Artificial intelligence underwriting utilizes machine learning algorithms and vast data sets to assess risk with high accuracy and speed, enhancing decision-making efficiency in insurance. Geospatial underwriting leverages geographic information systems (GIS) and spatial data to evaluate risk factors linked to location, such as environmental hazards and proximity to infrastructure. Explore how these innovative underwriting methods transform risk assessment and optimize insurance processes.
Why it is important
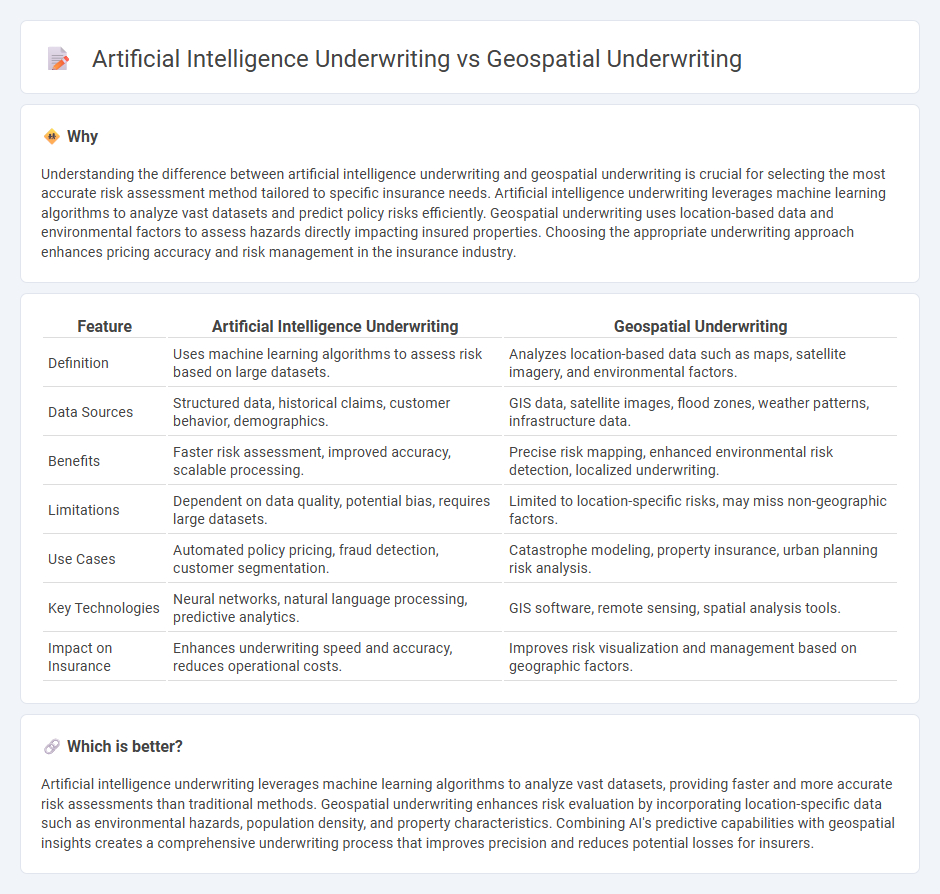
Understanding the difference between artificial intelligence underwriting and geospatial underwriting is crucial for selecting the most accurate risk assessment method tailored to specific insurance needs. Artificial intelligence underwriting leverages machine learning algorithms to analyze vast datasets and predict policy risks efficiently. Geospatial underwriting uses location-based data and environmental factors to assess hazards directly impacting insured properties. Choosing the appropriate underwriting approach enhances pricing accuracy and risk management in the insurance industry.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Artificial Intelligence Underwriting | Geospatial Underwriting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Uses machine learning algorithms to assess risk based on large datasets. | Analyzes location-based data such as maps, satellite imagery, and environmental factors. |
| Data Sources | Structured data, historical claims, customer behavior, demographics. | GIS data, satellite images, flood zones, weather patterns, infrastructure data. |
| Benefits | Faster risk assessment, improved accuracy, scalable processing. | Precise risk mapping, enhanced environmental risk detection, localized underwriting. |
| Limitations | Dependent on data quality, potential bias, requires large datasets. | Limited to location-specific risks, may miss non-geographic factors. |
| Use Cases | Automated policy pricing, fraud detection, customer segmentation. | Catastrophe modeling, property insurance, urban planning risk analysis. |
| Key Technologies | Neural networks, natural language processing, predictive analytics. | GIS software, remote sensing, spatial analysis tools. |
| Impact on Insurance | Enhances underwriting speed and accuracy, reduces operational costs. | Improves risk visualization and management based on geographic factors. |
Which is better?
Artificial intelligence underwriting leverages machine learning algorithms to analyze vast datasets, providing faster and more accurate risk assessments than traditional methods. Geospatial underwriting enhances risk evaluation by incorporating location-specific data such as environmental hazards, population density, and property characteristics. Combining AI's predictive capabilities with geospatial insights creates a comprehensive underwriting process that improves precision and reduces potential losses for insurers.
Connection
Artificial intelligence underwriting enhances risk assessment by analyzing vast datasets and identifying patterns, while geospatial underwriting integrates location-based data to evaluate environmental and regional risk factors. Combining AI with geospatial data enables insurers to create more precise risk models, improving accuracy in premium pricing and claim predictions. This synergy supports dynamic underwriting processes, leading to optimized risk management and improved decision-making in the insurance industry.
Key Terms
**Geospatial Underwriting:**
Geospatial underwriting leverages location-based data and spatial analytics to assess risk by integrating satellite imagery, geographic information systems (GIS), and environmental factors. This method improves accuracy in property risk evaluation, natural disaster prediction, and market segmentation compared to traditional models. Discover how geospatial underwriting transforms risk assessment and decision-making processes.
Risk Mapping
Geospatial underwriting leverages satellite imagery, GIS data, and location analytics to assess property risk by analyzing environmental factors and disaster exposure, enhancing accuracy in risk mapping. Artificial intelligence underwriting uses machine learning algorithms to process vast datasets, identify patterns, and predict risk profiles more efficiently, enabling dynamic and real-time risk mapping. Explore further to understand how integrating these technologies transforms risk assessment strategies.
Location Data Analytics
Geospatial underwriting leverages precise location data analytics to assess risk by analyzing geographic factors such as flood zones, crime rates, and natural disaster history, enhancing accuracy in policy pricing. Artificial intelligence underwriting integrates machine learning algorithms to process vast datasets, including location-based information, to predict underwriting outcomes with greater efficiency and predictive power. Explore how combining geospatial technologies with AI transforms underwriting practices for a data-driven insurance industry.
Source and External Links
Guide to Geospatial Technology | BuildingMetrix - Geospatial underwriting uses mapping tools to visualize risk locations and their proximity, enabling real-time updates for accurate risk exposure management and improved underwriting efficiency.
Geospatial Intelligence: Revolutionizing Property Insurance Industry - Geospatial underwriting integrates geospatial data with AI and computer vision for enhanced risk assessment, disaster anticipation, loss minimization, and fraud detection in property insurance.
The Ultimate Guide to Geospatial Data for Insurance - Ecopia AI - In underwriting, geospatial data such as precise geocoding, building footprints, and 3D models provide insurers detailed location and structural context to improve risk assessment and pricing accuracy.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com