Carbon trading focuses on buying and selling emission allowances to limit greenhouse gases, creating market incentives for reducing carbon footprints. ESG investing evaluates companies based on environmental, social, and governance criteria to promote sustainable and ethical business practices. Explore how these distinct approaches drive financial strategies for environmental impact.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between carbon trading and ESG investing is crucial for effective financial decision-making and sustainability strategy implementation. Carbon trading specifically involves buying and selling carbon emission allowances to limit environmental impact, while ESG investing evaluates companies based on environmental, social, and governance criteria for long-term value creation. Recognizing these distinctions helps investors align portfolios with regulatory compliance and ethical standards, optimizing risk management and returns. Clear knowledge of both frameworks enhances the ability to support climate goals and sustainable business practices.
Comparison Table
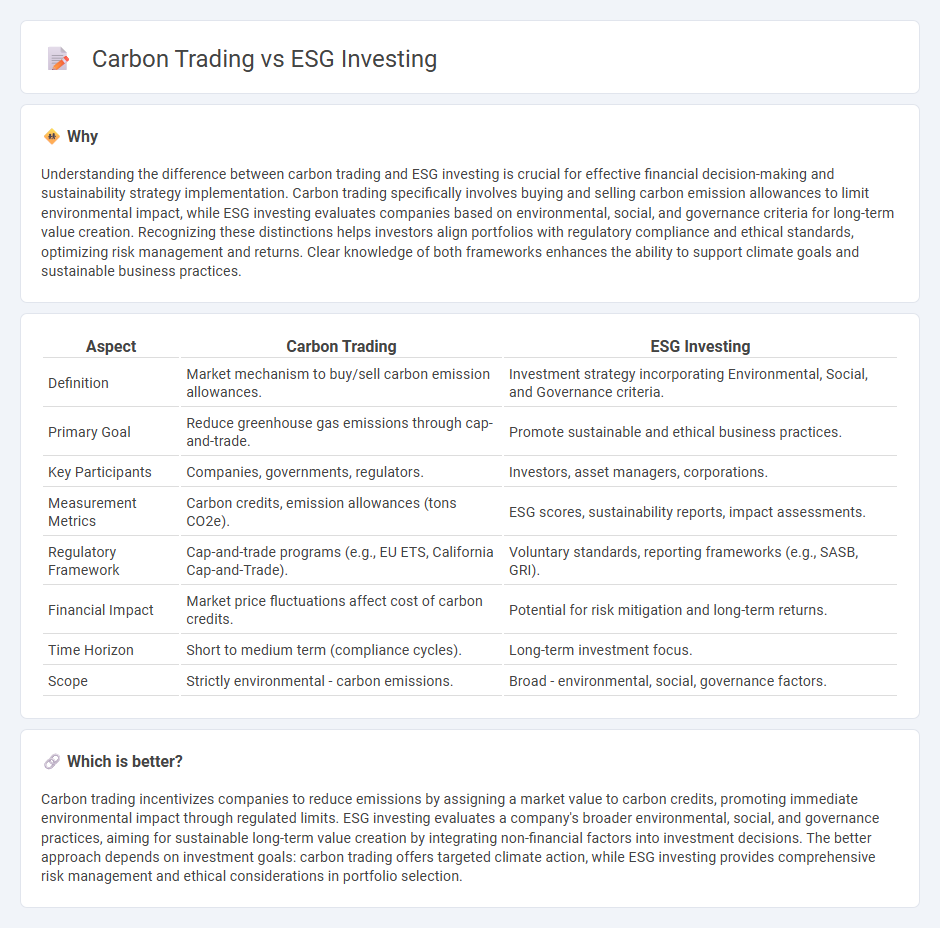
| Aspect | Carbon Trading | ESG Investing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Market mechanism to buy/sell carbon emission allowances. | Investment strategy incorporating Environmental, Social, and Governance criteria. |
| Primary Goal | Reduce greenhouse gas emissions through cap-and-trade. | Promote sustainable and ethical business practices. |
| Key Participants | Companies, governments, regulators. | Investors, asset managers, corporations. |
| Measurement Metrics | Carbon credits, emission allowances (tons CO2e). | ESG scores, sustainability reports, impact assessments. |
| Regulatory Framework | Cap-and-trade programs (e.g., EU ETS, California Cap-and-Trade). | Voluntary standards, reporting frameworks (e.g., SASB, GRI). |
| Financial Impact | Market price fluctuations affect cost of carbon credits. | Potential for risk mitigation and long-term returns. |
| Time Horizon | Short to medium term (compliance cycles). | Long-term investment focus. |
| Scope | Strictly environmental - carbon emissions. | Broad - environmental, social, governance factors. |
Which is better?
Carbon trading incentivizes companies to reduce emissions by assigning a market value to carbon credits, promoting immediate environmental impact through regulated limits. ESG investing evaluates a company's broader environmental, social, and governance practices, aiming for sustainable long-term value creation by integrating non-financial factors into investment decisions. The better approach depends on investment goals: carbon trading offers targeted climate action, while ESG investing provides comprehensive risk management and ethical considerations in portfolio selection.
Connection
Carbon trading directly supports ESG investing by providing a market-based mechanism to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, aligning with environmental criteria in ESG frameworks. Companies engaged in carbon trading demonstrate commitment to sustainability, enhancing their ESG scores and attracting responsible investors. This connection incentivizes corporate transparency and accountability in environmental performance, crucial for sustainable finance.
Key Terms
Sustainability
ESG investing prioritizes companies with strong environmental, social, and governance practices to drive long-term sustainable growth, while carbon trading directly targets emission reductions by allowing businesses to buy and sell carbon credits. Both approaches aim to combat climate change but operate through different mechanisms -- ESG investing influences corporate behavior broadly, and carbon trading provides financial incentives for lowering carbon footprints. Explore how integrating ESG strategies with carbon markets can accelerate sustainability efforts for lasting environmental impact.
Carbon Credits
Carbon credits are tradable certificates that represent the right to emit one metric ton of carbon dioxide, playing a crucial role in carbon trading markets aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions. ESG investing incorporates carbon credits as one component within broader environmental, social, and governance criteria to evaluate sustainable business practices and long-term financial performance. Explore how carbon credits intersect with ESG investing strategies to drive impactful climate solutions.
Regulatory Compliance
ESG investing emphasizes integrating environmental, social, and governance criteria into portfolio management to ensure companies meet regulatory standards and sustainable practices. Carbon trading operates as a market-based mechanism, allowing entities to buy and sell emission allowances to comply with government-imposed carbon caps and reduce overall greenhouse gas emissions. Explore deeper insights into how regulatory compliance shapes ESG investing and carbon trading strategies.
Source and External Links
Embracing Sustainable Investment Practices with ESG Investing - ESG investing integrates environmental, social, and governance risks into investment decisions, focusing on responsible business practices and offering growth and resilience benefits in the market.
What is ESG Investing? - ESG investing, also known as sustainable or socially responsible investing, prioritizes environmental, social, and governance factors and has roots in historic ethical investment practices, gaining modern prominence with the UN's Principles for Responsible Investments since 2006.
What is ESG investing? - Deutsche Bank Wealth Management - ESG investing considers environmental, social, and governance criteria alongside financial factors, aiming to support societal and environmental goals while investing, with $35.3 trillion invested globally under ESG principles by 2020.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com