Cyber risk insurance covers financial losses from data breaches, cyberattacks, and digital threats, while property insurance protects physical assets like buildings and equipment from damage or theft. Cyber risk involves intangible assets and evolving threats, necessitating specialized policies distinct from traditional property coverage. Explore the key differences and benefits of each insurance type to safeguard your business effectively.
Why it is important
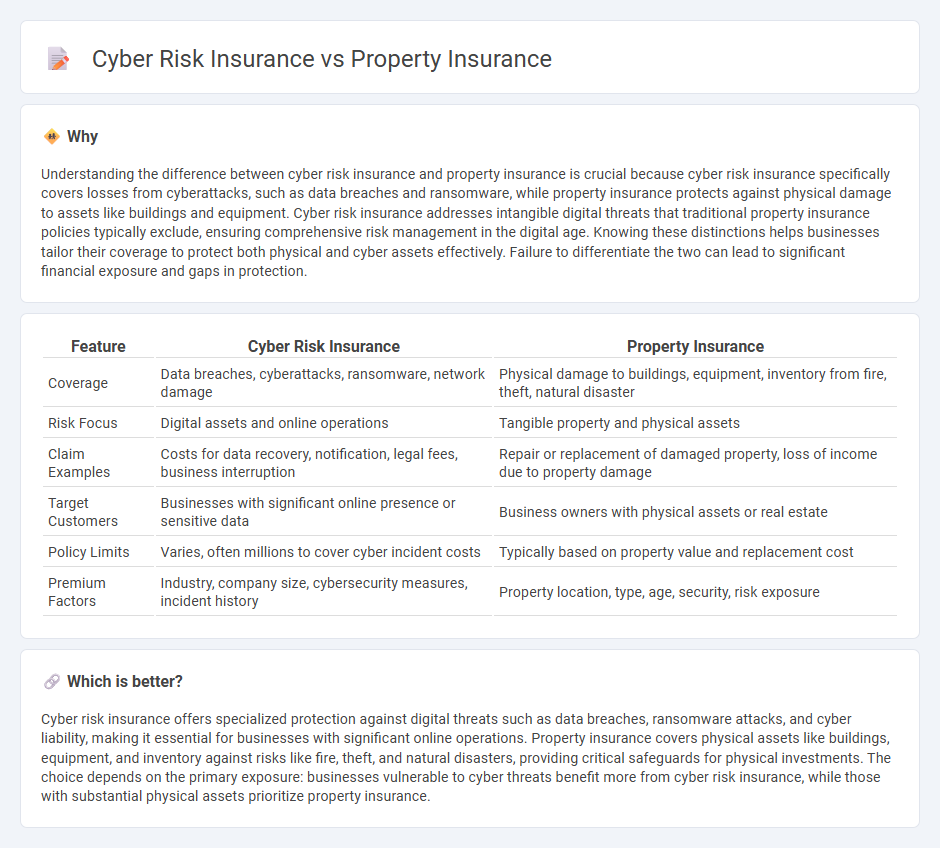
Understanding the difference between cyber risk insurance and property insurance is crucial because cyber risk insurance specifically covers losses from cyberattacks, such as data breaches and ransomware, while property insurance protects against physical damage to assets like buildings and equipment. Cyber risk insurance addresses intangible digital threats that traditional property insurance policies typically exclude, ensuring comprehensive risk management in the digital age. Knowing these distinctions helps businesses tailor their coverage to protect both physical and cyber assets effectively. Failure to differentiate the two can lead to significant financial exposure and gaps in protection.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Cyber Risk Insurance | Property Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Coverage | Data breaches, cyberattacks, ransomware, network damage | Physical damage to buildings, equipment, inventory from fire, theft, natural disaster |
| Risk Focus | Digital assets and online operations | Tangible property and physical assets |
| Claim Examples | Costs for data recovery, notification, legal fees, business interruption | Repair or replacement of damaged property, loss of income due to property damage |
| Target Customers | Businesses with significant online presence or sensitive data | Business owners with physical assets or real estate |
| Policy Limits | Varies, often millions to cover cyber incident costs | Typically based on property value and replacement cost |
| Premium Factors | Industry, company size, cybersecurity measures, incident history | Property location, type, age, security, risk exposure |
Which is better?
Cyber risk insurance offers specialized protection against digital threats such as data breaches, ransomware attacks, and cyber liability, making it essential for businesses with significant online operations. Property insurance covers physical assets like buildings, equipment, and inventory against risks like fire, theft, and natural disasters, providing critical safeguards for physical investments. The choice depends on the primary exposure: businesses vulnerable to cyber threats benefit more from cyber risk insurance, while those with substantial physical assets prioritize property insurance.
Connection
Cyber risk insurance and property insurance intersect in protecting businesses from losses related to digital and physical assets. Cyber risk insurance covers financial damages from data breaches, cyberattacks, and IT system failures, while property insurance safeguards against physical damage to buildings and equipment. Integrating these policies ensures comprehensive coverage by addressing both digital vulnerabilities and tangible property risks within an enterprise risk management strategy.
Key Terms
**Property Insurance:**
Property insurance provides coverage for physical assets such as buildings, equipment, and inventory against risks like fire, theft, and natural disasters, ensuring financial protection for tangible property damage. This type of insurance typically covers repair or replacement costs and business interruption losses linked to property damage. Explore more about how property insurance safeguards your physical assets and contrasts with cyber risk coverage.
Replacement Cost
Replacement cost coverage in property insurance reimburses the actual cost to repair or replace damaged physical assets without deducting depreciation, ensuring businesses restore their tangible property to its original condition. Cyber risk insurance, on the other hand, typically focuses on digital asset restoration, covering expenses related to data recovery, system repairs, and breach response rather than physical replacement costs. Explore more about how replacement cost provisions differ between these policies to safeguard both tangible and intangible business assets effectively.
Physical Damage
Property insurance primarily covers physical damage to buildings, equipment, and inventory caused by fire, theft, or natural disasters, ensuring tangible asset protection. Cyber risk insurance, on the other hand, focuses on digital threats such as data breaches, hacking, and cyber extortion, which do not cause physical damage but can disrupt business operations and lead to financial loss. Explore the key differences and benefits of both policies to safeguard your business comprehensively.
Source and External Links
Homeowners Insurance - Online Quotes - Homeowners insurance protects your home, belongings, and liability, covering repairs, replacements, temporary housing, and legal fees in case of damage, theft, or injury on your property.
Homeowners Insurance - Get a Home Insurance Quote - Homeowners insurance is a contract where you pay premiums in exchange for coverage against future damages to your home and personal property, with premiums determined by factors like location and home materials.
Homeowners Insurance: Get a free quote today - Homeowners insurance covers your dwelling and belongings, with additional coverage options such as flood and earthquake insurance often available, and may be required by lenders depending on your state.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com