Greenium refers to the premium investors pay for green bonds due to their environmentally sustainable projects, reflecting strong demand for eco-friendly investments. Social bonds finance projects with positive societal impacts, focusing on issues such as affordable housing, education, and healthcare improvements. Explore more to understand how greenium and social bonds influence sustainable finance strategies.
Why it is important
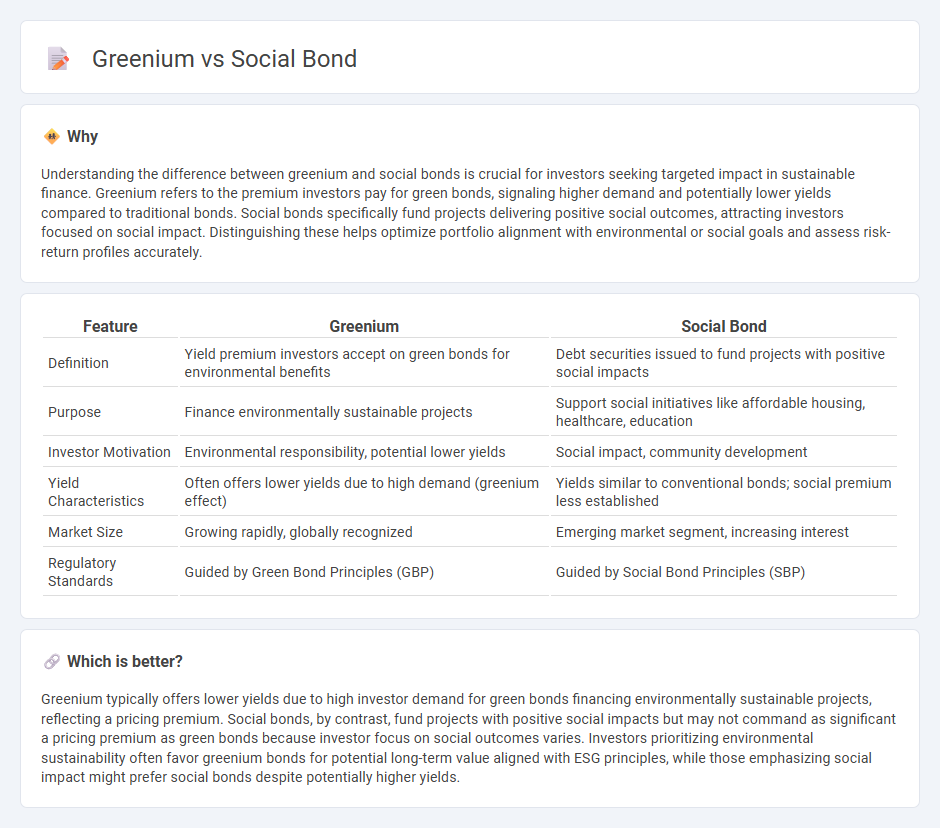
Understanding the difference between greenium and social bonds is crucial for investors seeking targeted impact in sustainable finance. Greenium refers to the premium investors pay for green bonds, signaling higher demand and potentially lower yields compared to traditional bonds. Social bonds specifically fund projects delivering positive social outcomes, attracting investors focused on social impact. Distinguishing these helps optimize portfolio alignment with environmental or social goals and assess risk-return profiles accurately.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Greenium | Social Bond |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Yield premium investors accept on green bonds for environmental benefits | Debt securities issued to fund projects with positive social impacts |
| Purpose | Finance environmentally sustainable projects | Support social initiatives like affordable housing, healthcare, education |
| Investor Motivation | Environmental responsibility, potential lower yields | Social impact, community development |
| Yield Characteristics | Often offers lower yields due to high demand (greenium effect) | Yields similar to conventional bonds; social premium less established |
| Market Size | Growing rapidly, globally recognized | Emerging market segment, increasing interest |
| Regulatory Standards | Guided by Green Bond Principles (GBP) | Guided by Social Bond Principles (SBP) |
Which is better?
Greenium typically offers lower yields due to high investor demand for green bonds financing environmentally sustainable projects, reflecting a pricing premium. Social bonds, by contrast, fund projects with positive social impacts but may not command as significant a pricing premium as green bonds because investor focus on social outcomes varies. Investors prioritizing environmental sustainability often favor greenium bonds for potential long-term value aligned with ESG principles, while those emphasizing social impact might prefer social bonds despite potentially higher yields.
Connection
Greenium refers to the premium investors are willing to pay for green bonds, reflecting increased demand for environmentally sustainable investments. Social bonds, like green bonds, are labeled debt instruments issued to finance projects with positive social outcomes, often commanding a socialium that parallels greenium dynamics. Both instruments leverage investor preference for sustainability, creating price differentials that reward issuers for advancing environmental and social objectives.
Key Terms
Environmental Impact
Social bonds finance projects with positive social outcomes, such as affordable housing and healthcare, while green bonds fund environmentally beneficial initiatives like renewable energy and pollution reduction. Greenium represents the premium investors are willing to pay for green bonds due to their environmental impact, often resulting in lower yields compared to traditional bonds. Explore how these financial instruments drive sustainable development and investment strategies.
Yield Differential
Yield differential between social bonds and greeniums highlights investor preferences in sustainable finance markets. Social bonds typically offer slightly higher yields due to perceived higher social impact risks, whereas greeniums reflect reduced yields on green bonds driven by strong demand for environmental projects. Explore detailed analyses to understand how yield differentials influence investment strategies in ESG-focused portfolios.
Use of Proceeds
Social bonds direct proceeds toward projects that address social issues such as affordable housing, education, and healthcare; green bonds allocate funds exclusively to environmental initiatives like renewable energy and climate change mitigation. The use of proceeds in social bonds emphasizes community impact and social welfare, while green bonds focus on sustainability and reducing environmental footprint, leading to distinct investor appeal and market dynamics reflected in their pricing and demand. Explore the detailed differences and market implications of social bonds versus green bonds to optimize your investment strategy.
Source and External Links
Building Social Bonds - Social networks and relationships can reduce stress, lower heart-related risks, and are linked to longer life and better mental and physical health.
Social Bonds: Definition & Benefits - Social bonds are fixed-income financial instruments issued to fund projects with clear, measurable social benefits like affordable housing, healthcare, and education, following strict guidelines for transparency and impact.
Social impact bond - Social impact bonds are outcomes-based contracts where private investors fund social programs and are repaid by the government only if predefined social outcomes are achieved.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com