Climate-linked derivatives offer targeted exposure to climate risk and carbon pricing, allowing investors to hedge against or profit from environmental changes. ESG indices aggregate companies based on their environmental, social, and governance performance, providing a broader sustainable investment framework. Explore how these financial instruments shape the future of responsible investing and risk management.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between Climate-linked derivatives and ESG indices is crucial for effective risk management and investment strategy alignment in finance. Climate-linked derivatives specifically hedge climate-related risks or capitalize on climate opportunities, directly influencing portfolio resilience to regulatory and environmental changes. ESG indices aggregate companies based on environmental, social, and governance performance, guiding sustainable investment decisions and reflecting broader ethical considerations. Accurate differentiation enables investors to optimize financial returns while supporting climate action and responsible corporate practices.
Comparison Table
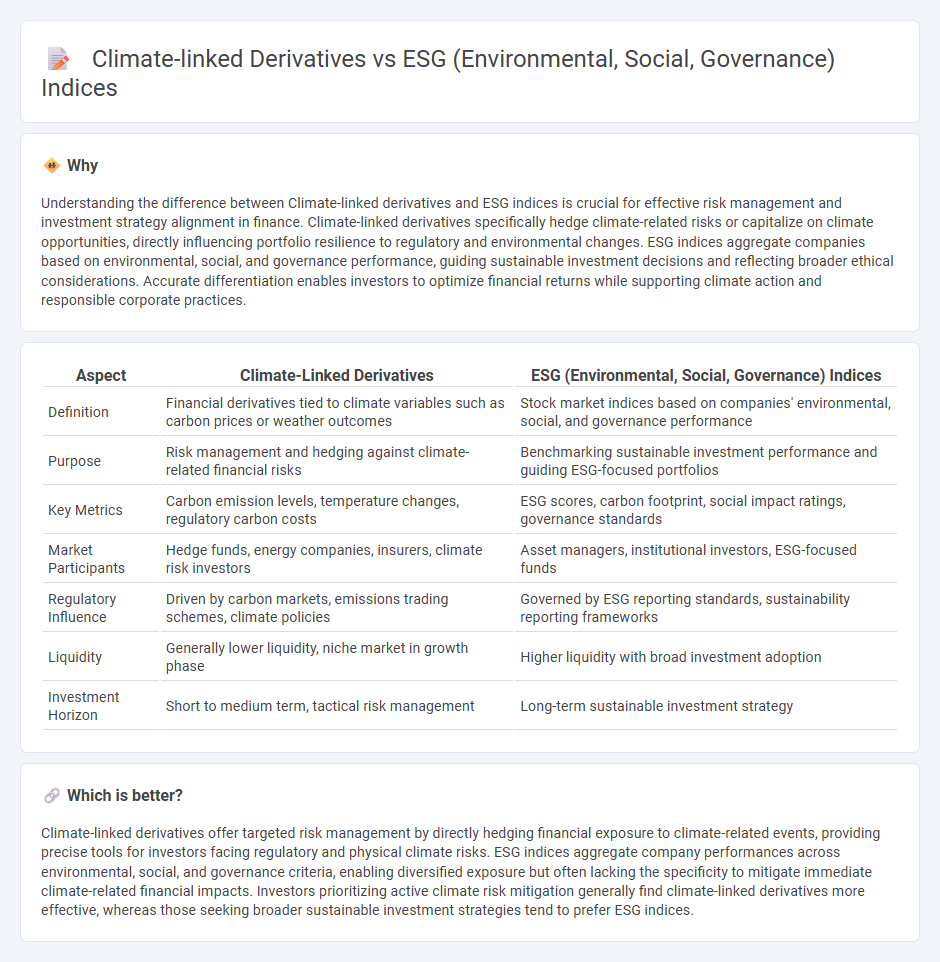
| Aspect | Climate-Linked Derivatives | ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) Indices |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Financial derivatives tied to climate variables such as carbon prices or weather outcomes | Stock market indices based on companies' environmental, social, and governance performance |
| Purpose | Risk management and hedging against climate-related financial risks | Benchmarking sustainable investment performance and guiding ESG-focused portfolios |
| Key Metrics | Carbon emission levels, temperature changes, regulatory carbon costs | ESG scores, carbon footprint, social impact ratings, governance standards |
| Market Participants | Hedge funds, energy companies, insurers, climate risk investors | Asset managers, institutional investors, ESG-focused funds |
| Regulatory Influence | Driven by carbon markets, emissions trading schemes, climate policies | Governed by ESG reporting standards, sustainability reporting frameworks |
| Liquidity | Generally lower liquidity, niche market in growth phase | Higher liquidity with broad investment adoption |
| Investment Horizon | Short to medium term, tactical risk management | Long-term sustainable investment strategy |
Which is better?
Climate-linked derivatives offer targeted risk management by directly hedging financial exposure to climate-related events, providing precise tools for investors facing regulatory and physical climate risks. ESG indices aggregate company performances across environmental, social, and governance criteria, enabling diversified exposure but often lacking the specificity to mitigate immediate climate-related financial impacts. Investors prioritizing active climate risk mitigation generally find climate-linked derivatives more effective, whereas those seeking broader sustainable investment strategies tend to prefer ESG indices.
Connection
Climate-linked derivatives are financial instruments designed to hedge risks associated with environmental changes, while ESG indices aggregate companies based on their environmental, social, and governance performance. These derivatives utilize data from ESG indices to price climate-related risks accurately, fostering better risk management and investment strategies aligned with sustainability goals. The integration of ESG metrics into climate-linked derivatives promotes transparency and encourages capital flow towards greener, more responsible enterprises.
Key Terms
Sustainability Metrics
ESG indices aggregate corporate performance based on environmental, social, and governance criteria, offering investors metrics to evaluate sustainable practices at a portfolio level. Climate-linked derivatives serve as financial instruments specifically designed to hedge or speculate on climate-related risks, directly linking payouts to sustainability outcomes like carbon emissions or weather events. Explore how integrating ESG indices with climate-linked derivatives can enhance strategic investment decisions in sustainability.
Carbon Pricing
ESG indices incorporate a broad range of environmental, social, and governance criteria to evaluate company performance, while climate-linked derivatives specifically target carbon pricing mechanisms to hedge or speculate on carbon emissions costs. Carbon pricing through derivatives like carbon credits and futures provides direct financial incentives for reducing greenhouse gas emissions and facilitates market-based climate risk management. Explore how these financial tools influence sustainable investing and carbon markets to better understand their impact on corporate climate strategies.
Risk Hedging
ESG indices aggregate companies based on environmental responsibility, social impact, and governance quality, providing investors with a diversified benchmark aligned with sustainability goals. Climate-linked derivatives offer targeted risk hedging by enabling market participants to manage exposure to specific climate-related financial risks such as carbon prices or weather events. Explore in-depth comparisons to understand how these financial instruments optimize risk management in the transition to a low-carbon economy.
Source and External Links
What Is an ESG Index? Learn its Definition and Purpose - An ESG Index evaluates companies based on environmental, social, and governance practices using criteria such as carbon footprint, diversity, and board ethics to guide responsible investment decisions.
About the ESG Index - The ESGI is a unique global index scoring countries on environment, human rights, and health & safety risks, designed to support legal and ethical risk analysis based on international human rights and environmental standards.
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) indices - LSEG - LSEG offers various ESG indices, including benchmarks for best corporate social responsibility practices, fossil-free portfolios, and indices selecting companies based on ESG performance with additional financial criteria like low volatility and dividend yield.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com