Blockchain rollups enhance scalability by aggregating multiple transactions off-chain and submitting them as a single batch to the main chain, reducing congestion and fees while maintaining security. Subnets, or subnetworks, partition a blockchain into smaller, independent segments that operate their own consensus and governance, enabling customizability and faster transaction processing. Explore the nuanced differences between blockchain rollups and subnets to optimize your financial technology strategies.
Why it is important
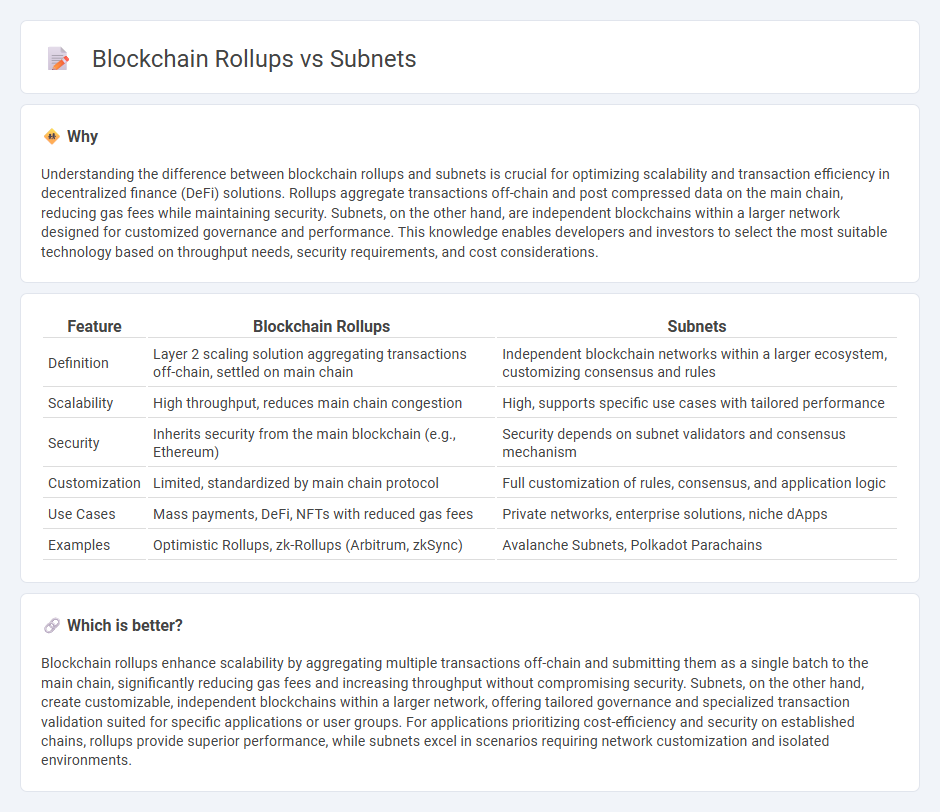
Understanding the difference between blockchain rollups and subnets is crucial for optimizing scalability and transaction efficiency in decentralized finance (DeFi) solutions. Rollups aggregate transactions off-chain and post compressed data on the main chain, reducing gas fees while maintaining security. Subnets, on the other hand, are independent blockchains within a larger network designed for customized governance and performance. This knowledge enables developers and investors to select the most suitable technology based on throughput needs, security requirements, and cost considerations.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Blockchain Rollups | Subnets |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Layer 2 scaling solution aggregating transactions off-chain, settled on main chain | Independent blockchain networks within a larger ecosystem, customizing consensus and rules |
| Scalability | High throughput, reduces main chain congestion | High, supports specific use cases with tailored performance |
| Security | Inherits security from the main blockchain (e.g., Ethereum) | Security depends on subnet validators and consensus mechanism |
| Customization | Limited, standardized by main chain protocol | Full customization of rules, consensus, and application logic |
| Use Cases | Mass payments, DeFi, NFTs with reduced gas fees | Private networks, enterprise solutions, niche dApps |
| Examples | Optimistic Rollups, zk-Rollups (Arbitrum, zkSync) | Avalanche Subnets, Polkadot Parachains |
Which is better?
Blockchain rollups enhance scalability by aggregating multiple transactions off-chain and submitting them as a single batch to the main chain, significantly reducing gas fees and increasing throughput without compromising security. Subnets, on the other hand, create customizable, independent blockchains within a larger network, offering tailored governance and specialized transaction validation suited for specific applications or user groups. For applications prioritizing cost-efficiency and security on established chains, rollups provide superior performance, while subnets excel in scenarios requiring network customization and isolated environments.
Connection
Blockchain rollups enhance scalability by bundling multiple transactions into a single batch on the main chain, reducing congestion and fees. Subnets, often used within networks like Avalanche, isolate specific blockchain environments for tailored performance and security while maintaining interoperability with the main chain. Together, rollups and subnets optimize transaction throughput and customization, driving efficient decentralized finance (DeFi) and enterprise blockchain applications.
Key Terms
Scalability
Subnets enhance scalability by creating separate, customizable blockchain networks that operate in parallel, reducing congestion on the main chain and improving transaction throughput. Blockchain rollups increase scalability through off-chain transaction processing, bundling multiple operations into a single batch to minimize on-chain data and fees. Explore deeper insights into how subnets and rollups transform blockchain scalability in practice.
Interoperability
Subnets and blockchain rollups both address scalability and interoperability in distinct ways; subnets create customizable, interconnected networks within a blockchain ecosystem, while rollups bundle transactions off-chain and post them on a main chain for validation. Subnets enhance interoperability by allowing tailored consensus mechanisms and specialized transaction rules across different subnetworks, facilitating diverse blockchain applications. Explore deeper insights into how subnets and rollups transform blockchain interoperability and scalability solutions.
Transaction Throughput
Subnets significantly increase transaction throughput by enabling parallel processing within interoperable blockchain environments, effectively reducing congestion on the main chain. Blockchain rollups enhance throughput by aggregating multiple transactions into a single batch that's processed off-chain, then finalized on the main blockchain, achieving scalability without sacrificing security. Explore the detailed mechanics and comparative benefits of subnets versus rollups to understand their impact on blockchain scalability.
Source and External Links
Subnet - Wikipedia - A subnet, or subnetwork, is a logical subdivision of an IP network, dividing an IP address into a network prefix and a host identifier to efficiently route traffic within smaller network segments, often expressed in CIDR notation like 198.51.100.0/24 for IPv4 networks.
What is a subnet (subnetwork)? | Definition from TechTarget - A subnet is a segmented piece of a larger IP network designed to break down large networks into smaller, more efficient parts to reduce traffic, improve routing, and enhance network performance and management.
Introduction To Subnetting - GeeksforGeeks - Subnetting divides a large network into smaller subnets, improving IP address use efficiency, reducing network congestion, and enhancing security by isolating network groups such as departments within an organization.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com