk transfer. | Ideal for risk-tolerant owners with sufficient capital. |
Which is better?
NFT insurance offers protection against risks such as theft, loss, or fraud related to digital assets, providing policyholders with peace of mind and financial security. Self-insurance involves setting aside personal funds to cover potential losses, allowing for greater control but requiring substantial financial discipline and risk tolerance. Choosing between NFT insurance and self-insurance depends on factors like asset value, risk exposure, and individual financial capacity.
Connection
NFT insurance leverages blockchain technology to provide transparent and customizable coverage for unique digital assets, while self-insurance enables individuals or organizations to retain risk internally rather than purchasing traditional policies. Both methods emphasize greater control over risk management and cost efficiency, with NFT insurance addressing the protection of intangible assets and self-insurance focusing on internal funding mechanisms to cover potential losses. The integration of smart contracts in NFT insurance aligns with self-insurance principles by automating claims and reducing reliance on third-party insurers.
Key Terms
Risk retention
Risk retention in self-insurance involves an organization accepting financial responsibility for potential losses, minimizing reliance on third-party insurers. NFT insurance offers tailored coverage for risks unique to digital assets, addressing market volatility and cyber threats. Explore the distinct advantages and strategies of these approaches to optimize your risk management portfolio.
Blockchain
Self-insurance leverages blockchain technology to enable organizations to autonomously manage and finance their risk without intermediaries, optimizing transparency and reducing costs. NFT insurance utilizes non-fungible tokens to create unique, blockchain-backed policies that enhance security, traceability, and personalized coverage options. Explore the future of risk management by understanding how blockchain is transforming insurance landscapes with self-insurance and NFT innovations.
Decentralization
Self-insurance leverages decentralized risk management by allowing individuals or organizations to pool funds without intermediaries, enhancing control and cost-efficiency. NFT insurance utilizes blockchain technology to provide transparent, immutable contracts for digital asset protection, reducing fraud and increasing trust in decentralized marketplaces. Explore the evolving landscape of decentralized insurance to understand how these models redefine risk and trust in the digital age.
Source and External Links
Self-insurance - Wikipedia - Self-insurance is a risk management method where an organization bears its own risks without third-party insurance, setting aside funds to cover potential losses.
A Guide to Self-Insurance - APP Tech - This guide outlines steps to manage self-insurance, including creating a strong team, conducting a cash flow analysis, and obtaining stop-loss insurance.
Self-Insured Vs. Fully Insured Health Plans - Aetna - Self-insurance, or self-funded plans, allow employers to cover most or all benefit claims, offering flexibility and potential cost savings.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com