Alternative data scraping captures diverse financial signals from online sources such as social media, web traffic, and transactional data to uncover market trends and consumer behavior. Satellite imagery analysis leverages high-resolution images to monitor economic activities like crop health, shipping traffic, and construction progress, offering unique insights into real-time asset performance. Explore the advantages and applications of these innovative data sources in transforming financial decision-making.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between alternative data scraping and satellite imagery analysis is crucial in finance as it allows investors to diversify data sources for more accurate market predictions. Alternative data scraping extracts real-time, unstructured data from websites and social media to gauge consumer behavior, while satellite imagery analysis provides visual intelligence on physical assets like retail store traffic or crop health. The complementary insights from both methods enhance risk assessment and strategic decision-making in asset management. Choosing the appropriate data technique directly impacts portfolio optimization and competitive advantage in financial markets.
Comparison Table
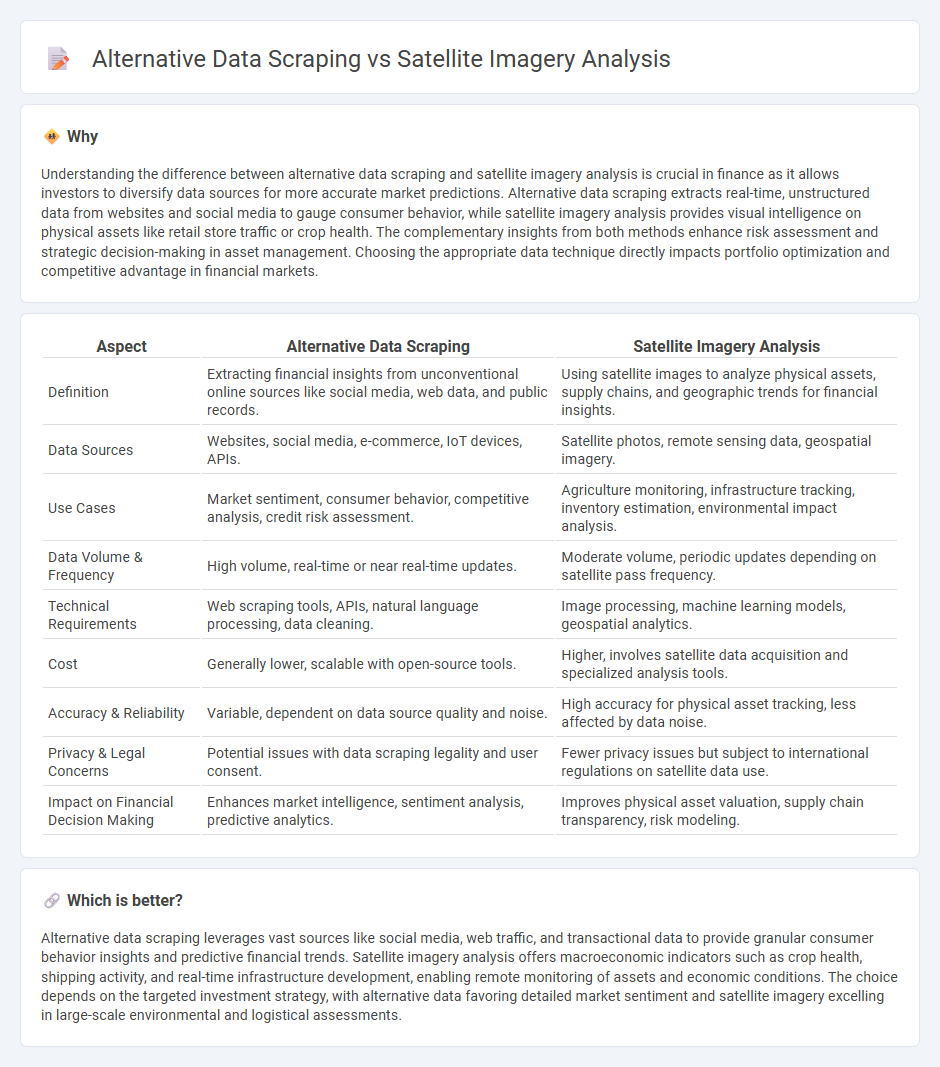
| Aspect | Alternative Data Scraping | Satellite Imagery Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Extracting financial insights from unconventional online sources like social media, web data, and public records. | Using satellite images to analyze physical assets, supply chains, and geographic trends for financial insights. |
| Data Sources | Websites, social media, e-commerce, IoT devices, APIs. | Satellite photos, remote sensing data, geospatial imagery. |
| Use Cases | Market sentiment, consumer behavior, competitive analysis, credit risk assessment. | Agriculture monitoring, infrastructure tracking, inventory estimation, environmental impact analysis. |
| Data Volume & Frequency | High volume, real-time or near real-time updates. | Moderate volume, periodic updates depending on satellite pass frequency. |
| Technical Requirements | Web scraping tools, APIs, natural language processing, data cleaning. | Image processing, machine learning models, geospatial analytics. |
| Cost | Generally lower, scalable with open-source tools. | Higher, involves satellite data acquisition and specialized analysis tools. |
| Accuracy & Reliability | Variable, dependent on data source quality and noise. | High accuracy for physical asset tracking, less affected by data noise. |
| Privacy & Legal Concerns | Potential issues with data scraping legality and user consent. | Fewer privacy issues but subject to international regulations on satellite data use. |
| Impact on Financial Decision Making | Enhances market intelligence, sentiment analysis, predictive analytics. | Improves physical asset valuation, supply chain transparency, risk modeling. |
Which is better?
Alternative data scraping leverages vast sources like social media, web traffic, and transactional data to provide granular consumer behavior insights and predictive financial trends. Satellite imagery analysis offers macroeconomic indicators such as crop health, shipping activity, and real-time infrastructure development, enabling remote monitoring of assets and economic conditions. The choice depends on the targeted investment strategy, with alternative data favoring detailed market sentiment and satellite imagery excelling in large-scale environmental and logistical assessments.
Connection
Alternative data scraping and satellite imagery analysis intersect in finance by providing unique, real-time insights beyond traditional market data. Scraping alternative data sources, such as social media trends or web traffic, complements satellite imagery analysis that tracks physical assets, crop health, or shipping activity to forecast market movements. Integrating these datasets enhances predictive models, allowing investors to make more informed decisions based on comprehensive, multi-dimensional financial intelligence.
Key Terms
Geospatial Analytics
Satellite imagery analysis offers high-resolution, real-time geospatial data essential for applications like environmental monitoring, urban planning, and disaster response. Alternative data scraping gathers diverse geospatial insights from sources such as social media, mobile devices, and IoT sensors, enhancing location intelligence through dynamic, user-generated content. Discover how integrating satellite imagery with alternative data scraping revolutionizes geospatial analytics for smarter decision-making.
Data Integration
Satellite imagery analysis provides high-resolution geospatial data critical for real-time monitoring and environmental assessment, while alternative data scraping aggregates diverse datasets such as social media trends and web activity to enrich insights. Effective data integration combines these sources to enable comprehensive analytics, leveraging machine learning algorithms to enhance predictive accuracy and decision-making. Explore how integrating satellite imagery with alternative data scraping can transform your data strategy.
Predictive Modeling
Satellite imagery analysis leverages high-resolution geospatial data to detect patterns and trends in environmental changes, urban development, and agricultural productivity, enhancing the accuracy of predictive models. Alternative data scraping collects diverse online sources such as social media, web traffic, and transaction data, providing real-time behavioral insights that augment traditional forecasting techniques. Explore how integrating these data sources can revolutionize predictive modeling strategies and improve decision-making accuracy.
Source and External Links
How To Interpret Satellite Images: Methods, Elements & Uses - Explains key elements of satellite image interpretation such as shape, size, pattern, shadow, tone, texture, location, and resolution, which are crucial for extracting valuable insights from Earth observation data in various industries.
Satellite Imagery Analytics - Describes Planet's use of deep learning and computer vision to transform daily satellite images into analytic feeds that detect, classify, and monitor geographic features and changes over time at scale.
Introduction to Satellite Imagery - Polar Geospatial Center - Provides an overview of satellite imagery concepts including spatial and spectral resolution, sensor types, revisit times, and scientific applications made possible by satellite data.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com