Climate-linked derivatives offer financial instruments that hedge risks associated with climate change, enabling investors to manage exposure to environmental uncertainties. Blue bonds finance ocean-related projects and promote sustainable marine practices by channeling capital toward ocean conservation and restoration. Explore deeper insights into how these innovative financial tools drive sustainable investment and climate resilience.
Why it is important
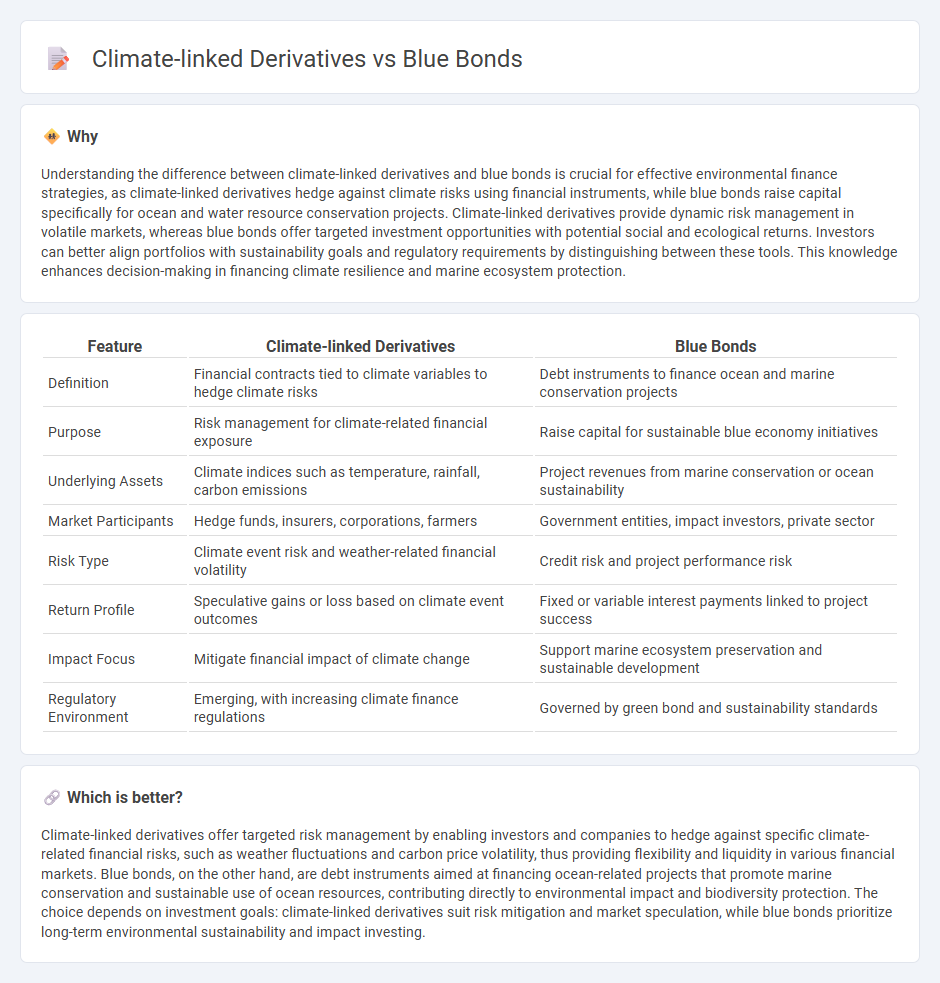
Understanding the difference between climate-linked derivatives and blue bonds is crucial for effective environmental finance strategies, as climate-linked derivatives hedge against climate risks using financial instruments, while blue bonds raise capital specifically for ocean and water resource conservation projects. Climate-linked derivatives provide dynamic risk management in volatile markets, whereas blue bonds offer targeted investment opportunities with potential social and ecological returns. Investors can better align portfolios with sustainability goals and regulatory requirements by distinguishing between these tools. This knowledge enhances decision-making in financing climate resilience and marine ecosystem protection.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Climate-linked Derivatives | Blue Bonds |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Financial contracts tied to climate variables to hedge climate risks | Debt instruments to finance ocean and marine conservation projects |
| Purpose | Risk management for climate-related financial exposure | Raise capital for sustainable blue economy initiatives |
| Underlying Assets | Climate indices such as temperature, rainfall, carbon emissions | Project revenues from marine conservation or ocean sustainability |
| Market Participants | Hedge funds, insurers, corporations, farmers | Government entities, impact investors, private sector |
| Risk Type | Climate event risk and weather-related financial volatility | Credit risk and project performance risk |
| Return Profile | Speculative gains or loss based on climate event outcomes | Fixed or variable interest payments linked to project success |
| Impact Focus | Mitigate financial impact of climate change | Support marine ecosystem preservation and sustainable development |
| Regulatory Environment | Emerging, with increasing climate finance regulations | Governed by green bond and sustainability standards |
Which is better?
Climate-linked derivatives offer targeted risk management by enabling investors and companies to hedge against specific climate-related financial risks, such as weather fluctuations and carbon price volatility, thus providing flexibility and liquidity in various financial markets. Blue bonds, on the other hand, are debt instruments aimed at financing ocean-related projects that promote marine conservation and sustainable use of ocean resources, contributing directly to environmental impact and biodiversity protection. The choice depends on investment goals: climate-linked derivatives suit risk mitigation and market speculation, while blue bonds prioritize long-term environmental sustainability and impact investing.
Connection
Climate-linked derivatives enable financial markets to hedge risks associated with environmental changes, directly supporting the development of blue bonds by providing risk management tools for ocean-related projects. Blue bonds finance sustainable marine activities, relying on derivatives to stabilize investment returns amid climate uncertainties affecting ocean health. Together, these instruments advance climate-resilient financing strategies for ocean conservation and sustainable resource management.
Key Terms
Ocean Conservation (Blue Bonds)
Blue bonds are debt instruments specifically designed to fund ocean conservation projects, enabling governments and organizations to invest in sustainable marine ecosystems while generating financial returns. Climate-linked derivatives, by contrast, are financial contracts whose values depend on environmental variables such as sea temperatures or carbon emissions, offering risk management tools to stakeholders involved in climate-sensitive ocean activities. Explore how these innovative financial instruments are transforming ocean conservation efforts and supporting sustainable blue economies.
Hedging (Climate-linked Derivatives)
Climate-linked derivatives offer tailored hedging solutions by enabling investors to manage risks associated with climate variables such as temperature, rainfall, and carbon pricing fluctuations. Unlike blue bonds, which provide direct financing for ocean-related environmental projects, these derivatives focus on risk transfer mechanisms to protect portfolios against climate-induced financial volatility. Explore how climate-linked derivatives enhance risk management strategies in sustainable finance.
Sustainability-linked Yield
Blue bonds finance ocean and marine conservation projects, offering investors fixed returns tied to environmental outcomes, while climate-linked derivatives hedge risks linked to climate variables like temperature or carbon prices, providing dynamic financial tools for sustainability goals. Both instruments align capital markets with environmental imperatives, but sustainability-linked yield emphasizes returns that adjust based on achieving predefined ESG targets, incentivizing corporate responsibility. Explore further to understand the evolving landscape of sustainable finance and how these instruments drive impactful investment strategies.
Source and External Links
Blue Bonds - Blue bonds are a type of green bond that finance marine and ocean projects focused on ecosystem restoration, climate adaptation, and sustainable marine industries, guided by IFC and Asian Development Bank frameworks.
Blue Bond | Research and Innovation - European Union - Blue Bonds are debt instruments issued by governments and corporations to raise finance for sustainable marine projects, with economic, environmental, and social benefits aligned with SDGs.
Blue Finance - IFC has facilitated billions in blue loans and bonds in regions including East Asia Pacific to support investments in marine plastic reduction, water management, fisheries, and other blue economy sectors.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com