Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) enable peer-to-peer cryptocurrency trading without intermediaries, enhancing transparency and security by utilizing blockchain technology. Synthetic asset platforms allow users to gain exposure to traditional financial instruments and cryptocurrencies through tokenized derivatives, offering diversified investment opportunities without owning the underlying assets. Explore how these innovative financial technologies are transforming market accessibility and asset management.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between decentralized exchanges (DEXs) and synthetic asset platforms is crucial for investors to navigate risks, liquidity, and regulatory implications effectively. DEXs enable direct peer-to-peer token trading without intermediaries, enhancing security and transparency. Synthetic asset platforms create derivatives that mimic real assets, offering exposure to traditional markets without owning the underlying asset. This knowledge helps users optimize portfolio strategies, manage exposure, and comply with compliance standards in the evolving decentralized finance ecosystem.
Comparison Table
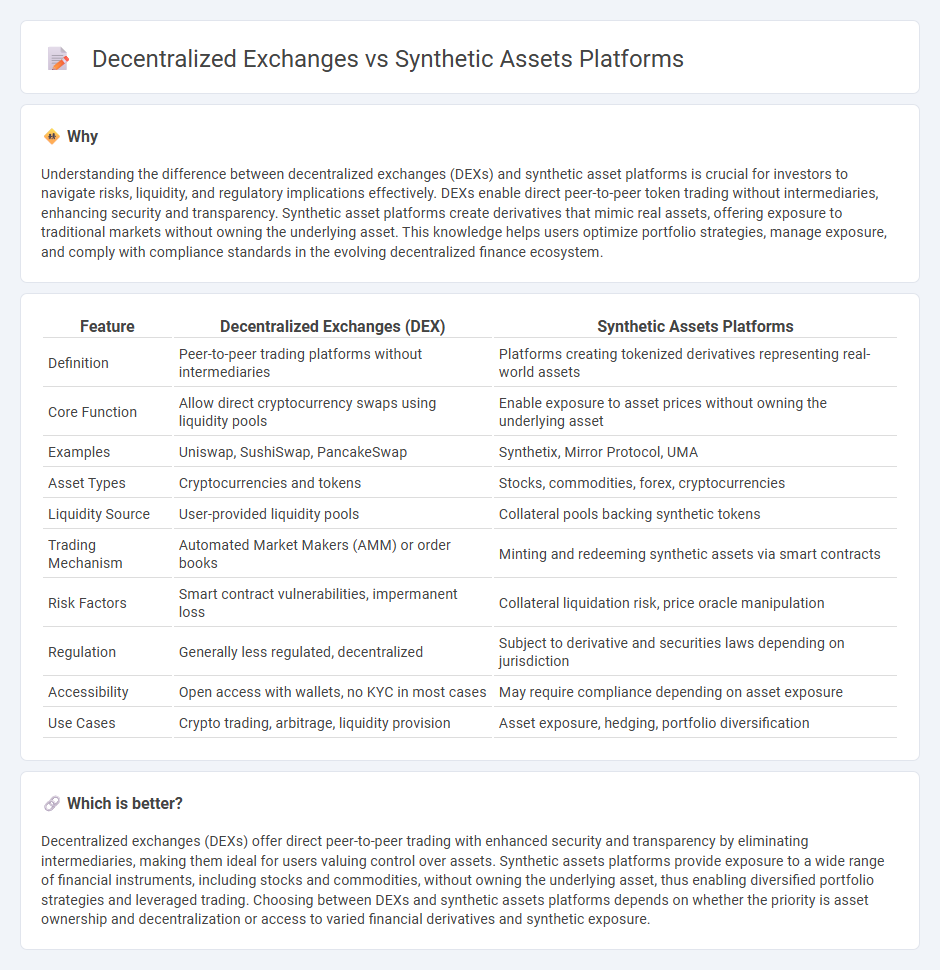
| Feature | Decentralized Exchanges (DEX) | Synthetic Assets Platforms |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Peer-to-peer trading platforms without intermediaries | Platforms creating tokenized derivatives representing real-world assets |
| Core Function | Allow direct cryptocurrency swaps using liquidity pools | Enable exposure to asset prices without owning the underlying asset |
| Examples | Uniswap, SushiSwap, PancakeSwap | Synthetix, Mirror Protocol, UMA |
| Asset Types | Cryptocurrencies and tokens | Stocks, commodities, forex, cryptocurrencies |
| Liquidity Source | User-provided liquidity pools | Collateral pools backing synthetic tokens |
| Trading Mechanism | Automated Market Makers (AMM) or order books | Minting and redeeming synthetic assets via smart contracts |
| Risk Factors | Smart contract vulnerabilities, impermanent loss | Collateral liquidation risk, price oracle manipulation |
| Regulation | Generally less regulated, decentralized | Subject to derivative and securities laws depending on jurisdiction |
| Accessibility | Open access with wallets, no KYC in most cases | May require compliance depending on asset exposure |
| Use Cases | Crypto trading, arbitrage, liquidity provision | Asset exposure, hedging, portfolio diversification |
Which is better?
Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) offer direct peer-to-peer trading with enhanced security and transparency by eliminating intermediaries, making them ideal for users valuing control over assets. Synthetic assets platforms provide exposure to a wide range of financial instruments, including stocks and commodities, without owning the underlying asset, thus enabling diversified portfolio strategies and leveraged trading. Choosing between DEXs and synthetic assets platforms depends on whether the priority is asset ownership and decentralization or access to varied financial derivatives and synthetic exposure.
Connection
Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) facilitate peer-to-peer trading of synthetic assets by providing liquidity pools and trustless marketplaces essential for their seamless operation. Synthetic asset platforms leverage smart contracts to create tokenized representations of real-world assets, which are actively traded on DEXs without relying on traditional intermediaries. This symbiotic relationship enhances market accessibility, reduces counterparty risk, and fosters innovation in decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystems.
Key Terms
**Synthetic Assets Platforms:**
Synthetic assets platforms enable users to create and trade tokenized derivatives that replicate the value of real-world assets such as stocks, commodities, and currencies without owning the underlying asset. These platforms leverage smart contracts on blockchain networks to provide decentralized exposure, high liquidity, and reduced counterparty risk compared to traditional financial markets. Explore how synthetic assets platforms transform asset management and trading by offering broader access and innovative financial instruments.
Collateralization
Synthetic assets platforms rely on over-collateralization, often requiring assets valued at 150% or more of the synthetic token's worth to ensure stability and minimize liquidation risk. Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) typically do not require collateral for trading but depend on liquidity pools and direct asset swaps to facilitate transactions. Explore detailed comparisons to understand how collateralization impacts risk and efficiency in these decentralized financial tools.
Oracles
Synthetic asset platforms rely heavily on oracles to provide accurate, real-time data that supports the creation and management of synthetic tokens representing real-world assets. Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) use oracles less extensively, as they primarily facilitate peer-to-peer trading without the need for external data feeds. Explore how oracle integration impacts security and price stability in both synthetic asset platforms and DEXs to understand their distinct functionalities.
Source and External Links
The Evolution of Synthetic Assets in DeFi: Opportunities and Risks - Synthetix (SNX) is a leading platform allowing users to create and trade synthetic assets called Synths, which represent various real-world assets by locking SNX tokens as collateral through smart contracts on DeFi networks.
Top 6 Crypto Synthetic Asset Platforms In 2025 - The top platforms include Synthetix Network (SNX), UMA Protocol (UMA), Indigo Protocol (INDY), Offshift (XFT), and Cryptex Finance (CTX), which utilize decentralized oracles and smart contracts to provide blockchain-based synthetic assets representing real-world assets for global trading access and liquidity.
Synthetic Assets: The Versatile Solution for DeFi Traders - Webisoft - Synthetix stands out as a dominant decentralized synthetic asset platform on Ethereum, where users can stake SNX tokens as collateral to mint diverse synthetic assets and trade them on its decentralized exchange Kwenta that supports crypto and physical asset exposure.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com