Quantamental investing combines quantitative models with fundamental analysis to identify undervalued stocks exhibiting strong financial metrics and positive market sentiment. Smart beta investing uses rule-based strategies to weight portfolio components by factors like volatility, momentum, or dividends, rather than market capitalization, aiming for enhanced risk-adjusted returns. Explore the nuances of quantamental and smart beta strategies to optimize your investment approach.
Why it is important
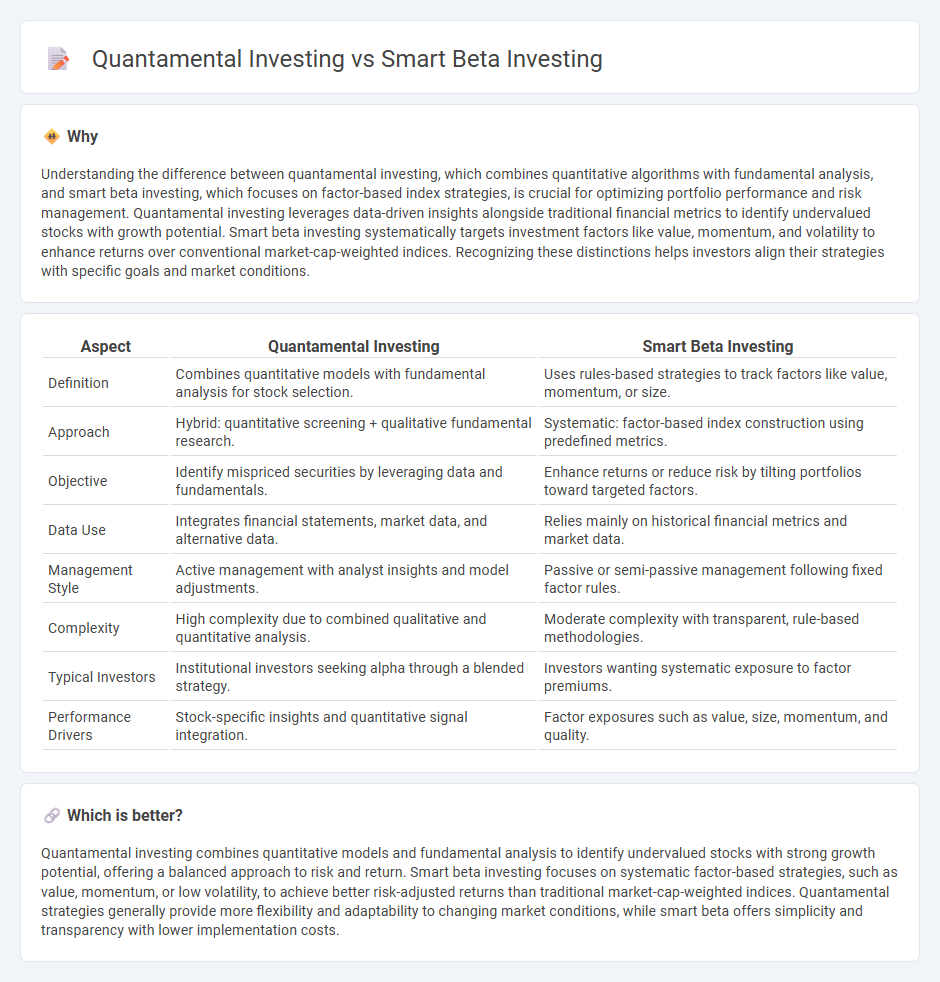
Understanding the difference between quantamental investing, which combines quantitative algorithms with fundamental analysis, and smart beta investing, which focuses on factor-based index strategies, is crucial for optimizing portfolio performance and risk management. Quantamental investing leverages data-driven insights alongside traditional financial metrics to identify undervalued stocks with growth potential. Smart beta investing systematically targets investment factors like value, momentum, and volatility to enhance returns over conventional market-cap-weighted indices. Recognizing these distinctions helps investors align their strategies with specific goals and market conditions.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Quantamental Investing | Smart Beta Investing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combines quantitative models with fundamental analysis for stock selection. | Uses rules-based strategies to track factors like value, momentum, or size. |
| Approach | Hybrid: quantitative screening + qualitative fundamental research. | Systematic: factor-based index construction using predefined metrics. |
| Objective | Identify mispriced securities by leveraging data and fundamentals. | Enhance returns or reduce risk by tilting portfolios toward targeted factors. |
| Data Use | Integrates financial statements, market data, and alternative data. | Relies mainly on historical financial metrics and market data. |
| Management Style | Active management with analyst insights and model adjustments. | Passive or semi-passive management following fixed factor rules. |
| Complexity | High complexity due to combined qualitative and quantitative analysis. | Moderate complexity with transparent, rule-based methodologies. |
| Typical Investors | Institutional investors seeking alpha through a blended strategy. | Investors wanting systematic exposure to factor premiums. |
| Performance Drivers | Stock-specific insights and quantitative signal integration. | Factor exposures such as value, size, momentum, and quality. |
Which is better?
Quantamental investing combines quantitative models and fundamental analysis to identify undervalued stocks with strong growth potential, offering a balanced approach to risk and return. Smart beta investing focuses on systematic factor-based strategies, such as value, momentum, or low volatility, to achieve better risk-adjusted returns than traditional market-cap-weighted indices. Quantamental strategies generally provide more flexibility and adaptability to changing market conditions, while smart beta offers simplicity and transparency with lower implementation costs.
Connection
Quantamental investing integrates quantitative analysis with fundamental research, leveraging data-driven models alongside traditional financial metrics to identify investment opportunities. Smart beta investing employs factor-based strategies that systematically exploit market inefficiencies, often using academic factors like value, momentum, or low volatility to enhance returns. Both approaches use quantitative methods to optimize portfolios by combining empirical data with strategic asset selection, aiming to improve risk-adjusted performance.
Key Terms
**Smart Beta Investing:**
Smart beta investing strategically blends passive investing with factor-based strategies, emphasizing systematic exposure to factors such as value, momentum, size, and low volatility for enhanced risk-adjusted returns. This approach targets predefined rules to optimize portfolio performance by exploiting market inefficiencies and reducing biases common in traditional index investing. Discover the key differences and potential benefits by exploring deeper insights into smart beta methodologies.
Factor Exposure
Smart beta investing systematically targets specific factor exposures like value, momentum, and low volatility to enhance returns and manage risk through rule-based approaches. Quantamental investing combines quantitative models with fundamental analysis, enhancing factor exposure insights by integrating human judgment and data-driven signals. Explore these strategies in depth to understand how factor exposure shapes portfolio outcomes.
Systematic Indexing
Smart beta investing systematically targets specific factors such as value, momentum, and low volatility to enhance index returns beyond market capitalization weighting. Quantamental investing combines quantitative models with fundamental analysis to uncover mispriced securities, aiming for alpha generation through rigorous data integration. Explore in-depth strategies and benefits of systematic indexing to optimize your investment portfolio.
Source and External Links
What are smart beta strategies? A guide to modern diversification - Smart beta investing blends passive and active investing to improve diversification, potentially increase returns, manage risk better, and offers cost-efficient customization by focusing on factors like value, momentum, and low volatility rather than market-cap weighting alone.
Smart Beta - Overview, How It Works, Trading Strategies - Smart beta is a hybrid investing approach that applies active portfolio optimization techniques to passively track indexes, seeking to capture market inefficiencies by weighting investments based on factors such as value, quality, momentum, and liquidity.
Smart Beta ETFs | Charles Schwab - Smart beta ETFs use rules-based indexes that weight stocks based on factors other than market capitalization, such as equal weighting or low volatility, allowing investors to tailor exposure to market segments or risk profiles while maintaining lower costs than active management.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com