Zero-day options offer traders the chance to capitalize on ultra-short-term market movements with contracts that expire within 24 hours, creating opportunities for quick profits but requiring precise timing and risk management. Perpetual options, by contrast, provide continuous exposure without expiration dates, allowing investors to hedge or speculate over an indefinite horizon with greater flexibility in position management. Explore detailed strategies and market implications to better understand these innovative financial instruments.
Why it is important
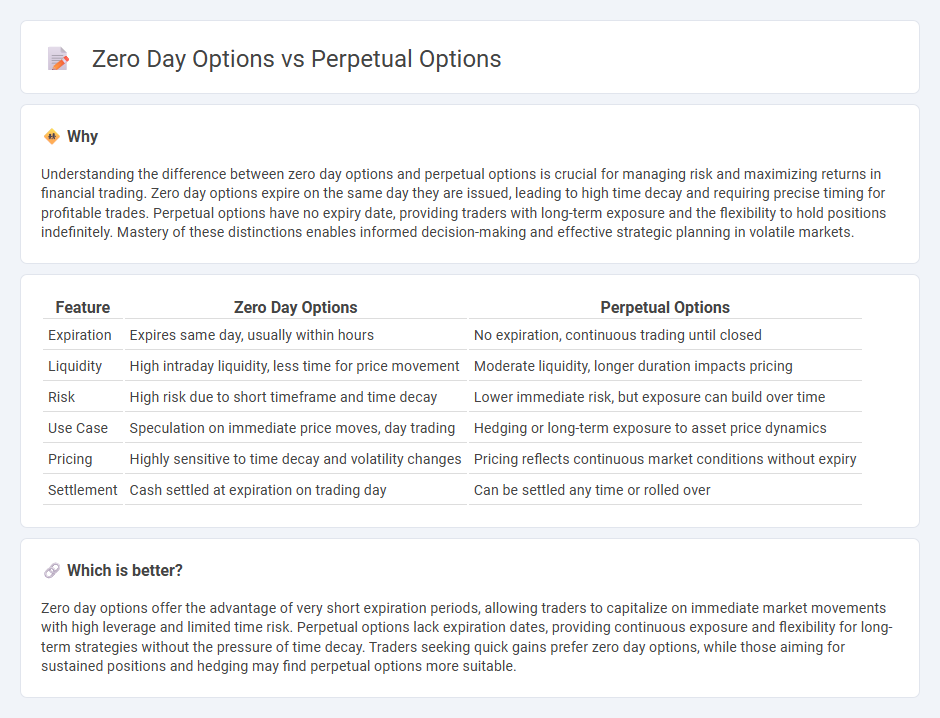
Understanding the difference between zero day options and perpetual options is crucial for managing risk and maximizing returns in financial trading. Zero day options expire on the same day they are issued, leading to high time decay and requiring precise timing for profitable trades. Perpetual options have no expiry date, providing traders with long-term exposure and the flexibility to hold positions indefinitely. Mastery of these distinctions enables informed decision-making and effective strategic planning in volatile markets.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Zero Day Options | Perpetual Options |
|---|---|---|
| Expiration | Expires same day, usually within hours | No expiration, continuous trading until closed |
| Liquidity | High intraday liquidity, less time for price movement | Moderate liquidity, longer duration impacts pricing |
| Risk | High risk due to short timeframe and time decay | Lower immediate risk, but exposure can build over time |
| Use Case | Speculation on immediate price moves, day trading | Hedging or long-term exposure to asset price dynamics |
| Pricing | Highly sensitive to time decay and volatility changes | Pricing reflects continuous market conditions without expiry |
| Settlement | Cash settled at expiration on trading day | Can be settled any time or rolled over |
Which is better?
Zero day options offer the advantage of very short expiration periods, allowing traders to capitalize on immediate market movements with high leverage and limited time risk. Perpetual options lack expiration dates, providing continuous exposure and flexibility for long-term strategies without the pressure of time decay. Traders seeking quick gains prefer zero day options, while those aiming for sustained positions and hedging may find perpetual options more suitable.
Connection
Zero day options and perpetual options are connected through their impact on trading strategies and market liquidity in the finance sector. Zero day options refer to contracts that expire the same day they are traded, significantly increasing short-term volatility and risk management needs. Perpetual options, meanwhile, offer indefinite expiry, allowing continuous exposure and hedging opportunities, thus complementing zero day options by providing a long-term strategic balance in derivative markets.
Key Terms
Time to Maturity
Perpetual options have no expiration date, allowing traders to hold positions indefinitely without worrying about time decay, unlike zero day options which expire within a single trading day, making their value highly sensitive to the time remaining. This fundamental difference in time to maturity impacts risk management strategies and premium pricing, with perpetual options typically having more stable premiums and zero day options offering high leverage for short-term volatility. Explore the key distinctions in how time to maturity influences trading dynamics and portfolio strategies in options markets.
Pricing Models
Perpetual options use a pricing model based on continuous time decay and stochastic volatility, often incorporating advanced techniques like the Heston model to capture fluctuating market dynamics. Zero day options rely on a simplified pricing framework that heavily factors in implied volatility and rapid time decay, reflecting their imminent expiration within the same trading day. Explore detailed comparisons of volatility assumptions and time decay impacts to understand how these models affect option valuation.
Risk Profile
Perpetual options carry ongoing exposure to market volatility and time decay, resulting in a complex risk profile influenced by shifting underlying asset prices and implied volatility over an indefinite period. Zero day options, expiring within a single trading day, concentrate risk into a short timeframe, leading to heightened sensitivity to intraday price movements and rapid time decay, which can cause swift gains or losses. Explore more to understand how these risk profiles impact strategic trading decisions and portfolio management.
Source and External Links
Introduction to Perpetual Options - Paradex | Documentation - Perpetual options are crypto derivatives combining option-like upside with protected downside and can be held indefinitely without expiration, involving continuous funding and lower liquidation risk compared to perpetual futures.
Perpetual Option Explained: Strategies, Benefits, and Risks - Cbonds - Perpetual options are exotic options with no fixed expiration date, allowing holders to exercise their right indefinitely, mainly traded over-the-counter due to limited practical usage and lack of listing on major exchanges.
Perpetual Option (XPO) | Definition and Meaning - Capital.com - Perpetual options are American-style exotic options that never expire, giving holders unlimited time to exercise; they are primarily traded OTC without centralised exchange involvement.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com