Parametric insurance provides predetermined payouts based on specific triggering events or parameters, such as weather data or natural disasters, ensuring fast and transparent claims processing. Mutual insurance operates on a cooperative model where policyholders are also owners, sharing risks and profits among members, fostering aligned interests and community support. Explore the differences further to determine which insurance model suits your needs best.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between parametric insurance and mutual insurance is crucial for choosing the right coverage tailored to specific risk needs. Parametric insurance offers pre-agreed payouts triggered by measurable events, providing quick claims without loss assessment delays. Mutual insurance pools resources from members to cover collective risks, fostering shared responsibility and potential dividends. Selecting the appropriate insurance model impacts financial protection efficiency and risk management outcomes.
Comparison Table
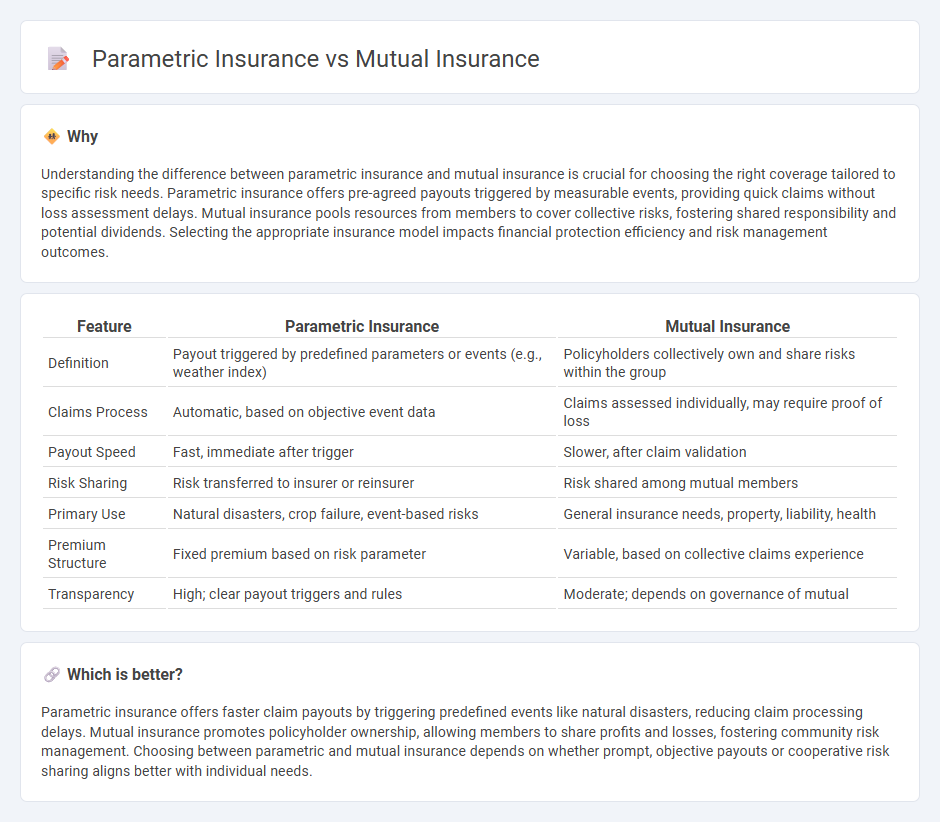
| Feature | Parametric Insurance | Mutual Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Payout triggered by predefined parameters or events (e.g., weather index) | Policyholders collectively own and share risks within the group |
| Claims Process | Automatic, based on objective event data | Claims assessed individually, may require proof of loss |
| Payout Speed | Fast, immediate after trigger | Slower, after claim validation |
| Risk Sharing | Risk transferred to insurer or reinsurer | Risk shared among mutual members |
| Primary Use | Natural disasters, crop failure, event-based risks | General insurance needs, property, liability, health |
| Premium Structure | Fixed premium based on risk parameter | Variable, based on collective claims experience |
| Transparency | High; clear payout triggers and rules | Moderate; depends on governance of mutual |
Which is better?
Parametric insurance offers faster claim payouts by triggering predefined events like natural disasters, reducing claim processing delays. Mutual insurance promotes policyholder ownership, allowing members to share profits and losses, fostering community risk management. Choosing between parametric and mutual insurance depends on whether prompt, objective payouts or cooperative risk sharing aligns better with individual needs.
Connection
Parametric insurance and mutual insurance share a focus on risk pooling, with parametric insurance providing predefined payouts based on specific event triggers, such as natural disasters, without the need for loss adjustment. Mutual insurance operates on a cooperative model where policyholders collectively share risks and profits, aligning incentives toward mutual benefit and cost reduction. Integrating parametric triggers within mutual insurance frameworks can enhance transparency, expedite claim settlements, and optimize risk management for members.
Key Terms
Risk Sharing
Mutual insurance involves policyholders pooling their premiums to share risks collectively, providing coverage based on actual losses experienced, fostering community risk-sharing and financial solidarity. Parametric insurance offers predetermined payouts based on specific triggers or parameters, such as weather events or natural disasters, enabling faster claims settlements but without verifying individual losses. Explore the advantages of these distinct risk-sharing models to determine which best suits your coverage needs.
Payout Structure
Mutual insurance pools risk among members, paying claims based on documented losses, while parametric insurance offers predetermined payouts triggered by specific parameters like weather events or earthquake magnitude. The payout structure of mutual insurance depends on actual loss assessments, leading to variable claim amounts, whereas parametric insurance provides rapid, fixed payments, reducing claim processing time and uncertainty. Explore how these distinct payout models impact risk management strategies.
Policyholder Ownership
Mutual insurance is characterized by policyholder ownership, where insured individuals collectively own and govern the insurer, sharing profits and decision-making powers. Parametric insurance, in contrast, does not confer ownership to policyholders; it provides pre-agreed payouts based on specific event triggers rather than indemnifying losses, often under traditional or commercial ownership structures. Explore the dynamics of policyholder rights and benefits in both models for a comprehensive understanding.
Source and External Links
Mutual Insurance - A mutual insurance company is owned entirely by its policyholders, distributing profits to them in the form of dividends or reduced premiums.
Nationwide - Originated as a mutual auto insurance company but now offers a wide range of insurance and financial services as a Fortune 100 company.
Jewelers Mutual - Specializes in jewelry insurance with over 110 years of expertise and offers comprehensive coverage for jewelry items.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com