Silent cyber coverage addresses gaps in traditional insurance policies by explicitly covering or excluding cyber risks that may be unintentionally included. Embedded cyber risk involves cyber threats inherently present in standard insurance lines without clear delineation, potentially leading to ambiguous claims handling. Explore detailed differences and implications between silent cyber coverage and embedded cyber risk to better protect your assets.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between silent cyber coverage and embedded cyber risk is crucial for businesses to accurately assess their exposure to cyber threats and ensure adequate protection in insurance policies. Silent cyber coverage specifically addresses cyber-related losses that are not explicitly included or excluded in traditional policies, while embedded cyber risk refers to potential cyber incidents inherently covered within standard insurance contracts. Clarifying these distinctions prevents gaps in coverage and financial surprises following a cyberattack. Proper knowledge helps companies tailor their risk management strategies and choose suitable cyber insurance solutions.
Comparison Table
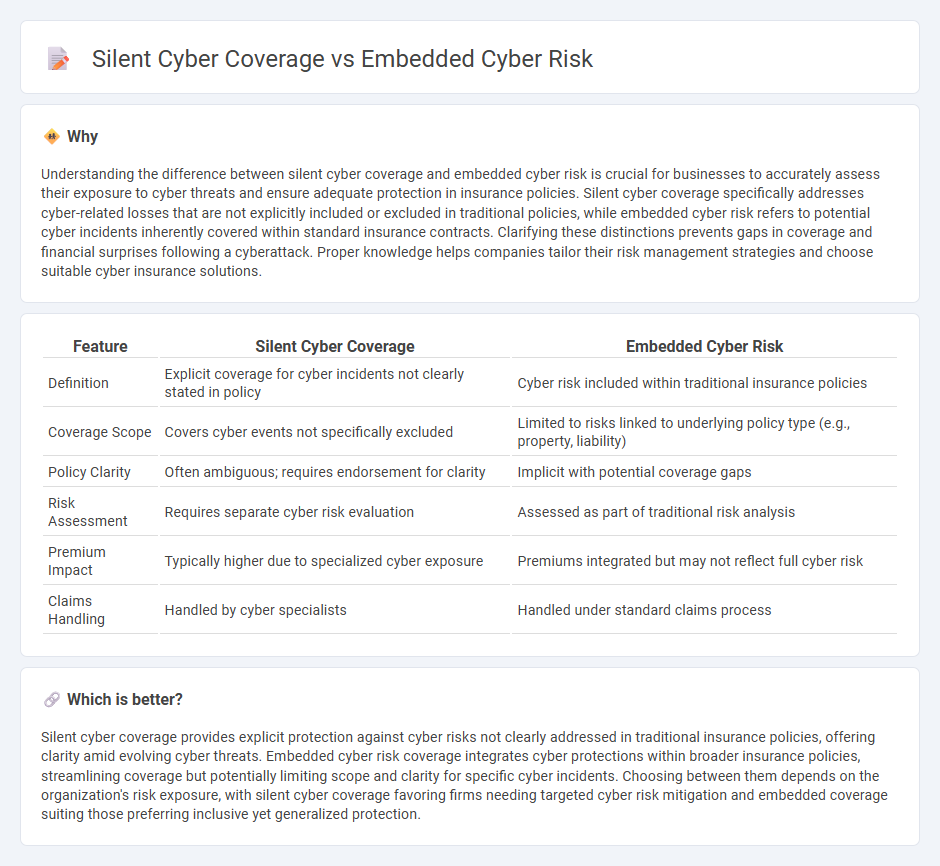
| Feature | Silent Cyber Coverage | Embedded Cyber Risk |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Explicit coverage for cyber incidents not clearly stated in policy | Cyber risk included within traditional insurance policies |
| Coverage Scope | Covers cyber events not specifically excluded | Limited to risks linked to underlying policy type (e.g., property, liability) |
| Policy Clarity | Often ambiguous; requires endorsement for clarity | Implicit with potential coverage gaps |
| Risk Assessment | Requires separate cyber risk evaluation | Assessed as part of traditional risk analysis |
| Premium Impact | Typically higher due to specialized cyber exposure | Premiums integrated but may not reflect full cyber risk |
| Claims Handling | Handled by cyber specialists | Handled under standard claims process |
Which is better?
Silent cyber coverage provides explicit protection against cyber risks not clearly addressed in traditional insurance policies, offering clarity amid evolving cyber threats. Embedded cyber risk coverage integrates cyber protections within broader insurance policies, streamlining coverage but potentially limiting scope and clarity for specific cyber incidents. Choosing between them depends on the organization's risk exposure, with silent cyber coverage favoring firms needing targeted cyber risk mitigation and embedded coverage suiting those preferring inclusive yet generalized protection.
Connection
Silent cyber coverage addresses cyber-related losses not explicitly covered in traditional insurance policies, revealing gaps caused by embedded cyber risk, which is the inherent vulnerability within non-cyber-specific policies. Embedded cyber risk arises from the increasing digitization of business operations, where traditional insurance lines like property or liability may inadvertently expose carriers to cyber threats. Understanding the connection helps insurers develop clearer underwriting guidelines and explicitly include or exclude cyber risks, reducing ambiguities in coverage.
Key Terms
Policy Exclusions
Embedded cyber risk coverage often includes cyber-related losses within traditional insurance policies but typically contains specific policy exclusions for certain cyber incidents, limiting protection against sophisticated attacks. Silent cyber coverage refers to unintentional cyber risk exposure in non-cyber policies, where exclusions are crucial to identify gaps and clarify insurer liability. Explore further to understand the intricate differences in policy exclusions shaping cyber risk management strategies.
Affirmative Coverage
Affirmative cyber coverage explicitly includes cyber risks within an insurance policy, providing clear protection against losses from data breaches, ransomware, and other cyber threats. In contrast, silent cyber coverage refers to cyber risk exposures that are unintentionally covered under traditional policies not designed for cyber incidents, creating ambiguity in claim handling. Explore the distinctions and benefits of affirmative coverage to better understand how to safeguard your business against evolving cyber threats.
Underwriting Clarity
Embedded cyber risk integrates cyber threats directly into traditional insurance policies, complicating underwriting by blending cyber exposure with conventional coverage, often leading to ambiguous risk assessment. Silent cyber coverage refers to cyber risks inadvertently covered under non-cyber policies without explicit underwriting, creating potential gaps and uncertainties in liability and claim handling. Explore expert insights to gain clearer understanding of underwriting clarity between embedded cyber risk and silent cyber coverage.
Source and External Links
10 Best Practices to Ensure Embedded System Security - This article discusses key risks to embedded system security and provides expert tips to protect against common attacks.
How Hackers Are Targeting Embedded Systems - It highlights why embedded systems are vulnerable, including dual attack surfaces and the prioritization of functionality over security.
The Hidden Risks in Embedded Systems - This report explores vulnerabilities in embedded devices, emphasizing the need for a multilayered security approach beyond standard hardware protections.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com