Artificial intelligence underwriting leverages machine learning algorithms and data analytics to assess risk quickly and accurately, reducing human error and processing time. Peer review underwriting involves experienced underwriters evaluating each case based on professional judgment and industry knowledge, providing nuanced insights and adaptability. Discover how these distinct methods impact efficiency, accuracy, and decision-making in insurance risk assessment.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between artificial intelligence underwriting and peer review underwriting is crucial for optimizing risk assessment and improving claim accuracy. AI underwriting leverages data algorithms to rapidly analyze large datasets, enhancing predictive accuracy and consistency. Peer review underwriting relies on human expertise and judgment, allowing for nuanced decision-making in complex cases. Knowing these distinctions helps insurers choose the best approach for efficiency, accuracy, and customer satisfaction.
Comparison Table
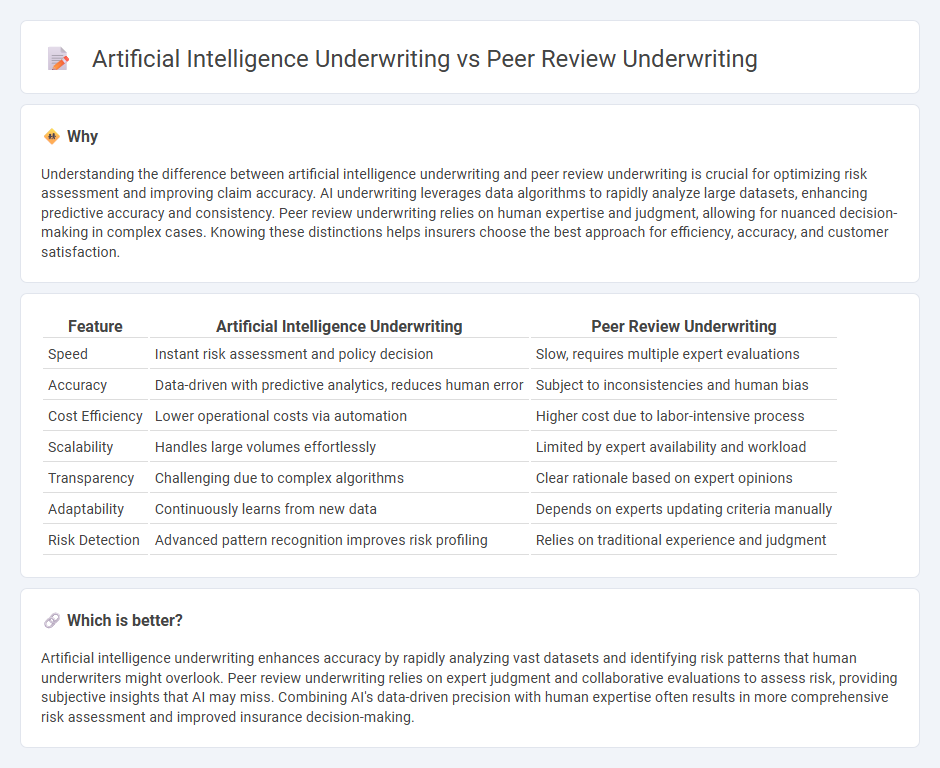
| Feature | Artificial Intelligence Underwriting | Peer Review Underwriting |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Instant risk assessment and policy decision | Slow, requires multiple expert evaluations |
| Accuracy | Data-driven with predictive analytics, reduces human error | Subject to inconsistencies and human bias |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower operational costs via automation | Higher cost due to labor-intensive process |
| Scalability | Handles large volumes effortlessly | Limited by expert availability and workload |
| Transparency | Challenging due to complex algorithms | Clear rationale based on expert opinions |
| Adaptability | Continuously learns from new data | Depends on experts updating criteria manually |
| Risk Detection | Advanced pattern recognition improves risk profiling | Relies on traditional experience and judgment |
Which is better?
Artificial intelligence underwriting enhances accuracy by rapidly analyzing vast datasets and identifying risk patterns that human underwriters might overlook. Peer review underwriting relies on expert judgment and collaborative evaluations to assess risk, providing subjective insights that AI may miss. Combining AI's data-driven precision with human expertise often results in more comprehensive risk assessment and improved insurance decision-making.
Connection
Artificial intelligence underwriting enhances risk assessment accuracy by analyzing vast datasets and identifying patterns, which supports peer review underwriting by providing objective insights for human experts. Peer review underwriting leverages AI-generated data to validate and refine underwriting decisions, reducing errors and bias. This integration improves overall underwriting efficiency and decision quality in insurance.
Key Terms
Human judgment
Peer review underwriting emphasizes human judgment by leveraging the expertise and nuanced decision-making skills of underwriters to assess risk and approve insurance applications. Artificial intelligence underwriting utilizes machine learning algorithms and vast datasets to analyze patterns and predict outcomes, offering increased efficiency but sometimes lacking the contextual understanding inherent in human evaluation. Explore the balance between human intuition and AI-driven accuracy in underwriting to understand how combining both can enhance decision-making processes.
Algorithmic decision-making
Peer review underwriting relies on human expertise to assess risk through detailed analysis and subjective judgment, ensuring nuanced evaluation of complex cases. Artificial intelligence underwriting utilizes algorithmic decision-making, analyzing vast datasets and identifying patterns with speed and consistency to enhance accuracy and efficiency. Explore the differences in decision-making processes to better understand how AI is transforming underwriting practices.
Bias detection
Peer review underwriting involves human experts analyzing insurance applications to identify potential biases and ensure fairness, relying on their experience and judgment to detect subjective patterns. Artificial intelligence underwriting utilizes advanced algorithms and machine learning models to systematically identify hidden biases in data and decision-making processes by analyzing large datasets and uncovering correlations that may be overlooked by human reviewers. Explore how integrating both approaches can enhance bias detection and promote equitable underwriting outcomes.
Source and External Links
How to Improve the Underwriting Process - Peer review in underwriting involves regular reviews of each other's work to maintain high quality standards and compliance.
Independent Reviewers - Peer review in underwriting contexts at Lloyd's focuses on whether underwriting authorities and procedures have been followed for individual risks.
Peer Review - Peer review is a process where professionals review and critique each other's work, particularly important for preventing claims in professional firms, including underwriting.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com