Yield farming maximizes returns by providing liquidity to decentralized finance protocols in exchange for rewards, often involving multiple tokens and complex strategies. Staking involves locking cryptocurrencies in a network to support blockchain operations and earn predictable rewards with lower risk. Explore the differences between yield farming and staking to optimize your crypto investment strategy.
Why it is important
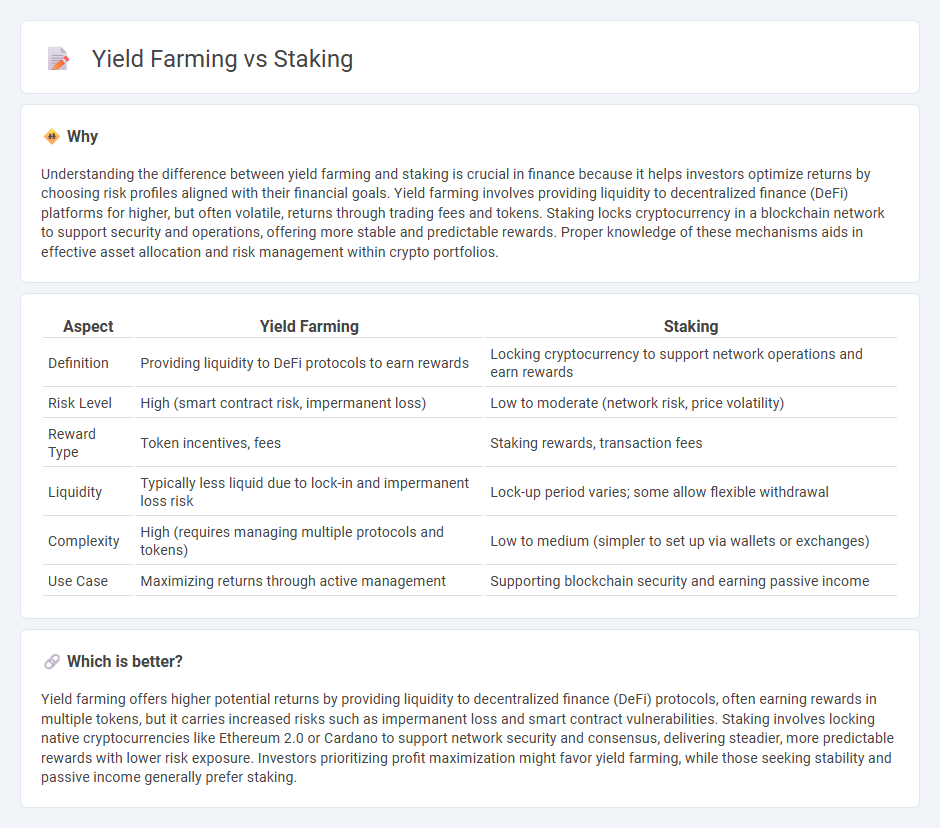
Understanding the difference between yield farming and staking is crucial in finance because it helps investors optimize returns by choosing risk profiles aligned with their financial goals. Yield farming involves providing liquidity to decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms for higher, but often volatile, returns through trading fees and tokens. Staking locks cryptocurrency in a blockchain network to support security and operations, offering more stable and predictable rewards. Proper knowledge of these mechanisms aids in effective asset allocation and risk management within crypto portfolios.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Yield Farming | Staking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Providing liquidity to DeFi protocols to earn rewards | Locking cryptocurrency to support network operations and earn rewards |
| Risk Level | High (smart contract risk, impermanent loss) | Low to moderate (network risk, price volatility) |
| Reward Type | Token incentives, fees | Staking rewards, transaction fees |
| Liquidity | Typically less liquid due to lock-in and impermanent loss risk | Lock-up period varies; some allow flexible withdrawal |
| Complexity | High (requires managing multiple protocols and tokens) | Low to medium (simpler to set up via wallets or exchanges) |
| Use Case | Maximizing returns through active management | Supporting blockchain security and earning passive income |
Which is better?
Yield farming offers higher potential returns by providing liquidity to decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols, often earning rewards in multiple tokens, but it carries increased risks such as impermanent loss and smart contract vulnerabilities. Staking involves locking native cryptocurrencies like Ethereum 2.0 or Cardano to support network security and consensus, delivering steadier, more predictable rewards with lower risk exposure. Investors prioritizing profit maximization might favor yield farming, while those seeking stability and passive income generally prefer staking.
Connection
Yield farming and staking are connected through their core principle of earning passive income by locking cryptocurrency assets within decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols. Both methods involve providing liquidity or securing network operations, with yield farming focusing on liquidity pools to generate returns via trading fees and rewards, while staking entails validating transactions in proof-of-stake blockchains to obtain staking rewards. The convergence of these mechanisms enhances capital efficiency and incentivizes participation across various DeFi ecosystems.
Key Terms
APY (Annual Percentage Yield)
Staking typically offers a fixed APY based on the protocol's rewards for locking up tokens, providing a more predictable income stream. Yield farming involves variable APYs driven by liquidity pool incentives, token price fluctuations, and market demand, often resulting in higher but riskier returns. Explore the detailed comparison of staking and yield farming APYs to optimize your crypto investment strategy.
Liquidity Pool
Liquidity pools in staking involve locking tokens to support network functions and earn rewards, often with lower risk and stable returns. Yield farming typically requires providing liquidity to decentralized exchanges by pairing tokens, aiming for higher rewards through transaction fees and protocol incentives, but with increased impermanent loss risk. Explore the nuances of liquidity pool strategies to maximize your DeFi earnings.
Validator
Validator roles in staking involve securing blockchain networks by validating transactions and adding new blocks, earning rewards directly linked to their stake and network performance. Yield farming focuses on liquidity provision in DeFi protocols, where validators are less central but users earn income through interest and fees by locking assets. Discover how staking as a validator can influence network security and maximize your crypto returns.
Source and External Links
What is crypto staking and how does it work? - Fidelity Investments - Crypto staking is the process used by blockchains like Ethereum where users lock tokens to validate transactions via proof-of-stake, earning rewards while their coins are staked and locked until withdrawal.
Staking - Solana - Staking on Solana involves delegating SOL tokens to validators to increase their voting weight in consensus, while token holders retain full control over their tokens and earn rewards for supporting network security.
What is staking? - Coinbase - Staking is a way to earn rewards by putting your crypto to work on a blockchain network, helping it run securely without lending out your assets, making it a safe and popular method to grow crypto holdings over time.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com