Social prescribing insurance focuses on covering interventions that connect individuals to community resources for improved well-being, while disability insurance provides financial protection by replacing income lost due to illness or injury impairing work ability. Both insurance types address different aspects of health and support, emphasizing preventive care versus income security. Explore how these insurance options can complement each other to enhance overall health and financial stability.
Why it is important
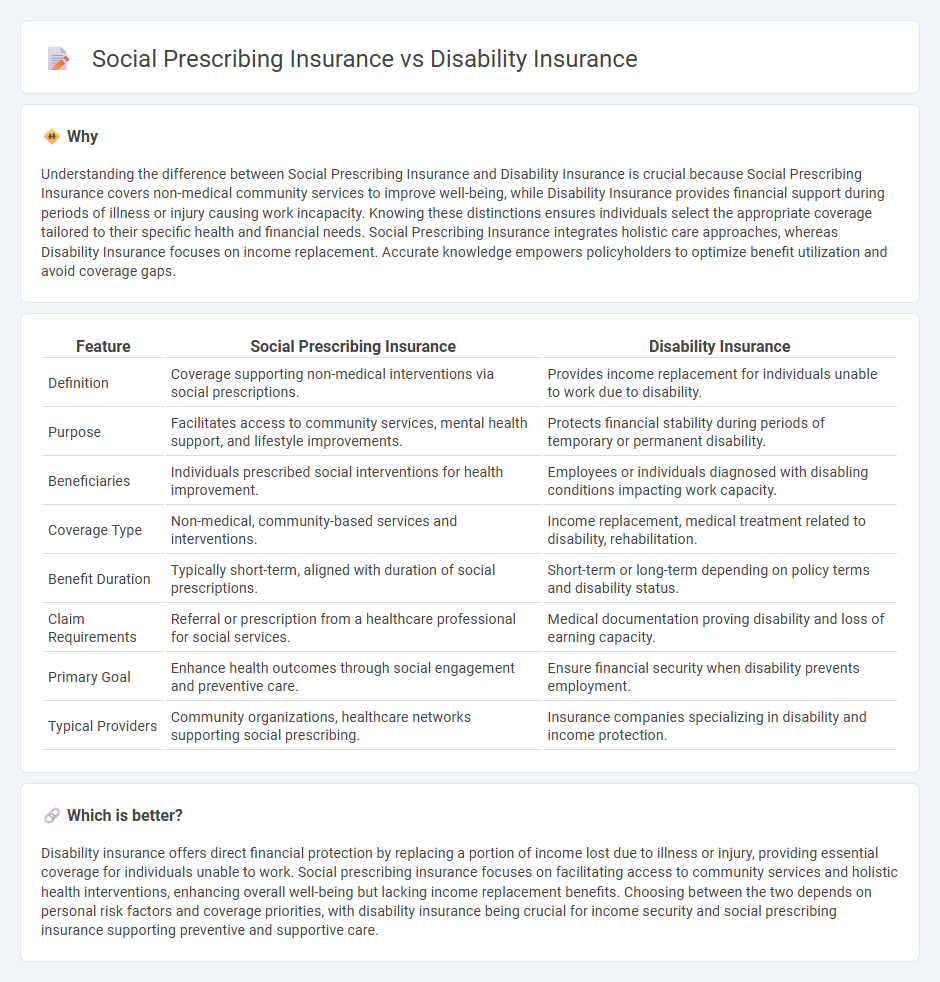
Understanding the difference between Social Prescribing Insurance and Disability Insurance is crucial because Social Prescribing Insurance covers non-medical community services to improve well-being, while Disability Insurance provides financial support during periods of illness or injury causing work incapacity. Knowing these distinctions ensures individuals select the appropriate coverage tailored to their specific health and financial needs. Social Prescribing Insurance integrates holistic care approaches, whereas Disability Insurance focuses on income replacement. Accurate knowledge empowers policyholders to optimize benefit utilization and avoid coverage gaps.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Social Prescribing Insurance | Disability Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Coverage supporting non-medical interventions via social prescriptions. | Provides income replacement for individuals unable to work due to disability. |
| Purpose | Facilitates access to community services, mental health support, and lifestyle improvements. | Protects financial stability during periods of temporary or permanent disability. |
| Beneficiaries | Individuals prescribed social interventions for health improvement. | Employees or individuals diagnosed with disabling conditions impacting work capacity. |
| Coverage Type | Non-medical, community-based services and interventions. | Income replacement, medical treatment related to disability, rehabilitation. |
| Benefit Duration | Typically short-term, aligned with duration of social prescriptions. | Short-term or long-term depending on policy terms and disability status. |
| Claim Requirements | Referral or prescription from a healthcare professional for social services. | Medical documentation proving disability and loss of earning capacity. |
| Primary Goal | Enhance health outcomes through social engagement and preventive care. | Ensure financial security when disability prevents employment. |
| Typical Providers | Community organizations, healthcare networks supporting social prescribing. | Insurance companies specializing in disability and income protection. |
Which is better?
Disability insurance offers direct financial protection by replacing a portion of income lost due to illness or injury, providing essential coverage for individuals unable to work. Social prescribing insurance focuses on facilitating access to community services and holistic health interventions, enhancing overall well-being but lacking income replacement benefits. Choosing between the two depends on personal risk factors and coverage priorities, with disability insurance being crucial for income security and social prescribing insurance supporting preventive and supportive care.
Connection
Social prescribing insurance and disability insurance intersect by addressing holistic health needs and long-term support for individuals with chronic conditions. Social prescribing insurance often funds non-medical interventions such as community activities, which can prevent disability or aid in rehabilitation, while disability insurance provides financial protection against loss of income due to illness or impairment. Both types of insurance work together to enhance patient well-being and reduce healthcare costs through integrated care models.
Key Terms
Income Replacement
Disability insurance provides income replacement if you are unable to work due to illness or injury, ensuring financial stability by covering a portion of your lost wages. Social prescribing insurance, while less common, supports holistic health management through access to community resources but does not directly replace income. Explore detailed comparisons to understand how each option benefits your financial and health needs.
Occupational Assessment
Disability insurance primarily covers income loss due to work-related injuries or illnesses, with occupational assessments evaluating the extent of impairment and job capabilities to determine eligibility and benefit levels. Social prescribing insurance, emerging in holistic health models, integrates occupational assessments to identify non-medical needs and recommend community-based interventions that support overall well-being and work reintegration. Explore how occupational assessments shape the effectiveness of both insurance types and their impact on workplace health management.
Preventive Health Programs
Disability insurance provides income protection during illness or injury, focusing on mitigating financial risks, while social prescribing insurance supports access to preventive health programs emphasizing holistic well-being. Preventive health programs under social prescribing insurance often include lifestyle interventions, mental health support, and community resources that reduce the incidence of chronic diseases. Explore how integrating these insurance models can enhance long-term health outcomes and financial security.
Source and External Links
What is Social Security Disability Insurance? - This webpage explains how Social Security Disability Insurance provides monthly benefits to workers unable to work due to significant illnesses or impairments, based on their past earnings and work history.
Affordable Disability Insurance Plans - Guardian offers disability insurance plans for individuals and businesses to replace income if illness or injury prevents working, providing financial protection and stability.
Types of Disability Insurance - This webpage discusses the two main types of disability insurance: Short-Term Disability (STD) and Long-Term Disability (LTD), which offer different durations of income protection.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com