Ghost broking involves illegal insurance brokers who manipulate policies to sell fraudulent coverage, often leading to invalid claims and financial loss for genuine policyholders. Forgery in insurance refers to the deliberate falsification of documents or signatures to commit insurance fraud, undermining trust in the industry and resulting in significant legal consequences. Explore more about the differences between ghost broking and forgery to protect yourself from insurance scams.
Why it is important
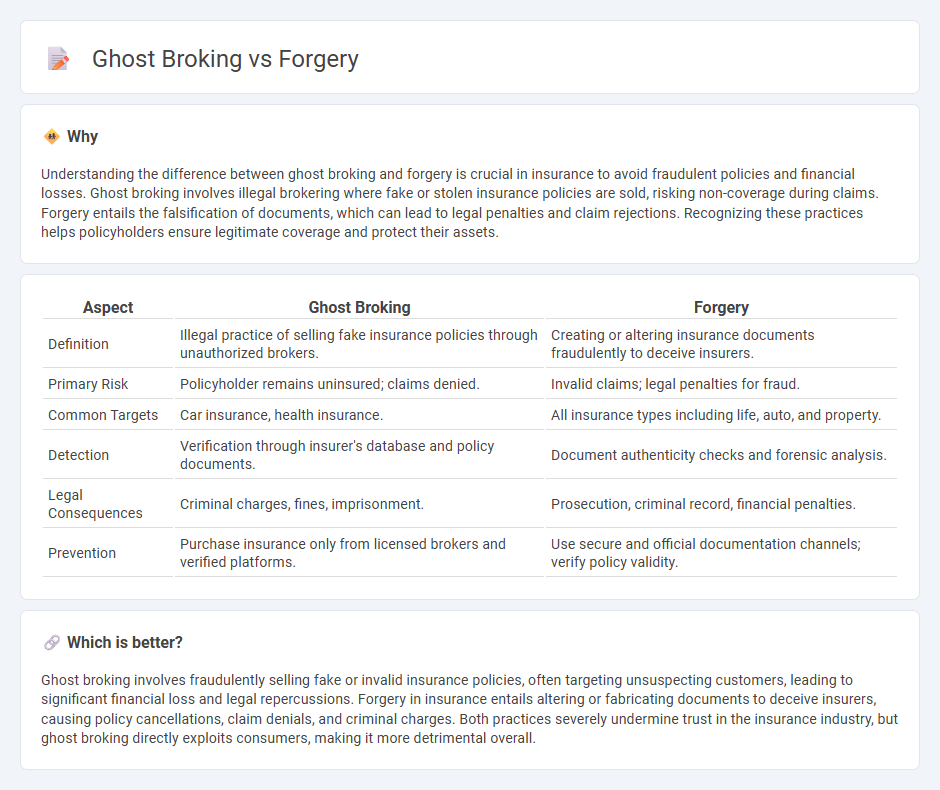
Understanding the difference between ghost broking and forgery is crucial in insurance to avoid fraudulent policies and financial losses. Ghost broking involves illegal brokering where fake or stolen insurance policies are sold, risking non-coverage during claims. Forgery entails the falsification of documents, which can lead to legal penalties and claim rejections. Recognizing these practices helps policyholders ensure legitimate coverage and protect their assets.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Ghost Broking | Forgery |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Illegal practice of selling fake insurance policies through unauthorized brokers. | Creating or altering insurance documents fraudulently to deceive insurers. |
| Primary Risk | Policyholder remains uninsured; claims denied. | Invalid claims; legal penalties for fraud. |
| Common Targets | Car insurance, health insurance. | All insurance types including life, auto, and property. |
| Detection | Verification through insurer's database and policy documents. | Document authenticity checks and forensic analysis. |
| Legal Consequences | Criminal charges, fines, imprisonment. | Prosecution, criminal record, financial penalties. |
| Prevention | Purchase insurance only from licensed brokers and verified platforms. | Use secure and official documentation channels; verify policy validity. |
Which is better?
Ghost broking involves fraudulently selling fake or invalid insurance policies, often targeting unsuspecting customers, leading to significant financial loss and legal repercussions. Forgery in insurance entails altering or fabricating documents to deceive insurers, causing policy cancellations, claim denials, and criminal charges. Both practices severely undermine trust in the insurance industry, but ghost broking directly exploits consumers, making it more detrimental overall.
Connection
Ghost broking involves fraudulent intermediaries who illegally sell insurance policies, often using forged documents to deceive clients and insurers. This illegal practice relies heavily on forgery to create fake identification, policy documents, and claims, enabling criminals to bypass regulatory checks. Insurance companies incur significant financial losses due to ghost broking, as forged policies lead to unpaid claims and increased fraud investigation costs.
Key Terms
Fraud
Forgery involves creating counterfeit documents or signatures to deceive authorities, commonly used in insurance claims and financial transactions. Ghost broking is a specific type of insurance fraud where unauthorized individuals sell fake or invalid insurance policies using stolen or forged credentials. Explore the distinctions and impact of these fraudulent activities to better protect yourself from insurance scams.
Policyholder
Forgery involves creating fake insurance documents to deceive policyholders and insurers, compromising trust and financial security. Ghost broking tricks policyholders into buying invalid insurance policies through unauthorized intermediaries, leaving them unprotected and liable for legal penalties. Discover how to protect yourself from these insurance fraud risks and safeguard your coverage.
Underwriting
Forgery involves falsifying documents to deceive insurers, compromising the integrity of underwriting data and leading to inaccurate risk assessments. Ghost broking refers to unauthorized individuals selling insurance policies, often manipulating underwriting information to bypass standard checks and increase fraudulent claims. Explore how underwriting processes adapt to detect and prevent these distinct fraudulent practices.
Source and External Links
Forgery - FindLaw - Describes forgery as the creation, alteration, or unauthorized signing of a document with the intent to defraud, including legal contracts and historical papers.
Forgery | Wex | US Law - Explains forgery under common law as creating or altering a legal instrument with the intent to defraud.
Title 17-A, SS703: Forgery - Maine Legislature - Defines forgery in Maine as falsely making, completing, or altering a written instrument with the intent to defraud or deceive.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com