Flood risk mapping identifies vulnerable areas by analyzing rainfall patterns, water flow, and topography to predict and mitigate flood damage. Drought risk assessment evaluates long-term precipitation deficits, soil moisture levels, and vegetation health to forecast water shortages and agricultural impacts. Explore detailed methods and benefits of both approaches in modern insurance risk management.
Why it is important
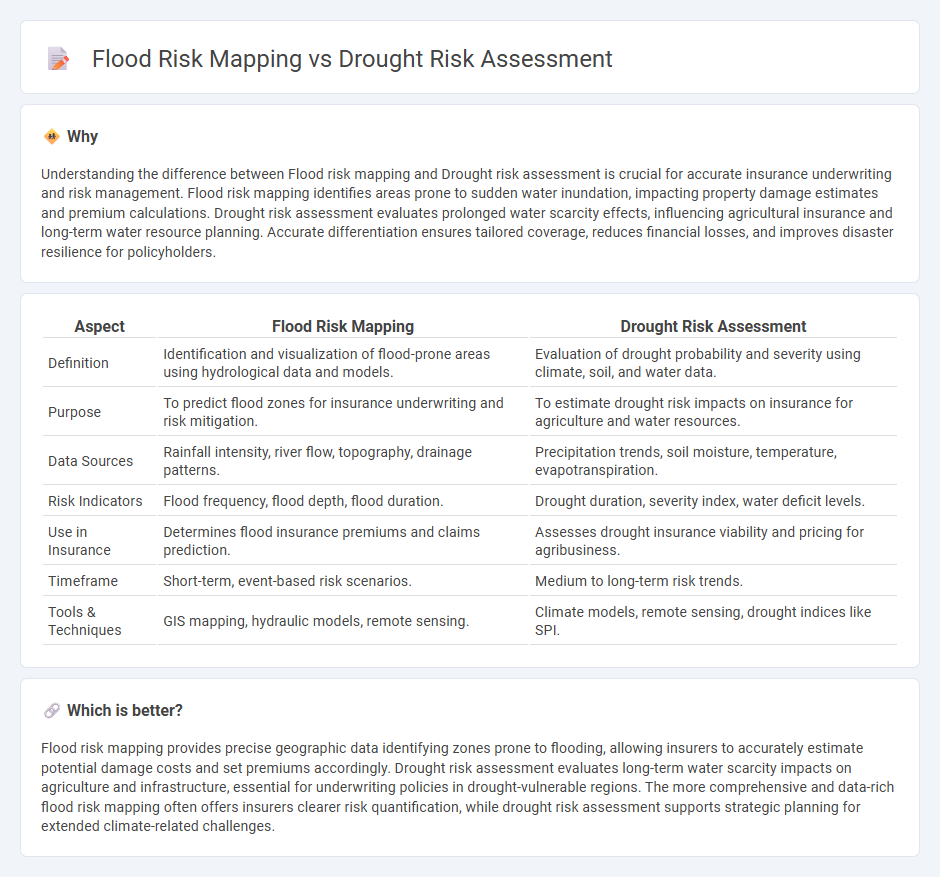
Understanding the difference between Flood risk mapping and Drought risk assessment is crucial for accurate insurance underwriting and risk management. Flood risk mapping identifies areas prone to sudden water inundation, impacting property damage estimates and premium calculations. Drought risk assessment evaluates prolonged water scarcity effects, influencing agricultural insurance and long-term water resource planning. Accurate differentiation ensures tailored coverage, reduces financial losses, and improves disaster resilience for policyholders.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Flood Risk Mapping | Drought Risk Assessment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Identification and visualization of flood-prone areas using hydrological data and models. | Evaluation of drought probability and severity using climate, soil, and water data. |
| Purpose | To predict flood zones for insurance underwriting and risk mitigation. | To estimate drought risk impacts on insurance for agriculture and water resources. |
| Data Sources | Rainfall intensity, river flow, topography, drainage patterns. | Precipitation trends, soil moisture, temperature, evapotranspiration. |
| Risk Indicators | Flood frequency, flood depth, flood duration. | Drought duration, severity index, water deficit levels. |
| Use in Insurance | Determines flood insurance premiums and claims prediction. | Assesses drought insurance viability and pricing for agribusiness. |
| Timeframe | Short-term, event-based risk scenarios. | Medium to long-term risk trends. |
| Tools & Techniques | GIS mapping, hydraulic models, remote sensing. | Climate models, remote sensing, drought indices like SPI. |
Which is better?
Flood risk mapping provides precise geographic data identifying zones prone to flooding, allowing insurers to accurately estimate potential damage costs and set premiums accordingly. Drought risk assessment evaluates long-term water scarcity impacts on agriculture and infrastructure, essential for underwriting policies in drought-vulnerable regions. The more comprehensive and data-rich flood risk mapping often offers insurers clearer risk quantification, while drought risk assessment supports strategic planning for extended climate-related challenges.
Connection
Flood risk mapping and drought risk assessment are interconnected through their evaluation of hydrological extremes affecting water availability and land use. Both use geospatial data and climate models to identify vulnerable regions, helping insurers quantify risk exposure more accurately. Integrating these assessments supports comprehensive risk management strategies for insurance policies covering water-related damages.
Key Terms
**Drought risk assessment:**
Drought risk assessment evaluates the likelihood and potential impacts of prolonged water shortages on agriculture, water supply, and ecosystems using climate models and historical data analysis. It incorporates factors such as precipitation patterns, soil moisture levels, and socio-economic vulnerability to predict drought severity and duration. Explore comprehensive drought risk methodologies and their applications to better understand regional resilience strategies.
Precipitation Index
Drought risk assessment and flood risk mapping both rely heavily on precipitation index data to evaluate vulnerability and predict events, with drought assessments focusing on prolonged deficits and flood mapping on excess rainfall patterns. The Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI) is a critical tool in measuring precipitation anomalies over various timescales, aiding in identifying drought onset, duration, and severity. Explore detailed methodologies and comparative analyses of precipitation indices to enhance risk management strategies for droughts and floods.
Soil Moisture Deficit
Drought risk assessment primarily relies on soil moisture deficit as a key indicator to evaluate the severity and duration of dry spells affecting agricultural productivity and water resources. In contrast, flood risk mapping incorporates soil moisture data to determine saturation levels that influence runoff and flood potential, but it emphasizes rainfall intensity and drainage capacity more heavily. Explore detailed methodologies and case studies to understand the critical role of soil moisture deficit in both drought and flood risk management.
Source and External Links
Drought Risk Assessment and Mapping - This document provides a technical description of drought risk assessment in Ukraine, highlighting its importance due to the country's climate conditions.
Vulnerability and Risk Assessment - This resource offers a comprehensive approach to assessing drought risk, incorporating factors such as vulnerability, hazard, and exposure.
Drought Risk and Resilience Assessment Methodology - This framework provides practical measures to build resilience across the drought cycle, helping governments address drought risks effectively.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com