Peer-to-peer insurance leverages decentralized risk-sharing among individuals, offering cost transparency and community-driven claims management, while captive insurance involves a company creating a wholly owned subsidiary to self-insure its risks, providing greater control over policies and potential tax advantages. Peer-to-peer models reduce administrative overhead through technology platforms, whereas captive insurance requires substantial capital and regulatory compliance but enhances tailored risk coverage. Explore how these insurance structures can optimize risk management strategies suited to your organizational needs.
Why it is important
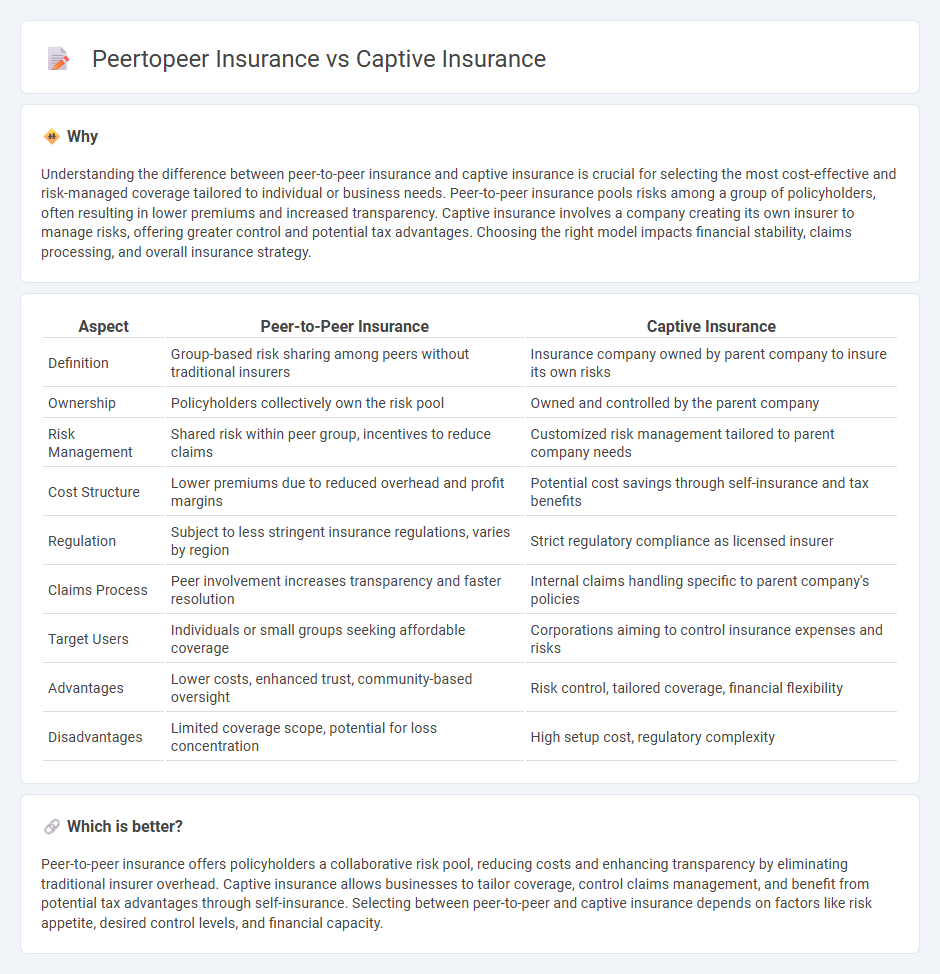
Understanding the difference between peer-to-peer insurance and captive insurance is crucial for selecting the most cost-effective and risk-managed coverage tailored to individual or business needs. Peer-to-peer insurance pools risks among a group of policyholders, often resulting in lower premiums and increased transparency. Captive insurance involves a company creating its own insurer to manage risks, offering greater control and potential tax advantages. Choosing the right model impacts financial stability, claims processing, and overall insurance strategy.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Peer-to-Peer Insurance | Captive Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Group-based risk sharing among peers without traditional insurers | Insurance company owned by parent company to insure its own risks |
| Ownership | Policyholders collectively own the risk pool | Owned and controlled by the parent company |
| Risk Management | Shared risk within peer group, incentives to reduce claims | Customized risk management tailored to parent company needs |
| Cost Structure | Lower premiums due to reduced overhead and profit margins | Potential cost savings through self-insurance and tax benefits |
| Regulation | Subject to less stringent insurance regulations, varies by region | Strict regulatory compliance as licensed insurer |
| Claims Process | Peer involvement increases transparency and faster resolution | Internal claims handling specific to parent company's policies |
| Target Users | Individuals or small groups seeking affordable coverage | Corporations aiming to control insurance expenses and risks |
| Advantages | Lower costs, enhanced trust, community-based oversight | Risk control, tailored coverage, financial flexibility |
| Disadvantages | Limited coverage scope, potential for loss concentration | High setup cost, regulatory complexity |
Which is better?
Peer-to-peer insurance offers policyholders a collaborative risk pool, reducing costs and enhancing transparency by eliminating traditional insurer overhead. Captive insurance allows businesses to tailor coverage, control claims management, and benefit from potential tax advantages through self-insurance. Selecting between peer-to-peer and captive insurance depends on factors like risk appetite, desired control levels, and financial capacity.
Connection
Peer-to-peer insurance and captive insurance both aim to reduce traditional insurer costs by fostering group risk-sharing among members. Peer-to-peer insurance pools premiums within a community to cover claims directly, while captive insurance involves a company creating its own insurance subsidiary to manage internal risks. Both models emphasize risk retention and cost efficiency, leveraging collective resources for more tailored and economical coverage solutions.
Key Terms
Risk Pooling
Captive insurance allows a company to self-insure risks by creating a wholly-owned subsidiary, providing tailored risk pooling and cost control benefits. Peer-to-peer insurance pools risks among individuals or businesses with similar profiles, leveraging collective funds to reduce premiums and increase transparency. Explore how these models revolutionize risk management and financial protection strategies.
Ownership Structure
Captive insurance involves a company creating its own insurance subsidiary to underwrite risks, providing direct control over policies and claims. Peer-to-peer insurance operates on a decentralized model where groups of individuals share risk and premiums, fostering communal risk management without traditional insurer intermediaries. Explore detailed comparisons to understand which ownership structure aligns best with your risk and financial goals.
Claims Management
Captive insurance offers centralized claims management, allowing businesses to tailor risk control and settlement processes to their specific needs, resulting in enhanced cost efficiency and quicker resolution times. Peer-to-peer insurance relies on collective risk sharing among members, which can lead to more transparent claims handling but potentially slower dispute resolutions due to decentralized decision-making. Explore detailed comparisons of claims management strategies and their impact on overall risk mitigation to make informed choices.
Source and External Links
Captive insurance - Wikipedia - Captive insurance is an alternative to self-insurance where insured parties establish a licensed insurance company for their own use, allowing more control over risk, pricing near cost, and tax benefits by treating premiums as deductible business expenses.
What Is Captive Insurance? - A captive insurer is wholly owned by its insureds and provides tailored coverage for risks that may be expensive or unavailable in commercial markets, offering pricing stability and direct control over claims and loss control.
What is Captive Insurance? - Alliant Insurance Services - A captive is a licensed insurance company wholly owned and controlled by its insured, enabling organizations to manage risks, underwrite insurance, stabilize premiums, and gain access to reinsurance markets.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com