Ghost broking involves fraudulent insurance practices where fake brokers sell illegitimate policies, putting clients at risk of non-coverage and legal issues. Fronting occurs when a legitimate policyholder obtains insurance primarily to meet legal requirements but does not intend to be the main risk bearer, often leading to policy disputes and claim denials. Explore the critical differences between ghost broking and fronting to protect yourself from insurance fraud and misrepresentation.
Why it is important
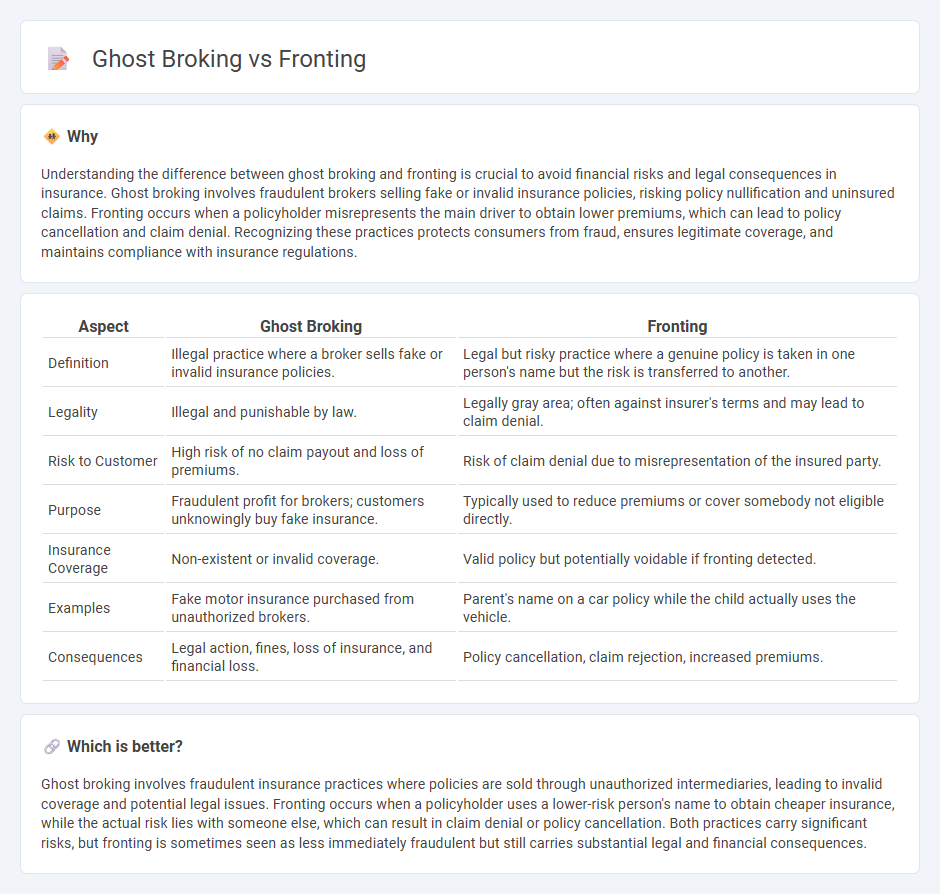
Understanding the difference between ghost broking and fronting is crucial to avoid financial risks and legal consequences in insurance. Ghost broking involves fraudulent brokers selling fake or invalid insurance policies, risking policy nullification and uninsured claims. Fronting occurs when a policyholder misrepresents the main driver to obtain lower premiums, which can lead to policy cancellation and claim denial. Recognizing these practices protects consumers from fraud, ensures legitimate coverage, and maintains compliance with insurance regulations.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Ghost Broking | Fronting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Illegal practice where a broker sells fake or invalid insurance policies. | Legal but risky practice where a genuine policy is taken in one person's name but the risk is transferred to another. |
| Legality | Illegal and punishable by law. | Legally gray area; often against insurer's terms and may lead to claim denial. |
| Risk to Customer | High risk of no claim payout and loss of premiums. | Risk of claim denial due to misrepresentation of the insured party. |
| Purpose | Fraudulent profit for brokers; customers unknowingly buy fake insurance. | Typically used to reduce premiums or cover somebody not eligible directly. |
| Insurance Coverage | Non-existent or invalid coverage. | Valid policy but potentially voidable if fronting detected. |
| Examples | Fake motor insurance purchased from unauthorized brokers. | Parent's name on a car policy while the child actually uses the vehicle. |
| Consequences | Legal action, fines, loss of insurance, and financial loss. | Policy cancellation, claim rejection, increased premiums. |
Which is better?
Ghost broking involves fraudulent insurance practices where policies are sold through unauthorized intermediaries, leading to invalid coverage and potential legal issues. Fronting occurs when a policyholder uses a lower-risk person's name to obtain cheaper insurance, while the actual risk lies with someone else, which can result in claim denial or policy cancellation. Both practices carry significant risks, but fronting is sometimes seen as less immediately fraudulent but still carries substantial legal and financial consequences.
Connection
Ghost broking involves fraudsters selling fake or altered insurance policies to unsuspecting customers, while fronting occurs when a genuine policyholder misrepresents their risk profile by using another person's details to obtain cheaper insurance. These practices intersect as both contribute to insurance fraud by distorting risk assessments, leading to financial losses for insurers and higher premiums for genuine policyholders. Understanding the link between ghost broking and fronting is crucial for improving fraud detection and maintaining the integrity of the insurance market.
Key Terms
Licensed Insurer (Fronting)
Fronting involves a licensed insurer issuing policies but transferring risk to a third party, maintaining regulatory compliance and ensuring policyholder protection. Ghost broking operates illegally, where unlicensed individuals sell counterfeit or unauthorized insurance policies, putting customers at significant financial risk. Explore the differences between fronting and ghost broking to safeguard your insurance investments effectively.
Fraudulent Policy (Ghost Broking)
Ghost broking involves the fraudulent sale of insurance policies using false documents or stolen identities, leading to invalid coverage and significant financial losses for victims. Fronting, a related illegal practice, occurs when a policyholder misrepresents who the insured is to obtain cheaper premiums, often leaving the insurer at risk and fraudulent claims unresolved. Discover more about the risks and prevention measures associated with these deceptive insurance schemes.
Regulatory Compliance
Fronting involves an authorized insurer issuing a policy but transferring most or all risk to an unauthorized entity, creating regulatory risks due to lack of transparency and solvency concerns. Ghost broking is the illegal practice where brokers sell fraudulent or unauthorized insurance policies, exposing clients to invalid coverage and regulatory penalties. Explore further to understand the compliance measures and industry safeguards against these practices.
Source and External Links
Fronting - IRMI - Fronting refers to the use of a licensed insurer to issue policies on behalf of a self-insured organization, retaining the risk internally.
What Is Fronting in Speech - Is Fronting a Speech Sound Disorder - Fronting is a phonological process where sounds are produced at the front of the mouth instead of their usual location.
Fronting - Wikipedia - Fronting can refer to a sound change, a prominent role in a group, or a controlling personality in a plural system.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com