Alternative data encompasses unconventional datasets such as social media activity, transaction records, and sensor outputs that provide unique financial insights beyond traditional sources. Geospatial data specifically refers to location-based information derived from satellite imagery, GPS, and remote sensing technologies, enabling precise analysis of physical world patterns impacting markets. Explore how integrating alternative and geospatial data can transform investment strategies and risk assessment models.
Why it is important
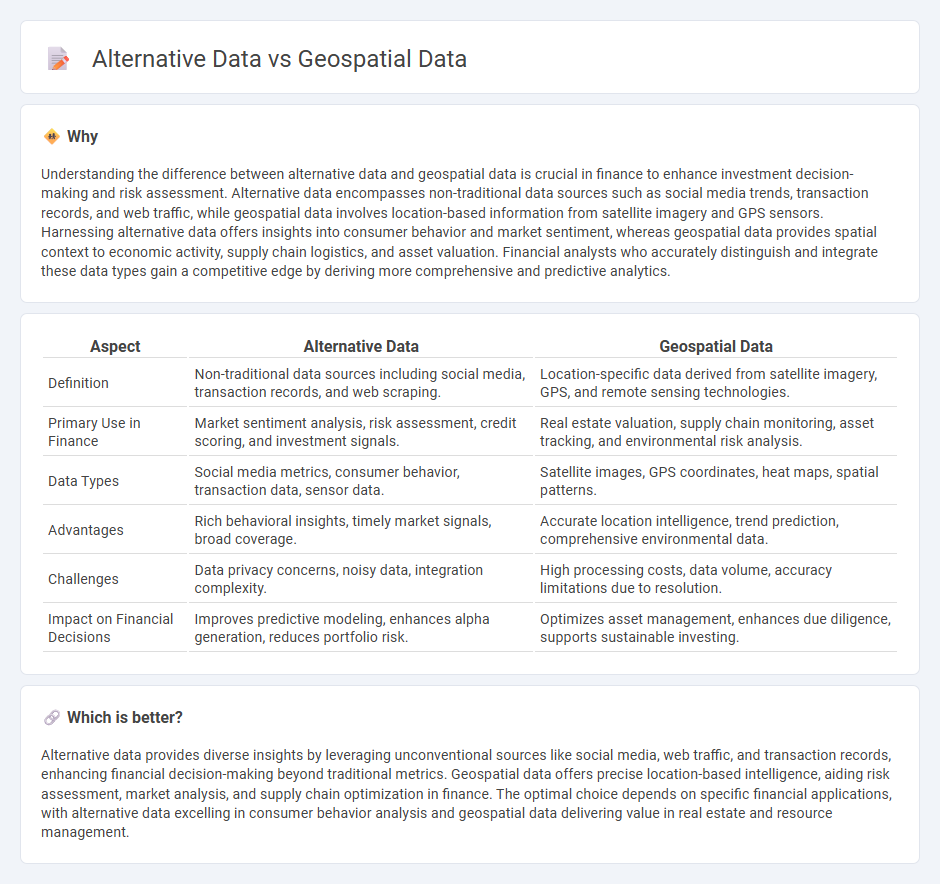
Understanding the difference between alternative data and geospatial data is crucial in finance to enhance investment decision-making and risk assessment. Alternative data encompasses non-traditional data sources such as social media trends, transaction records, and web traffic, while geospatial data involves location-based information from satellite imagery and GPS sensors. Harnessing alternative data offers insights into consumer behavior and market sentiment, whereas geospatial data provides spatial context to economic activity, supply chain logistics, and asset valuation. Financial analysts who accurately distinguish and integrate these data types gain a competitive edge by deriving more comprehensive and predictive analytics.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Alternative Data | Geospatial Data |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Non-traditional data sources including social media, transaction records, and web scraping. | Location-specific data derived from satellite imagery, GPS, and remote sensing technologies. |
| Primary Use in Finance | Market sentiment analysis, risk assessment, credit scoring, and investment signals. | Real estate valuation, supply chain monitoring, asset tracking, and environmental risk analysis. |
| Data Types | Social media metrics, consumer behavior, transaction data, sensor data. | Satellite images, GPS coordinates, heat maps, spatial patterns. |
| Advantages | Rich behavioral insights, timely market signals, broad coverage. | Accurate location intelligence, trend prediction, comprehensive environmental data. |
| Challenges | Data privacy concerns, noisy data, integration complexity. | High processing costs, data volume, accuracy limitations due to resolution. |
| Impact on Financial Decisions | Improves predictive modeling, enhances alpha generation, reduces portfolio risk. | Optimizes asset management, enhances due diligence, supports sustainable investing. |
Which is better?
Alternative data provides diverse insights by leveraging unconventional sources like social media, web traffic, and transaction records, enhancing financial decision-making beyond traditional metrics. Geospatial data offers precise location-based intelligence, aiding risk assessment, market analysis, and supply chain optimization in finance. The optimal choice depends on specific financial applications, with alternative data excelling in consumer behavior analysis and geospatial data delivering value in real estate and resource management.
Connection
Alternative data, including social media trends, transaction records, and web traffic, provides unique insights that enhance traditional financial analysis by revealing real-time consumer behavior and market sentiment. Geospatial data, such as satellite imagery and location-based information, complements alternative data by offering spatial context that helps predict economic activity, supply chain disruptions, and asset performance. Combining these data types enables financial institutions to improve risk assessment, optimize investment strategies, and identify emerging market opportunities with greater accuracy.
Key Terms
Location Analytics
Geospatial data, derived from satellite imagery, GPS coordinates, and geographic information systems (GIS), provides precise location-based insights essential for Location Analytics in sectors like retail, urban planning, and logistics. Alternative data encompasses diverse sources such as social media check-ins, mobile app usage, and sensor data, offering behavioral context that complements geospatial metrics for richer analysis. Explore how integrating geospatial and alternative data can revolutionize location-driven decision-making processes.
Satellite Imagery
Satellite imagery offers high-resolution geospatial data that enables precise monitoring of environmental changes, urban development, and agricultural patterns. Unlike alternative data sources such as social media or transaction data, satellite imagery provides objective, location-specific visual insights crucial for applications in disaster response, climate research, and defense. Explore more to understand how satellite imagery transforms decision-making across industries.
Transaction Data
Transaction data, a subset of alternative data, captures detailed records of financial exchanges, providing real-time insights into consumer behavior and market trends. Geospatial data, contrastingly, maps physical locations and movement patterns, enabling spatial analysis for industries like logistics, real estate, and urban planning. Explore comprehensive comparisons to understand how transaction data complements geospatial data in enhancing decision-making processes.
Source and External Links
What is Geospatial Data? | IBM - Geospatial data is information describing objects, events, or features with a location on or near Earth's surface, combining coordinates, attributes, and temporal details for analysis and visualization.
What is Geospatial Data? | AWS - Geospatial data includes location-based information that can be mapped to real-world phenomena, enabling the creation of maps and 3D models to reveal patterns and trends on Earth's surface.
What Is a Geospatial Database? | Oracle - A geospatial database stores and queries data representing objects in geometric space, such as points, lines, and polygons, along with their attributes, for advanced geographic analysis and visualization.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com