Carbon trading enables companies to buy and sell carbon emission allowances, creating a market-driven approach to reducing greenhouse gases. Sustainable investing focuses on directing capital towards companies or projects that prioritize environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria to generate long-term value and positive impact. Explore the distinctions and benefits of these two financial strategies to enhance your environmental and financial goals.
Why it is important
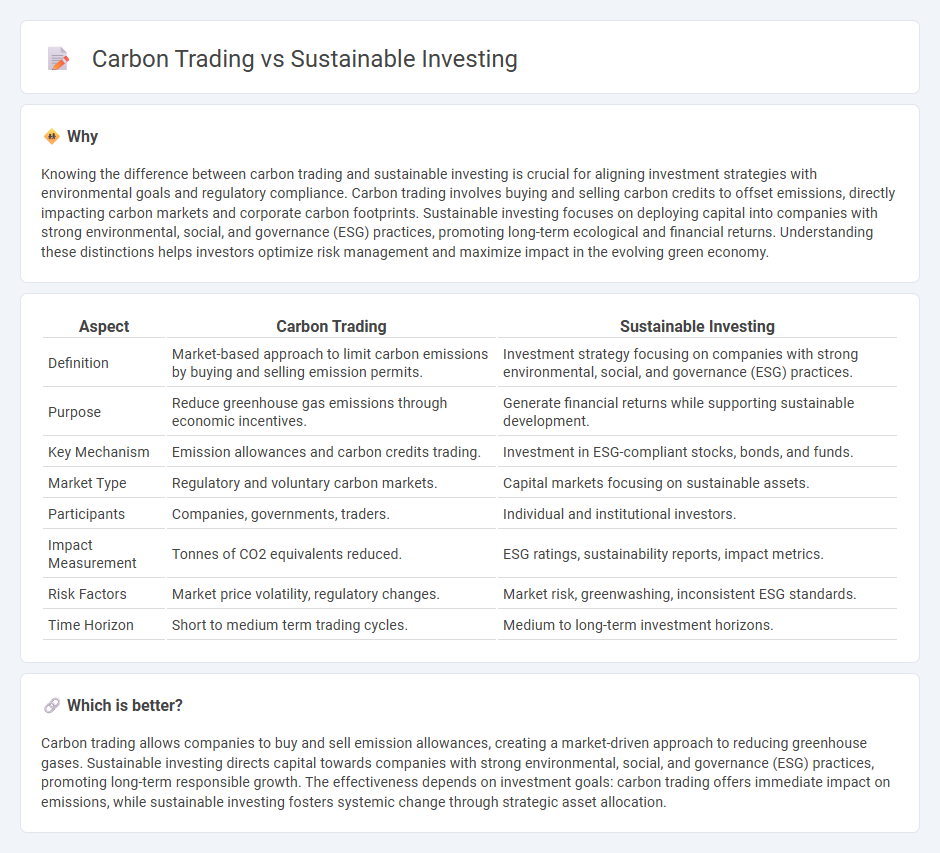
Knowing the difference between carbon trading and sustainable investing is crucial for aligning investment strategies with environmental goals and regulatory compliance. Carbon trading involves buying and selling carbon credits to offset emissions, directly impacting carbon markets and corporate carbon footprints. Sustainable investing focuses on deploying capital into companies with strong environmental, social, and governance (ESG) practices, promoting long-term ecological and financial returns. Understanding these distinctions helps investors optimize risk management and maximize impact in the evolving green economy.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Carbon Trading | Sustainable Investing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Market-based approach to limit carbon emissions by buying and selling emission permits. | Investment strategy focusing on companies with strong environmental, social, and governance (ESG) practices. |
| Purpose | Reduce greenhouse gas emissions through economic incentives. | Generate financial returns while supporting sustainable development. |
| Key Mechanism | Emission allowances and carbon credits trading. | Investment in ESG-compliant stocks, bonds, and funds. |
| Market Type | Regulatory and voluntary carbon markets. | Capital markets focusing on sustainable assets. |
| Participants | Companies, governments, traders. | Individual and institutional investors. |
| Impact Measurement | Tonnes of CO2 equivalents reduced. | ESG ratings, sustainability reports, impact metrics. |
| Risk Factors | Market price volatility, regulatory changes. | Market risk, greenwashing, inconsistent ESG standards. |
| Time Horizon | Short to medium term trading cycles. | Medium to long-term investment horizons. |
Which is better?
Carbon trading allows companies to buy and sell emission allowances, creating a market-driven approach to reducing greenhouse gases. Sustainable investing directs capital towards companies with strong environmental, social, and governance (ESG) practices, promoting long-term responsible growth. The effectiveness depends on investment goals: carbon trading offers immediate impact on emissions, while sustainable investing fosters systemic change through strategic asset allocation.
Connection
Carbon trading and sustainable investing are interlinked through their shared objective of reducing environmental impact while promoting economic growth. Carbon trading markets assign monetary value to carbon emissions, creating incentives for companies to lower their carbon footprint, which aligns with the principles of sustainable investing focused on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria. This synergy directs capital towards businesses committed to sustainability, thereby accelerating the transition to a low-carbon economy.
Key Terms
ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance)
Sustainable investing integrates ESG criteria to drive long-term value by supporting companies with strong environmental stewardship, social responsibility, and governance practices, encouraging ethical and impactful capital allocation. Carbon trading, a market-based approach, specifically targets the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions by enabling companies to buy or sell carbon credits, incentivizing lower emissions and aligning with environmental goals within ESG frameworks. Explore in-depth how these strategies complement each other to enhance corporate sustainability and climate action.
Carbon Credits
Sustainable investing emphasizes long-term environmental, social, and governance (ESG) goals by integrating responsible practices into portfolio management, whereas carbon trading centers on the market mechanism of buying and selling carbon credits to limit greenhouse gas emissions. Carbon credits represent quantifiable, certified reductions in emissions, allowing businesses to offset their carbon footprint through verified projects like reforestation or renewable energy. Explore the nuances of carbon credits and their role in driving both environmental impact and financial returns.
Green Bonds
Sustainable investing prioritizes long-term environmental impact by supporting projects like renewable energy and green infrastructure, while carbon trading enables companies to buy and sell emission allowances to meet regulatory targets. Green bonds specifically channel capital into environmentally beneficial projects, offering investors fixed-income securities that directly fund sustainability initiatives. Explore how green bonds bridge sustainable investing and carbon trading to drive global climate action.
Source and External Links
What Is Sustainable Investing? | HBS Online - Sustainable investing is an investment strategy that integrates environmental, social, and corporate governance (ESG) factors to achieve financial returns while promoting long-term social and environmental value.
Socially responsible investing - Socially responsible investing (SRI) involves strategies that consider ethical, social, and environmental goals alongside financial returns, including practices like screening investments for ESG risks and proactive impact investing.
SUSTAINABLE INVESTING - Major Sustainability - Penn State - Sustainable investing encompasses various approaches including negative and positive screening, ESG integration, and impact investing, all aiming to combine financial return with positive social and environmental impact.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com