Collateralized reinsurance involves securing reinsurance obligations with collateral to ensure claim payments, reducing counterparty risk for cedents. Quota share reinsurance requires the ceding insurer to share a fixed percentage of premiums and losses with the reinsurer, maintaining proportional risk transfer. Explore the distinct advantages and applications of collateralized reinsurance versus quota share structures to optimize your risk management strategies.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between collateralized reinsurance and quota share is crucial for risk management and financial stability in insurance. Collateralized reinsurance involves secured funds to guarantee claim payments, reducing counterparty risk for cedents, while quota share is a proportional sharing of premiums and losses between insurer and reinsurer. This distinction impacts cash flow, risk exposure, and regulatory capital requirements, influencing investment and underwriting strategies. Accurate knowledge aids in optimizing capital allocation and maintaining solvency margins.
Comparison Table
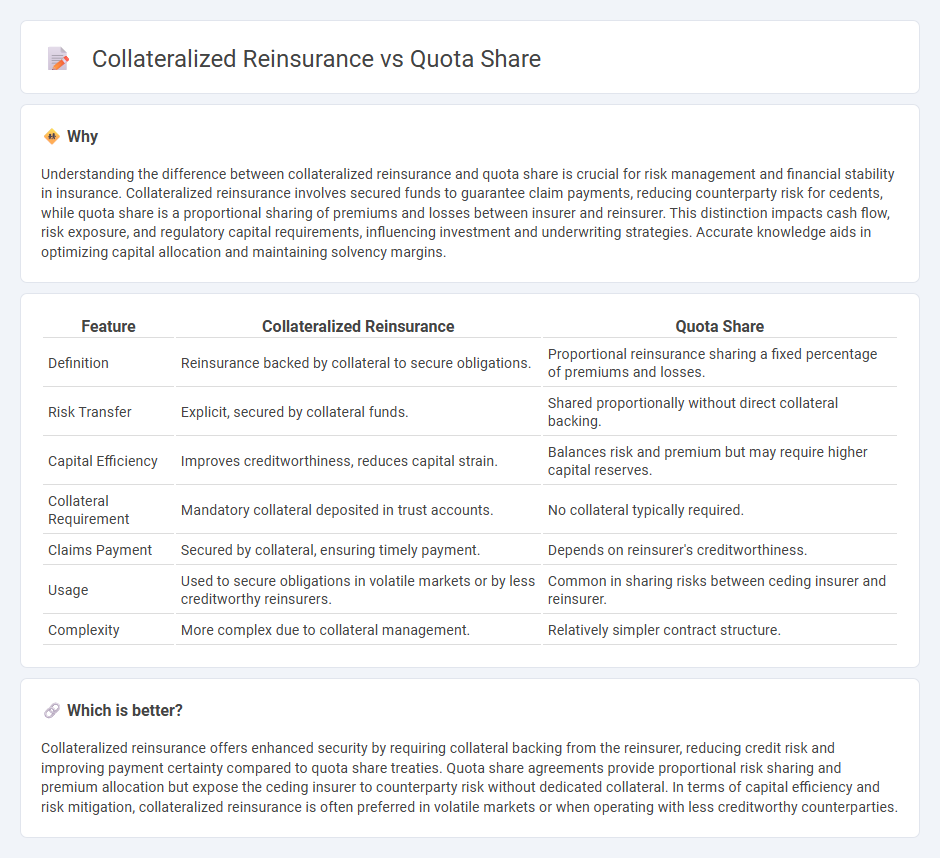
| Feature | Collateralized Reinsurance | Quota Share |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Reinsurance backed by collateral to secure obligations. | Proportional reinsurance sharing a fixed percentage of premiums and losses. |
| Risk Transfer | Explicit, secured by collateral funds. | Shared proportionally without direct collateral backing. |
| Capital Efficiency | Improves creditworthiness, reduces capital strain. | Balances risk and premium but may require higher capital reserves. |
| Collateral Requirement | Mandatory collateral deposited in trust accounts. | No collateral typically required. |
| Claims Payment | Secured by collateral, ensuring timely payment. | Depends on reinsurer's creditworthiness. |
| Usage | Used to secure obligations in volatile markets or by less creditworthy reinsurers. | Common in sharing risks between ceding insurer and reinsurer. |
| Complexity | More complex due to collateral management. | Relatively simpler contract structure. |
Which is better?
Collateralized reinsurance offers enhanced security by requiring collateral backing from the reinsurer, reducing credit risk and improving payment certainty compared to quota share treaties. Quota share agreements provide proportional risk sharing and premium allocation but expose the ceding insurer to counterparty risk without dedicated collateral. In terms of capital efficiency and risk mitigation, collateralized reinsurance is often preferred in volatile markets or when operating with less creditworthy counterparties.
Connection
Collateralized reinsurance enhances financial security by requiring upfront collateral to cover potential claims, mitigating credit risk for the ceding insurer. Quota share reinsurance involves sharing a fixed percentage of premiums and losses between the insurer and reinsurer, establishing proportional risk transfer. Their connection lies in combining quota share agreements with collateralized reinsurance to ensure timely payment and reduce counterparty risk in shared risk portfolios.
Key Terms
Proportional Reinsurance
Quota share reinsurance involves an insurer ceding a fixed percentage of premiums and losses to the reinsurer, maintaining proportional risk sharing. Collateralized reinsurance requires the reinsurer to provide collateral, ensuring funds are available for claims, which enhances security and mitigates credit risk in proportional arrangements. Explore more about how these reinsurance structures impact risk management and capital efficiency.
Collateral
Collateralized reinsurance involves the ceding company posting collateral to secure the reinsurer's obligations, enhancing creditworthiness and reducing counterparty risk compared to traditional quota share arrangements. This form of reinsurance ensures funds are readily available for claim payments, often held in trust or escrow accounts, providing greater financial security for both parties. Explore detailed mechanisms and benefits of collateralized reinsurance to optimize risk management strategies.
Risk Transfer
Quota share reinsurance involves ceding a fixed percentage of premiums and losses to the reinsurer, ensuring proportional risk transfer and shared underwriting results. Collateralized reinsurance transfers risk by securing obligations with collateral, enhancing credit protection without traditional underwriting exposure. Explore these mechanisms in detail to understand how each optimizes risk transfer and capital efficiency.
Source and External Links
Quota Share Reinsurance: A Straightforward Approach to Risk Sharing - This article explains quota share reinsurance as a proportional method where insurers cede a fixed percentage of policies to reinsurers, sharing premiums and losses accordingly.
Quota Share Reinsurance Meaning & Definition - Quota share reinsurance involves insurers ceding a fixed percentage of each policy to reinsurers, who then receive a corresponding percentage of premiums and cover a similar percentage of losses.
Building Coverage Limits: Quota Share vs. Excess Coverage - This article compares quota share with excess coverage, noting that quota share involves multiple carriers sharing a risk by percentage, often resulting in cost savings for the insured.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com