Cyber insurance protects businesses from financial losses due to data breaches, cyberattacks, and other digital threats, while credit insurance safeguards companies against non-payment risks related to customer credit defaults. Businesses facing increasing digital vulnerabilities require cyber insurance to manage cyber risk, whereas companies dealing with receivables and credit sales benefit from credit insurance to secure cash flow. Explore how these insurance types can enhance your risk management strategy.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between cyber insurance and credit insurance is crucial because cyber insurance protects businesses from data breaches and cyberattacks, while credit insurance covers losses from customer non-payment. Cyber risks include hacking, malware, and ransomware that can disrupt operations and lead to costly data recovery, whereas credit risk involves financial exposure due to credit defaults or insolvency of buyers. Choosing the right coverage ensures that companies adequately safeguard their assets based on specific vulnerabilities. This knowledge supports informed risk management and financial decision-making tailored to distinct insurance needs.
Comparison Table
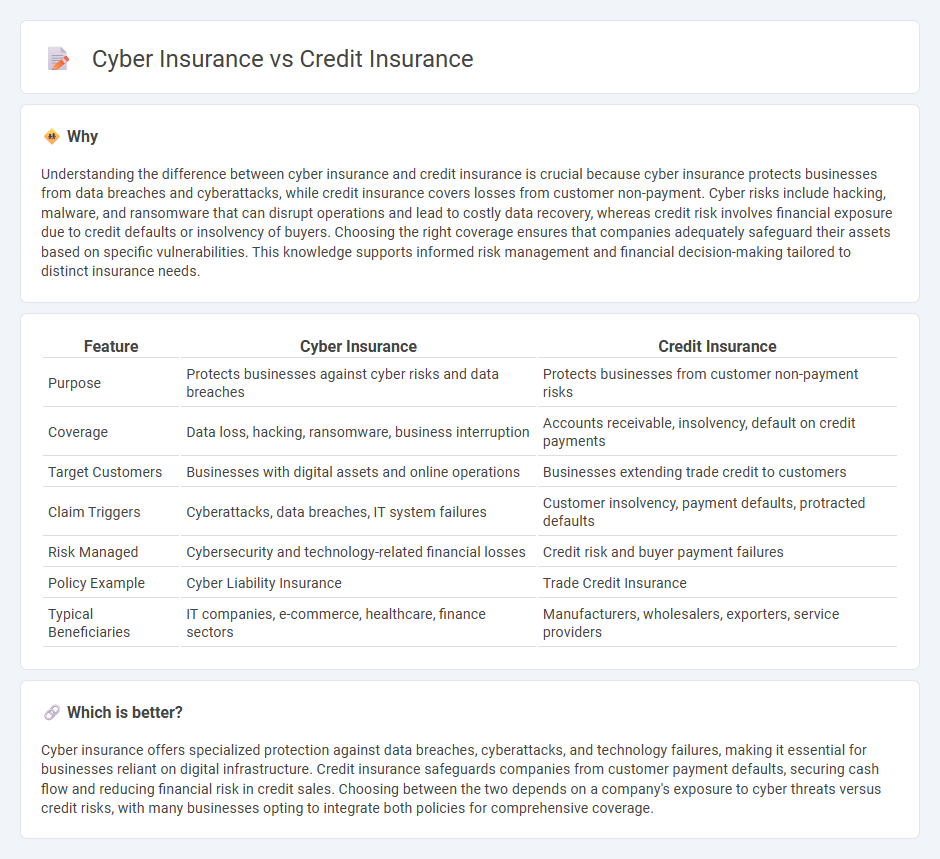
| Feature | Cyber Insurance | Credit Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Protects businesses against cyber risks and data breaches | Protects businesses from customer non-payment risks |
| Coverage | Data loss, hacking, ransomware, business interruption | Accounts receivable, insolvency, default on credit payments |
| Target Customers | Businesses with digital assets and online operations | Businesses extending trade credit to customers |
| Claim Triggers | Cyberattacks, data breaches, IT system failures | Customer insolvency, payment defaults, protracted defaults |
| Risk Managed | Cybersecurity and technology-related financial losses | Credit risk and buyer payment failures |
| Policy Example | Cyber Liability Insurance | Trade Credit Insurance |
| Typical Beneficiaries | IT companies, e-commerce, healthcare, finance sectors | Manufacturers, wholesalers, exporters, service providers |
Which is better?
Cyber insurance offers specialized protection against data breaches, cyberattacks, and technology failures, making it essential for businesses reliant on digital infrastructure. Credit insurance safeguards companies from customer payment defaults, securing cash flow and reducing financial risk in credit sales. Choosing between the two depends on a company's exposure to cyber threats versus credit risks, with many businesses opting to integrate both policies for comprehensive coverage.
Connection
Cyber insurance and credit insurance are connected through their shared role in mitigating financial risks for businesses. Cyber insurance covers losses from data breaches, cyberattacks, and digital threats, protecting company assets and reputation, while credit insurance safeguards businesses against customer payment defaults and insolvencies. Together, these insurance types provide comprehensive financial security by addressing both digital vulnerabilities and credit-related risks in the modern economy.
Key Terms
**Credit Insurance:**
Credit insurance protects businesses from losses due to customer non-payment of commercial debt, safeguarding cash flow and reducing bad debt risks. This type of insurance covers accounts receivable, enhancing financial stability for companies operating in volatile markets or extending credit terms. Explore how credit insurance can secure your financial operations and mitigate credit risks effectively.
Trade Credit Risk
Credit insurance safeguards businesses against losses from non-payment by customers, specifically covering trade credit risk when buyers default on invoices. Cyber insurance protects companies from financial consequences of cyberattacks, data breaches, and IT disruptions but does not cover trade credit defaults. Explore detailed comparisons to understand which insurance best mitigates your trade credit risk exposure.
Policyholder Limit
Credit insurance typically offers policyholder limits based on the buyer's creditworthiness and outstanding receivables, protecting businesses from non-payment risks. Cyber insurance policyholder limits are often determined by the potential impact of data breaches or cyberattacks, covering expenses like breach response, legal fees, and business interruption. Explore more about how these limits influence your risk management strategies and coverage adequacy.
Source and External Links
credit insurance | Wex | US Law | LII / Legal Information Institute - Credit insurance is a policy purchased by a borrower to protect the lender from loss due to the borrower's death, disability, insolvency, or unemployment, with benefits paid directly to the lender if a covered event occurs.
What Is Credit Insurance? - NerdWallet - It is an optional insurance that covers loan or credit card payments if you cannot pay due to death, disability, unemployment, or property damage, and benefits are typically paid to the lender, not the borrower.
Credit insurance | Office of the Insurance Commissioner - Credit insurance pays a lender on your behalf if you die, become disabled, or lose your job, but premiums are often added to your loan or credit, increasing total borrowing costs, and coverage is voluntary, not required by law.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com