Social prescribing insurance focuses on covering holistic health services such as community activities and wellness programs to enhance patient well-being beyond traditional medical treatments. Pharmacy benefit insurance primarily manages coverage for prescription medications, ensuring affordable access to essential drugs through negotiated pharmacy networks. Explore the key differences and benefits of both insurance types to determine which best suits your healthcare needs.
Why it is important
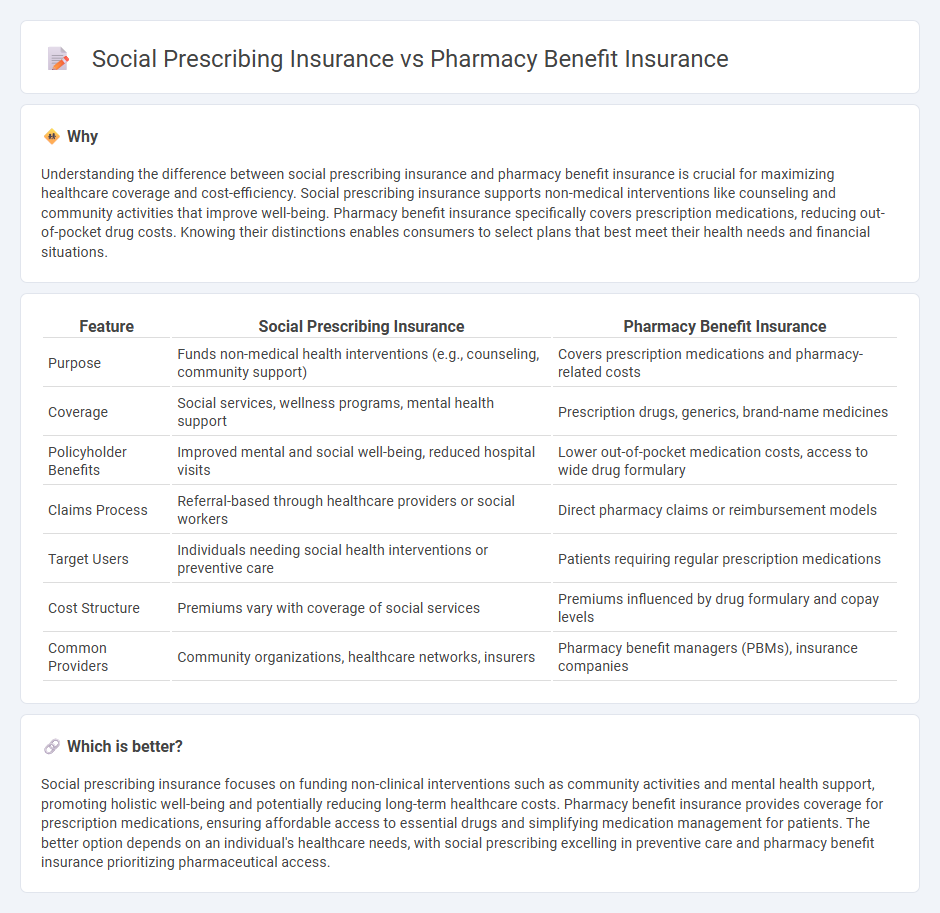
Understanding the difference between social prescribing insurance and pharmacy benefit insurance is crucial for maximizing healthcare coverage and cost-efficiency. Social prescribing insurance supports non-medical interventions like counseling and community activities that improve well-being. Pharmacy benefit insurance specifically covers prescription medications, reducing out-of-pocket drug costs. Knowing their distinctions enables consumers to select plans that best meet their health needs and financial situations.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Social Prescribing Insurance | Pharmacy Benefit Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Funds non-medical health interventions (e.g., counseling, community support) | Covers prescription medications and pharmacy-related costs |
| Coverage | Social services, wellness programs, mental health support | Prescription drugs, generics, brand-name medicines |
| Policyholder Benefits | Improved mental and social well-being, reduced hospital visits | Lower out-of-pocket medication costs, access to wide drug formulary |
| Claims Process | Referral-based through healthcare providers or social workers | Direct pharmacy claims or reimbursement models |
| Target Users | Individuals needing social health interventions or preventive care | Patients requiring regular prescription medications |
| Cost Structure | Premiums vary with coverage of social services | Premiums influenced by drug formulary and copay levels |
| Common Providers | Community organizations, healthcare networks, insurers | Pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs), insurance companies |
Which is better?
Social prescribing insurance focuses on funding non-clinical interventions such as community activities and mental health support, promoting holistic well-being and potentially reducing long-term healthcare costs. Pharmacy benefit insurance provides coverage for prescription medications, ensuring affordable access to essential drugs and simplifying medication management for patients. The better option depends on an individual's healthcare needs, with social prescribing excelling in preventive care and pharmacy benefit insurance prioritizing pharmaceutical access.
Connection
Social prescribing insurance and pharmacy benefit insurance are interconnected by their shared goal of enhancing patient outcomes and reducing healthcare costs through comprehensive care management. Social prescribing insurance supports non-medical interventions like community services that address social determinants of health, while pharmacy benefit insurance ensures affordable access to necessary medications. Together, they create a holistic approach that integrates medication management with social support, improving overall health and preventing hospital readmissions.
Key Terms
**Pharmacy benefit insurance:**
Pharmacy benefit insurance covers prescription medications, reducing out-of-pocket costs and improving medication adherence for patients managing chronic conditions. It provides access to a wide network of pharmacies and helps control healthcare spending by negotiating drug prices and managing formularies. Discover how pharmacy benefit insurance enhances medication access and affordability for better health outcomes.
Formulary
Pharmacy benefit insurance primarily centers on a predetermined formulary that dictates covered medications, optimizing cost control and standardized access to essential drugs. Social prescribing insurance, in contrast, integrates non-medical interventions beyond the traditional formulary, emphasizing community resources and holistic well-being. Explore further to understand how each approach shapes healthcare outcomes and patient empowerment.
Copayment
Pharmacy benefit insurance typically involves fixed or percentage-based copayments for prescription medications, ensuring predictable out-of-pocket costs for patients. Social prescribing insurance copayments may vary depending on the type of community services or interventions covered, often emphasizing holistic health outcomes rather than medication expenses. Explore how these copayment models impact overall healthcare affordability and patient engagement.
Source and External Links
The Value of Pharmacy Benefit Managers - CVS Health - Pharmacy benefit insurance covers medications typically picked up at a pharmacy or delivered to your home, with Pharmacy Benefit Managers (PBMs) working alongside health plans and employers to administer these benefits and help control costs.
PBM Regulations on Drug Spending | Commonwealth Fund - PBMs act as intermediaries that manage prescription drug benefits for insurers and employers by negotiating drug prices, creating pharmacy networks, and determining which medications are covered under a plan.
Insurance Topics | Pharmacy Benefit Managers - NAIC - PBMs create formularies, process claims, negotiate rebates with manufacturers, and manage pharmacy networks, all aimed at controlling prescription drug costs for health insurance plans.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com