Artificial intelligence underwriting leverages machine learning algorithms and big data analytics to assess risk more accurately by analyzing diverse data sources including medical records, social media, and financial behavior. Usage-based underwriting focuses on real-time behavior tracking, particularly in auto insurance, using telematics devices to monitor driving patterns and adjust premiums accordingly. Explore how these innovative underwriting methods transform insurance risk evaluation and pricing.
Why it is important
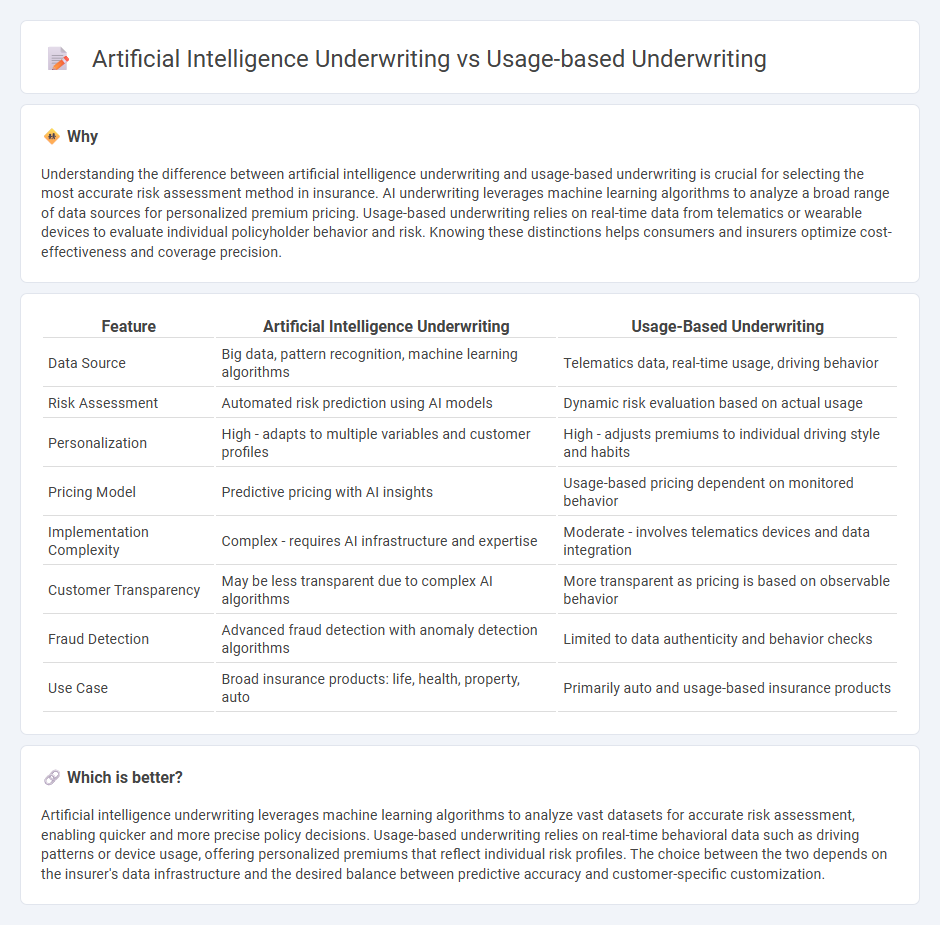
Understanding the difference between artificial intelligence underwriting and usage-based underwriting is crucial for selecting the most accurate risk assessment method in insurance. AI underwriting leverages machine learning algorithms to analyze a broad range of data sources for personalized premium pricing. Usage-based underwriting relies on real-time data from telematics or wearable devices to evaluate individual policyholder behavior and risk. Knowing these distinctions helps consumers and insurers optimize cost-effectiveness and coverage precision.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Artificial Intelligence Underwriting | Usage-Based Underwriting |
|---|---|---|
| Data Source | Big data, pattern recognition, machine learning algorithms | Telematics data, real-time usage, driving behavior |
| Risk Assessment | Automated risk prediction using AI models | Dynamic risk evaluation based on actual usage |
| Personalization | High - adapts to multiple variables and customer profiles | High - adjusts premiums to individual driving style and habits |
| Pricing Model | Predictive pricing with AI insights | Usage-based pricing dependent on monitored behavior |
| Implementation Complexity | Complex - requires AI infrastructure and expertise | Moderate - involves telematics devices and data integration |
| Customer Transparency | May be less transparent due to complex AI algorithms | More transparent as pricing is based on observable behavior |
| Fraud Detection | Advanced fraud detection with anomaly detection algorithms | Limited to data authenticity and behavior checks |
| Use Case | Broad insurance products: life, health, property, auto | Primarily auto and usage-based insurance products |
Which is better?
Artificial intelligence underwriting leverages machine learning algorithms to analyze vast datasets for accurate risk assessment, enabling quicker and more precise policy decisions. Usage-based underwriting relies on real-time behavioral data such as driving patterns or device usage, offering personalized premiums that reflect individual risk profiles. The choice between the two depends on the insurer's data infrastructure and the desired balance between predictive accuracy and customer-specific customization.
Connection
Artificial intelligence underwriting enhances usage-based underwriting by leveraging real-time data and machine learning algorithms to assess risk more accurately. Usage-based underwriting collects data from telematics, IoT devices, or mobile apps, allowing AI to analyze driving behavior, health metrics, or property usage patterns for personalized policy pricing. This synergy improves risk prediction, reduces underwriting time, and enables dynamic premium adjustments tailored to individual policyholders.
Key Terms
Telematics
Usage-based underwriting leverages telematics data such as driving behavior, mileage, and real-time vehicle usage to personalize insurance premiums and reduce risk accurately. Artificial intelligence underwriting integrates machine learning algorithms and vast datasets, including telematics signals, to automate risk assessment, detect fraud, and optimize policy pricing dynamically. Discover how telematics-driven data enhances both underwriting methods by visiting our detailed analysis.
Machine Learning
Usage-based underwriting leverages real-time data from telematics or IoT devices to tailor insurance premiums based on actual user behavior, enhancing risk assessment accuracy. Artificial intelligence underwriting, particularly through machine learning algorithms, processes vast datasets to identify patterns, automate decisions, and improve predictive analytics for underwriting. Explore more to understand how machine learning revolutionizes risk evaluation and insurance pricing models.
Risk Assessment
Usage-based underwriting leverages real-time data from telematics, sensors, and user behavior to provide dynamic risk assessment tailored to individual profiles, predominantly applied in auto and health insurance. Artificial intelligence underwriting employs machine learning algorithms and predictive analytics to analyze vast datasets, uncover complex patterns, and enhance accuracy in evaluating risk across multiple insurance domains. Explore further insights into how these cutting-edge methods transform risk assessment and optimize underwriting processes.
Source and External Links
What is Usage-Based Insurance? | Azuga Fleet Tracking Glossary - Usage-based insurance (UBI) tailors premiums based on real-time data about driving behavior, such as mileage, location, and habits like hard braking or rapid acceleration--allowing insurers to price risk more accurately and reward safer drivers with discounts.
Usage Based Insurance: Everything You Need To Know | Car and Driver - UBI programs typically fall into mileage-based or behavior-based categories, with premiums adjusted according to how much or how safely you drive, often resulting in significant discounts for low-mileage or cautious drivers.
On demand and usage based insurance | HFW - Usage-based underwriting leverages telematics, AI, and big data to segment risk at a granular level, enabling insurers to offer dynamic, per-use or per-mile policies that reflect individual risk profiles more precisely than traditional models.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com