ESG integration involves incorporating environmental, social, and governance factors into financial analysis to assess risks and opportunities, enhancing investment decisions. Positive screening focuses on selecting companies with strong ESG performance, actively promoting sustainable practices. Discover how these strategies can shape responsible investing and drive long-term value.
Why it is important
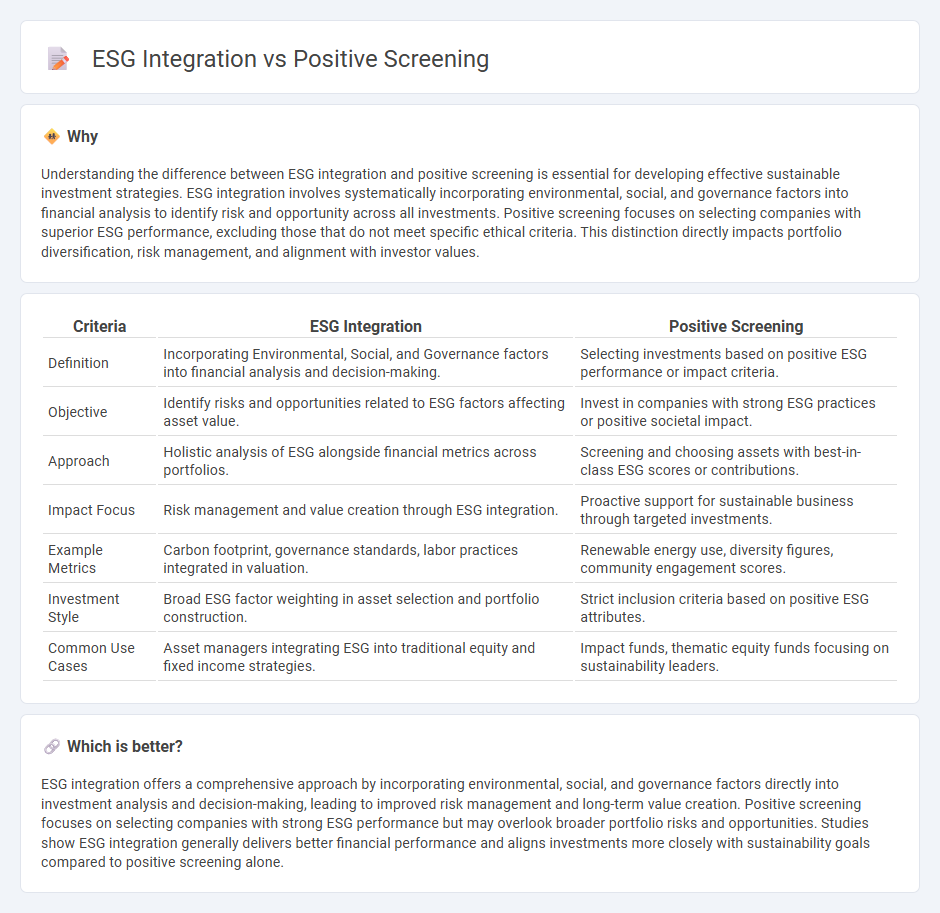
Understanding the difference between ESG integration and positive screening is essential for developing effective sustainable investment strategies. ESG integration involves systematically incorporating environmental, social, and governance factors into financial analysis to identify risk and opportunity across all investments. Positive screening focuses on selecting companies with superior ESG performance, excluding those that do not meet specific ethical criteria. This distinction directly impacts portfolio diversification, risk management, and alignment with investor values.
Comparison Table
| Criteria | ESG Integration | Positive Screening |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Incorporating Environmental, Social, and Governance factors into financial analysis and decision-making. | Selecting investments based on positive ESG performance or impact criteria. |
| Objective | Identify risks and opportunities related to ESG factors affecting asset value. | Invest in companies with strong ESG practices or positive societal impact. |
| Approach | Holistic analysis of ESG alongside financial metrics across portfolios. | Screening and choosing assets with best-in-class ESG scores or contributions. |
| Impact Focus | Risk management and value creation through ESG integration. | Proactive support for sustainable business through targeted investments. |
| Example Metrics | Carbon footprint, governance standards, labor practices integrated in valuation. | Renewable energy use, diversity figures, community engagement scores. |
| Investment Style | Broad ESG factor weighting in asset selection and portfolio construction. | Strict inclusion criteria based on positive ESG attributes. |
| Common Use Cases | Asset managers integrating ESG into traditional equity and fixed income strategies. | Impact funds, thematic equity funds focusing on sustainability leaders. |
Which is better?
ESG integration offers a comprehensive approach by incorporating environmental, social, and governance factors directly into investment analysis and decision-making, leading to improved risk management and long-term value creation. Positive screening focuses on selecting companies with strong ESG performance but may overlook broader portfolio risks and opportunities. Studies show ESG integration generally delivers better financial performance and aligns investments more closely with sustainability goals compared to positive screening alone.
Connection
ESG integration involves embedding environmental, social, and governance factors into investment analysis to identify risks and opportunities, while positive screening selects companies demonstrating strong ESG performance. Both strategies prioritize sustainable business practices by emphasizing companies with robust ESG criteria, enhancing portfolio resilience and ethical alignment. This connection fosters long-term value creation and supports responsible investment goals through targeted asset allocation.
Key Terms
Investment Criteria
Positive screening involves selecting investments based on specific ESG criteria such as companies with high environmental performance or strong social responsibility records. ESG integration embeds environmental, social, and governance factors directly into the financial analysis and decision-making process to identify risks and opportunities that traditional financial metrics might overlook. Explore deeper insights into how these approaches influence portfolio performance and risk management.
Sustainability Factors
Positive screening involves selecting investments based on specific sustainability criteria, such as companies with strong environmental performance or social responsibility. ESG integration incorporates environmental, social, and governance factors comprehensively into the investment analysis to assess risks and opportunities. Explore more to understand how these approaches impact sustainable investment strategies.
Risk Assessment
Positive screening targets investments by selecting companies excelling in specific ESG criteria, promoting sustainable practices without directly addressing potential financial risks. ESG integration incorporates environmental, social, and governance factors into traditional financial analysis to identify and mitigate risks that could impact investment performance. Explore detailed strategies to effectively balance positive screening and ESG integration for comprehensive risk assessment.
Source and External Links
Screening tests: a review with examples - PMC - Positive screening refers to a test result indicating a high probability that the subject has the disease, quantified as the positive predictive value (PPV), which is the probability that a subject with a positive test actually has the disease.
A Screen Positive Result: What does it mean and what do I ... - A "screen positive" result in prenatal screening means the risk of the baby having a condition like Down syndrome is high enough to warrant further diagnostic testing, though it does not confirm the presence of the condition.
Positive and Negative Investment Screening Explained - CNote - Positive screening in investing is a method that identifies and supports companies actively making positive social or environmental impacts, selecting the best-in-class rather than merely excluding harmful practices.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com