Digital asset custody involves securely storing cryptocurrencies and digital tokens using specialized technology solutions, ensuring asset protection through encryption and multi-signature wallets. Third-party custodians act as intermediaries, managing digital assets on behalf of clients while providing regulatory compliance, insurance, and risk mitigation services. Explore how these custody options impact security, control, and trust in the evolving digital finance landscape.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between digital asset custody and third-party custodians is crucial for managing security risks and ensuring asset control in finance. Digital asset custody involves holding private keys directly, providing greater autonomy and reduced counterparty risk. Third-party custodians store assets on behalf of clients, offering convenience but exposing users to potential trust issues and regulatory compliance concerns. Clear knowledge of these distinctions enables informed decisions about safeguarding digital investments and regulatory adherence.
Comparison Table
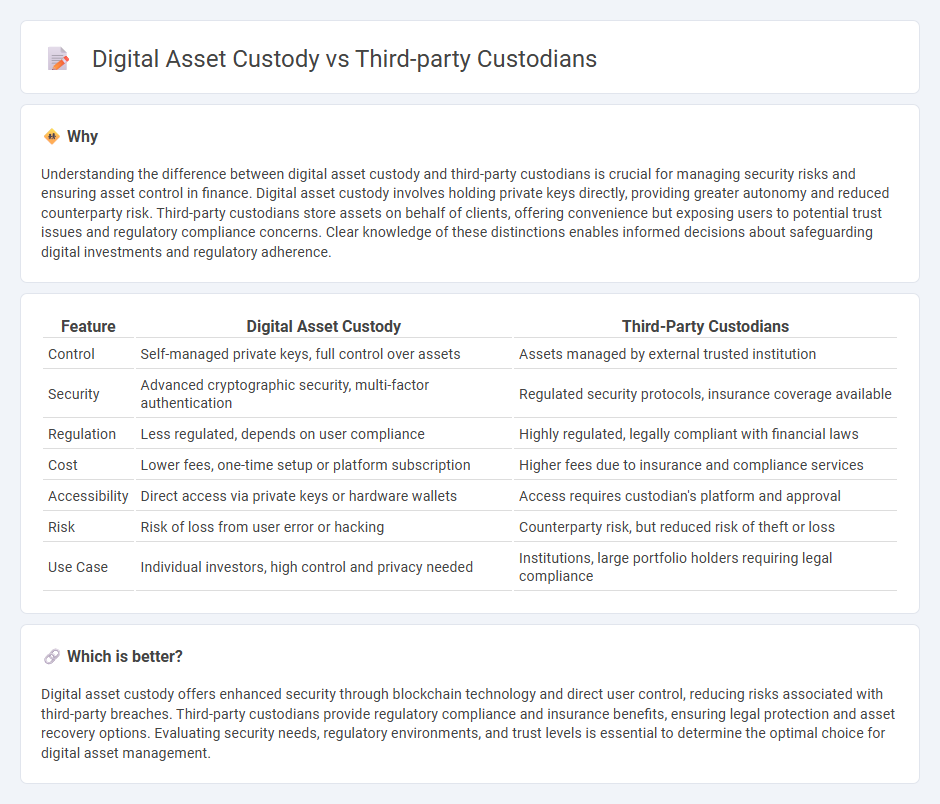
| Feature | Digital Asset Custody | Third-Party Custodians |
|---|---|---|
| Control | Self-managed private keys, full control over assets | Assets managed by external trusted institution |
| Security | Advanced cryptographic security, multi-factor authentication | Regulated security protocols, insurance coverage available |
| Regulation | Less regulated, depends on user compliance | Highly regulated, legally compliant with financial laws |
| Cost | Lower fees, one-time setup or platform subscription | Higher fees due to insurance and compliance services |
| Accessibility | Direct access via private keys or hardware wallets | Access requires custodian's platform and approval |
| Risk | Risk of loss from user error or hacking | Counterparty risk, but reduced risk of theft or loss |
| Use Case | Individual investors, high control and privacy needed | Institutions, large portfolio holders requiring legal compliance |
Which is better?
Digital asset custody offers enhanced security through blockchain technology and direct user control, reducing risks associated with third-party breaches. Third-party custodians provide regulatory compliance and insurance benefits, ensuring legal protection and asset recovery options. Evaluating security needs, regulatory environments, and trust levels is essential to determine the optimal choice for digital asset management.
Connection
Digital asset custody involves the secure storage and management of cryptocurrencies and blockchain-based tokens, requiring robust technological infrastructure and regulatory compliance. Third-party custodians provide specialized services to safeguard these digital assets, offering institutional-grade security solutions such as multi-signature wallets, cold storage, and insurance coverage. This connection enhances trust and reduces risks for investors by ensuring transparent asset handling and mitigating threats like hacking and fraud.
Key Terms
Security
Third-party custodians provide specialized security protocols, regulatory compliance, and insurance coverage for digital assets, mitigating risks of theft or loss. Digital asset custody involves advanced encryption, multi-signature wallets, and cold storage solutions to enhance protection against cyber threats. Explore our comprehensive guide to understand which security measures best suit your digital asset management needs.
Ownership
Third-party custodians provide secure storage and management of digital assets on behalf of owners, ensuring regulatory compliance and mitigating risks of loss or theft. Digital asset custody emphasizes direct ownership control, often through private keys, reducing reliance on intermediaries and enhancing asset sovereignty. Discover how ownership models impact security and control in digital asset management.
Regulation
Third-party custodians operate under stringent regulatory frameworks such as SEC, FINRA, or FCA oversight to safeguard digital assets, ensuring compliance with fiduciary duties and anti-money laundering laws. Digital asset custody solutions emphasize cryptographic security measures, multi-signature wallets, and decentralized control, often navigating emerging regulations like the Travel Rule and evolving crypto-specific guidelines from agencies like the SEC or FATF. Explore our detailed analysis to understand regulatory impacts on third-party custodians compared to digital asset custody practices.
Source and External Links
Third-party custodian - MarketsWiki - A third-party custodian acts as an intermediary between investment advisers or fund managers and clients, holding assets in a separate or omnibus account to prevent the fund manager from handling client funds directly, and providing services like trade settlement, income collection, and recordkeeping.
Using Safekeeping and Third-Party Custodian Services - GFOA - Governments use independent third-party custodians to safeguard investments, ensuring assets are legally separate from the bank, with fiduciary responsibility, automated cash sweeps, trade settlement flexibility, and comprehensive reporting.
Third-Party Custodians of Self-Directed IRAs and Other Qualified Accounts - NASAA - Third-party custodians hold and administer assets for self-directed IRAs but do not validate or ensure the legitimacy of investments; their primary role is to track contributions and distributions for IRS reporting, not to assess investment safety or accuracy.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com