Drone insurance specifically covers unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) against risks like damage, theft, and liability during commercial or recreational use, while aviation insurance typically protects manned aircraft and operators from a broader spectrum of hazards, including passenger injuries, hull damage, and third-party liability. Policies for drones often focus on emerging regulations and technology-specific risks, whereas aviation insurance involves complex underwriting due to larger aircraft and diverse operational environments. Explore detailed comparisons and coverage options to choose the best insurance tailored to your aerial vehicle needs.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between drone insurance and aviation insurance is crucial because drone insurance specifically covers risks related to unmanned aerial vehicles, such as damage, liability, and privacy issues, whereas aviation insurance encompasses manned aircraft with broader coverage including passenger liability and aircraft hull damage. Drone operations are governed by unique regulatory frameworks like the FAA's Part 107, necessitating tailored insurance policies that differ significantly from traditional aviation insurance terms. Knowing these distinctions helps operators ensure proper coverage, avoid legal liabilities, and protect investments effectively in the rapidly growing drone industry. Misclassification can lead to inadequate protection and potential financial loss in case of accidents or regulatory penalties.
Comparison Table
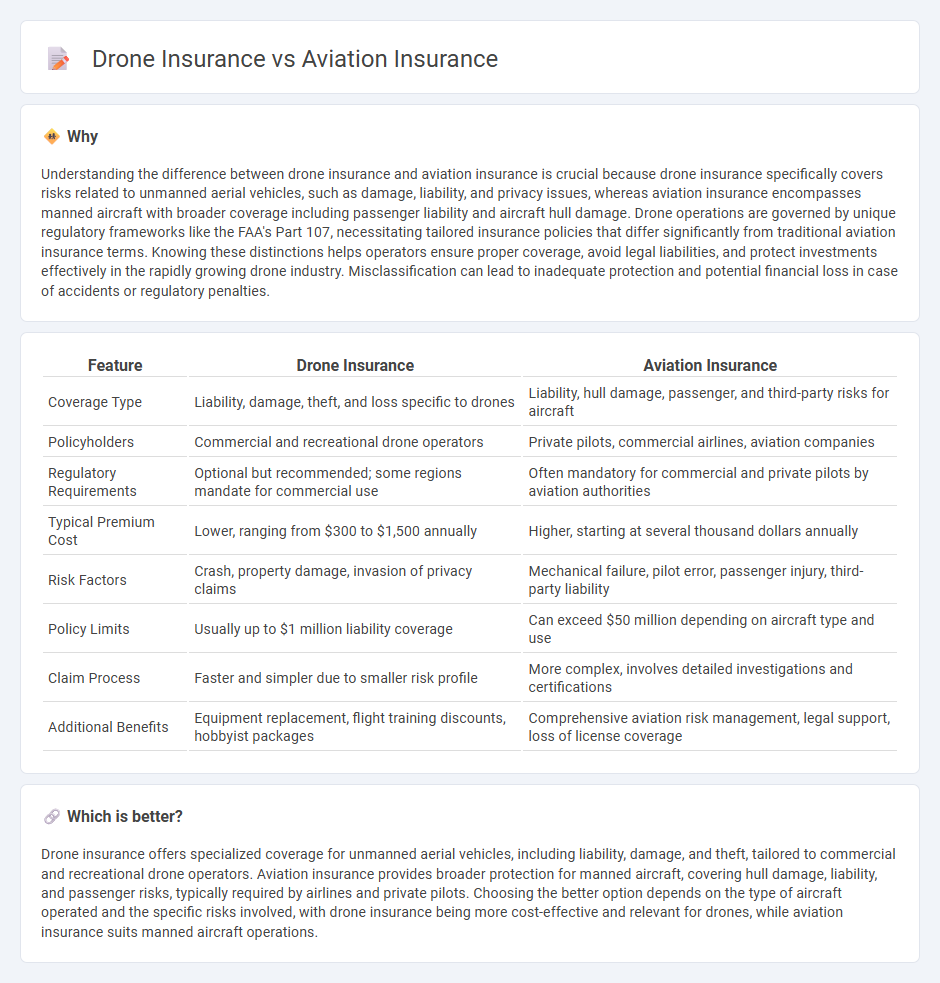
| Feature | Drone Insurance | Aviation Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Coverage Type | Liability, damage, theft, and loss specific to drones | Liability, hull damage, passenger, and third-party risks for aircraft |
| Policyholders | Commercial and recreational drone operators | Private pilots, commercial airlines, aviation companies |
| Regulatory Requirements | Optional but recommended; some regions mandate for commercial use | Often mandatory for commercial and private pilots by aviation authorities |
| Typical Premium Cost | Lower, ranging from $300 to $1,500 annually | Higher, starting at several thousand dollars annually |
| Risk Factors | Crash, property damage, invasion of privacy claims | Mechanical failure, pilot error, passenger injury, third-party liability |
| Policy Limits | Usually up to $1 million liability coverage | Can exceed $50 million depending on aircraft type and use |
| Claim Process | Faster and simpler due to smaller risk profile | More complex, involves detailed investigations and certifications |
| Additional Benefits | Equipment replacement, flight training discounts, hobbyist packages | Comprehensive aviation risk management, legal support, loss of license coverage |
Which is better?
Drone insurance offers specialized coverage for unmanned aerial vehicles, including liability, damage, and theft, tailored to commercial and recreational drone operators. Aviation insurance provides broader protection for manned aircraft, covering hull damage, liability, and passenger risks, typically required by airlines and private pilots. Choosing the better option depends on the type of aircraft operated and the specific risks involved, with drone insurance being more cost-effective and relevant for drones, while aviation insurance suits manned aircraft operations.
Connection
Drone insurance and aviation insurance both provide specialized coverage tailored to airborne vehicles, addressing risks such as liability, damage, and operational hazards. Drone insurance often falls under the broader scope of aviation insurance, covering unmanned aerial systems and their unique regulatory requirements. Insurers analyze flight patterns, payloads, and pilot expertise to mitigate claims across both sectors efficiently.
Key Terms
**Aviation Insurance:**
Aviation insurance covers manned aircraft such as airplanes and helicopters, protecting against liabilities including property damage, bodily injury, and hull loss during flight operations. This type of insurance is essential for commercial airlines, private pilots, and aviation businesses to mitigate risks associated with passenger transport, cargo, and aircraft maintenance. Explore the key differences between aviation insurance and drone insurance to better understand coverage options for aerial operations.
Hull Coverage
Hull coverage in aviation insurance primarily protects manned aircraft from physical damage caused by accidents, weather, or other hazards, encompassing both ground and in-flight incidents. Drone insurance hull coverage similarly safeguards the physical structure of drones, including rotors, cameras, and other components, but often includes specialized clauses addressing risks unique to unmanned aerial systems. Explore how tailored hull coverage options can mitigate your specific liabilities and asset risks in manned versus unmanned aviation for comprehensive protection.
Passenger Liability
Aviation insurance primarily covers commercial aircraft, focusing on passenger liability to protect against injury or death claims during flights, often involving larger sums due to the higher number of passengers. Drone insurance, on the other hand, includes passenger liability only in specific scenarios where drones are used to transport people, which is less common and typically involves smaller coverage amounts. Explore comprehensive guides on aviation and drone insurance to understand passenger liability nuances and ensure optimal coverage.
Source and External Links
Avemco Owned Aircraft Insurance - Provides personal aircraft insurance with liability and hull coverage options, offering personalized policies based on individual situations.
Starr Aviation Insurance - Offers customized property and casualty insurance solutions for the aviation and aerospace industry, covering various risks worldwide.
Great American Aviation Insurance - Specializes in hull, liability, and excess liability insurance for a wide range of aviation-related risks, providing tailored coverage options.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com