Catastrophe bonds transfer disaster-related risks from insurers to capital markets by issuing securities that pay high yields unless a specified event occurs, providing insurers financial protection against catastrophic losses. Swap contracts are derivative agreements where two parties exchange cash flows or financial instruments, often used to hedge interest rate or currency risks. Explore the differences and advantages of catastrophe bonds versus swap contracts for effective risk management strategies.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between catastrophe bonds and swap contracts is crucial for effective risk management and investment strategy in finance. Catastrophe bonds transfer insurance risk to capital markets, providing capital relief and diversification, while swap contracts are derivatives used to hedge against interest rate or currency fluctuations. Recognizing their distinct structures and purposes enables investors to optimize portfolio performance and mitigate specific risks. Knowledge of these instruments supports informed decision-making in managing exposure to natural disasters and market volatility.
Comparison Table
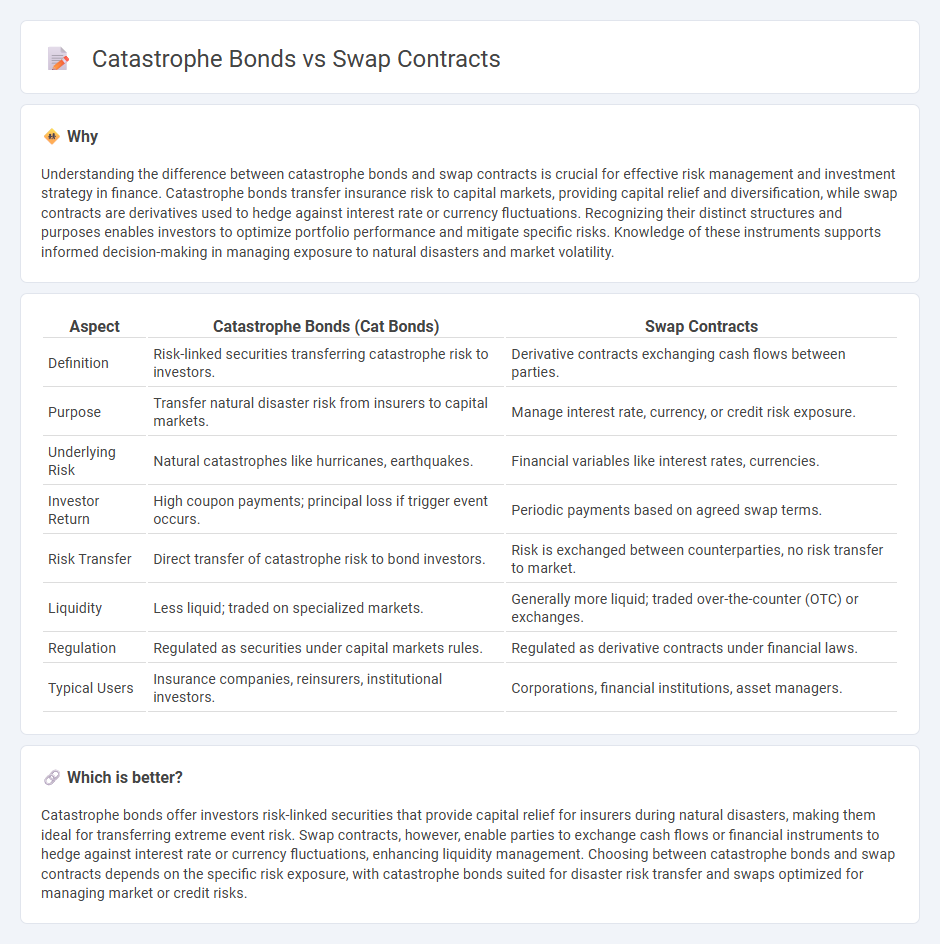
| Aspect | Catastrophe Bonds (Cat Bonds) | Swap Contracts |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Risk-linked securities transferring catastrophe risk to investors. | Derivative contracts exchanging cash flows between parties. |
| Purpose | Transfer natural disaster risk from insurers to capital markets. | Manage interest rate, currency, or credit risk exposure. |
| Underlying Risk | Natural catastrophes like hurricanes, earthquakes. | Financial variables like interest rates, currencies. |
| Investor Return | High coupon payments; principal loss if trigger event occurs. | Periodic payments based on agreed swap terms. |
| Risk Transfer | Direct transfer of catastrophe risk to bond investors. | Risk is exchanged between counterparties, no risk transfer to market. |
| Liquidity | Less liquid; traded on specialized markets. | Generally more liquid; traded over-the-counter (OTC) or exchanges. |
| Regulation | Regulated as securities under capital markets rules. | Regulated as derivative contracts under financial laws. |
| Typical Users | Insurance companies, reinsurers, institutional investors. | Corporations, financial institutions, asset managers. |
Which is better?
Catastrophe bonds offer investors risk-linked securities that provide capital relief for insurers during natural disasters, making them ideal for transferring extreme event risk. Swap contracts, however, enable parties to exchange cash flows or financial instruments to hedge against interest rate or currency fluctuations, enhancing liquidity management. Choosing between catastrophe bonds and swap contracts depends on the specific risk exposure, with catastrophe bonds suited for disaster risk transfer and swaps optimized for managing market or credit risks.
Connection
Catastrophe bonds and swap contracts are interconnected financial instruments used to manage and transfer risk in the insurance and finance sectors. Catastrophe bonds provide insurers with capital relief by transferring catastrophe risk to investors, while swap contracts enable parties to exchange cash flows or risk exposures, often linked to interest rates or credit events. Together, they facilitate sophisticated risk management strategies, allowing for diversification and cushioning against significant financial losses from natural disasters.
Key Terms
Counterparty risk
Swap contracts expose parties to counterparty risk, where the failure of one party to fulfill payment obligations can lead to significant financial losses. Catastrophe bonds transfer this risk to investors, effectively removing counterparty risk by using a predefined trigger event to determine payouts. Explore how these mechanisms influence risk management strategies in insurance and reinsurance markets.
Trigger event
Swap contracts activate based on predefined financial indices, such as interest rates or credit spreads, while catastrophe bonds rely on specific trigger events like hurricanes, earthquakes, or other natural disasters. Trigger events in catastrophe bonds are parametric, indemnity, or modeled loss based, directly linking payout to the occurrence and severity of the catastrophe. Explore the nuances of trigger mechanisms to understand the risk management strategies in these financial instruments.
Hedging
Swap contracts provide customized hedging solutions by allowing parties to exchange cash flows based on underlying risk factors, effectively mitigating financial exposure to specific risks such as interest rate fluctuations or credit defaults. Catastrophe bonds offer risk transfer by enabling issuers to raise capital from investors, with payouts triggered by predefined disaster events, thus providing a hedge against extreme natural catastrophes. Discover more about how these financial instruments strategically manage risk in volatile markets.
Source and External Links
Swap - Definition, Types, Applications, Example - A swap is a derivative contract between two parties involving the exchange of pre-agreed cash flows of two financial instruments, typically used to hedge risks or alter financial exposures, and usually traded over-the-counter rather than on exchanges.
Swap (finance) - Wikipedia - Swaps are agreements in which two counterparties exchange cash flows or payments based on a notional principal amount and can be used for hedging or speculation, with common types including fixed-for-floating interest rate swaps.
Swap Risks - Definition, Types & Example - Financial Edge Training - Swap contracts exchange streams of payments based on underlying financial instruments and carry risks such as price risk and counterparty risk, which can be mitigated through hedging, quality counterparties, and collateral.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com