Cyber risk underwriting focuses on assessing potential threats related to data breaches, hacking incidents, and digital asset vulnerabilities, utilizing advanced analytics and cybersecurity expertise. Health underwriting evaluates individual or group medical histories, lifestyle factors, and genetic predispositions to determine insurance eligibility and premium rates. Explore the key differences and methodologies in underwriting to better understand their respective impacts on risk management.
Why it is important
Knowing the difference between Cyber risk underwriting and Health underwriting is crucial because they involve distinct risk assessments: Cyber underwriting focuses on evaluating digital threats and data breaches, while Health underwriting assesses an individual's medical history and physical condition. Cyber risk policies require analysis of cybersecurity measures, data sensitivity, and potential financial losses from cyberattacks, whereas Health underwriting demands thorough evaluation of pre-existing conditions, lifestyle factors, and potential healthcare costs. Understanding these distinctions enables insurers to accurately price premiums, manage exposure effectively, and tailor coverage to specific risks. Clear differentiation improves underwriting precision and protects both insurers and policyholders from unforeseen financial liabilities.
Comparison Table
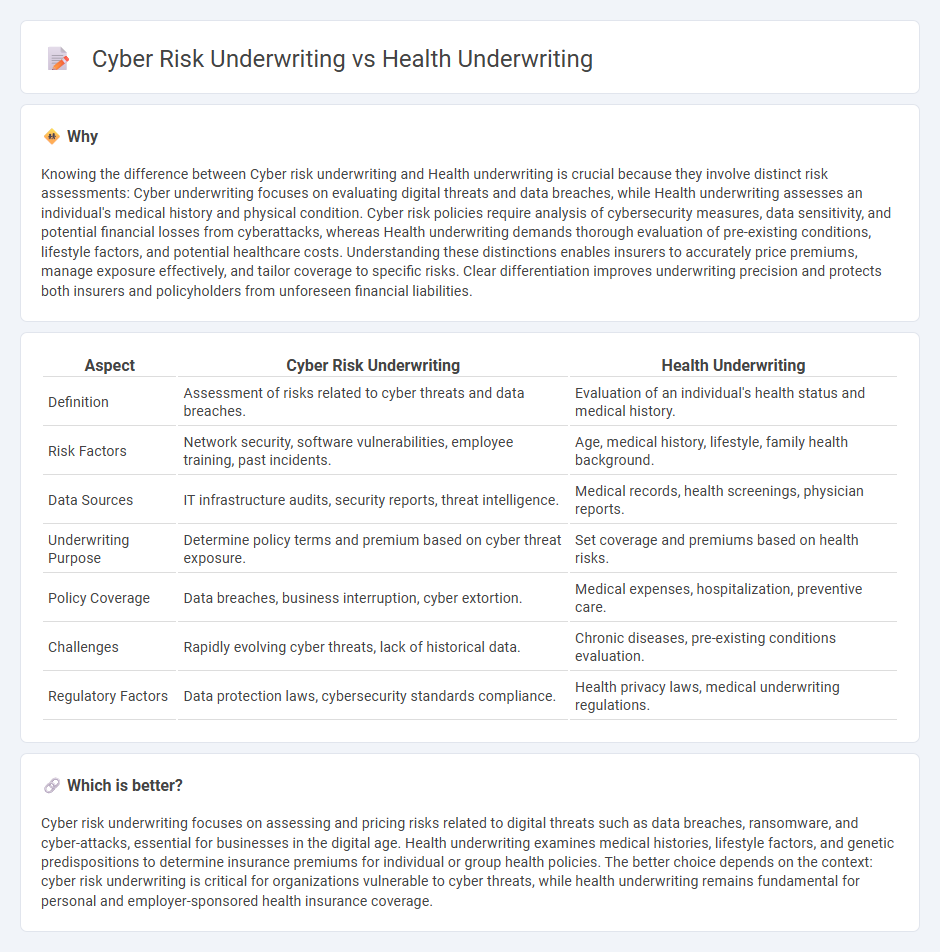
| Aspect | Cyber Risk Underwriting | Health Underwriting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Assessment of risks related to cyber threats and data breaches. | Evaluation of an individual's health status and medical history. |
| Risk Factors | Network security, software vulnerabilities, employee training, past incidents. | Age, medical history, lifestyle, family health background. |
| Data Sources | IT infrastructure audits, security reports, threat intelligence. | Medical records, health screenings, physician reports. |
| Underwriting Purpose | Determine policy terms and premium based on cyber threat exposure. | Set coverage and premiums based on health risks. |
| Policy Coverage | Data breaches, business interruption, cyber extortion. | Medical expenses, hospitalization, preventive care. |
| Challenges | Rapidly evolving cyber threats, lack of historical data. | Chronic diseases, pre-existing conditions evaluation. |
| Regulatory Factors | Data protection laws, cybersecurity standards compliance. | Health privacy laws, medical underwriting regulations. |
Which is better?
Cyber risk underwriting focuses on assessing and pricing risks related to digital threats such as data breaches, ransomware, and cyber-attacks, essential for businesses in the digital age. Health underwriting examines medical histories, lifestyle factors, and genetic predispositions to determine insurance premiums for individual or group health policies. The better choice depends on the context: cyber risk underwriting is critical for organizations vulnerable to cyber threats, while health underwriting remains fundamental for personal and employer-sponsored health insurance coverage.
Connection
Cyber risk underwriting and health underwriting intersect through the evaluation of digital health data security and its potential impacts on insured individuals' well-being. Protecting sensitive health information from cyber threats is essential for minimizing risks related to data breaches, which can lead to identity theft, financial loss, and compromised medical treatments. Integrating cybersecurity measures into health underwriting enhances risk assessments by ensuring patient confidentiality and maintaining trust in healthcare insurance services.
Key Terms
**Health Underwriting:**
Health underwriting evaluates individual or group health risks by analyzing medical histories, lifestyle factors, and demographic data to determine policy terms and premiums. This process relies heavily on clinical data, risk factors such as pre-existing conditions, and actuarial models to predict future healthcare costs and claims. Explore our comprehensive guide to understand the key components and best practices in health underwriting.
Pre-existing Condition
Health underwriting heavily relies on identifying pre-existing conditions to assess an applicant's risk and determine premium rates, using extensive medical histories and diagnostic data. Cyber risk underwriting, however, focuses on evaluating existing vulnerabilities and past cyber incidents rather than traditional health conditions, emphasizing system security and incident response capabilities. Discover more about how each underwriting approach manages risk differently and the implications for insurance coverage.
Medical History
Health underwriting primarily evaluates an applicant's medical history, including pre-existing conditions, treatments, and lifestyle factors, to assess the risk of future health claims. Cyber risk underwriting, by contrast, focuses less on personal medical data and more on organizational security protocols, data protection measures, and incident response capabilities to gauge potential cyber threats. Explore detailed insights into how medical history impacts both underwriting types to optimize risk assessment strategies.
Source and External Links
Milliman Medical Underwriting Suite - Offers a suite of products to improve the medical underwriting process for insurance companies.
Medical Underwriting: How It Shapes Private Coverage Costs - Explains how medical underwriting influences health insurance coverage costs by assessing individual health risks.
What is medical underwriting? - Describes the process of evaluating applicants' health risks to determine insurance eligibility and premiums.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com