Altcoin staking involves locking crypto assets to support blockchain network operations, earning rewards proportional to the staked amount. Liquidity provision requires supplying tokens to decentralized exchanges, facilitating trades while earning fees and potential yield farming incentives. Explore the nuances and benefits of altcoin staking versus liquidity provision to optimize your crypto investment strategy.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between altcoin staking and liquidity provision is crucial for optimizing crypto investment returns and managing risk effectively. Altcoin staking involves locking coins to support blockchain operations and earn rewards, while liquidity provision entails depositing assets into decentralized exchanges to facilitate trading and earn fees. Knowing these distinctions helps investors choose strategies aligned with their risk tolerance, expected yields, and market conditions. Proper knowledge prevents potential losses from impermanent loss in liquidity provision or opportunity cost in staking.
Comparison Table
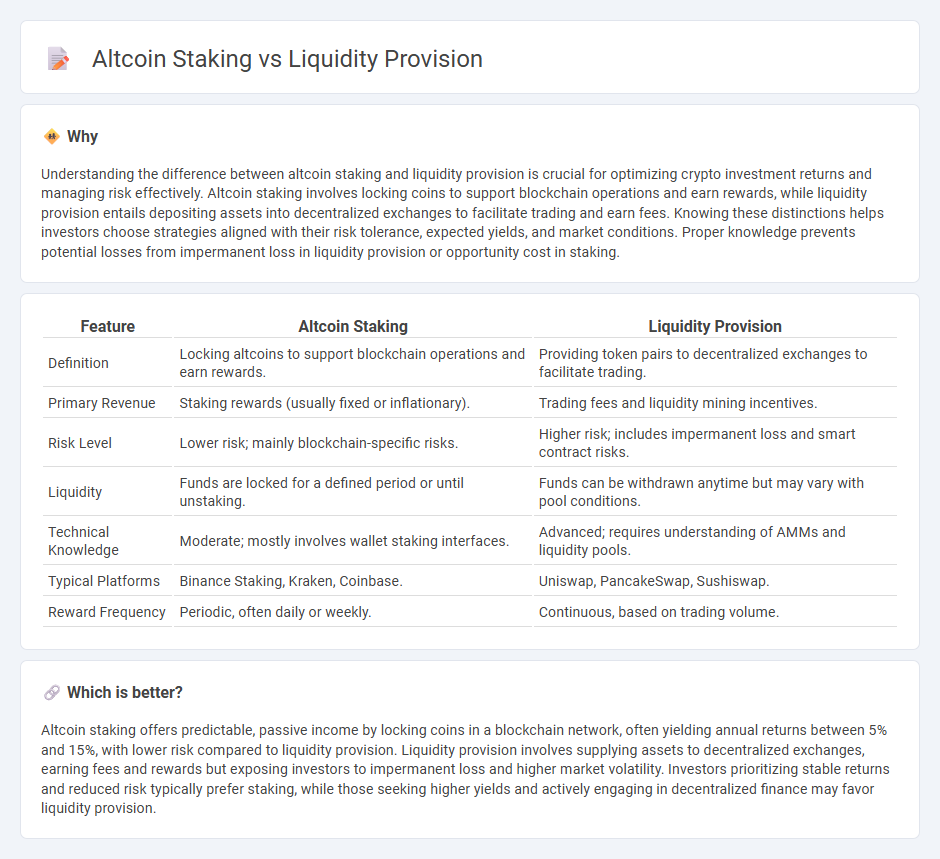
| Feature | Altcoin Staking | Liquidity Provision |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Locking altcoins to support blockchain operations and earn rewards. | Providing token pairs to decentralized exchanges to facilitate trading. |
| Primary Revenue | Staking rewards (usually fixed or inflationary). | Trading fees and liquidity mining incentives. |
| Risk Level | Lower risk; mainly blockchain-specific risks. | Higher risk; includes impermanent loss and smart contract risks. |
| Liquidity | Funds are locked for a defined period or until unstaking. | Funds can be withdrawn anytime but may vary with pool conditions. |
| Technical Knowledge | Moderate; mostly involves wallet staking interfaces. | Advanced; requires understanding of AMMs and liquidity pools. |
| Typical Platforms | Binance Staking, Kraken, Coinbase. | Uniswap, PancakeSwap, Sushiswap. |
| Reward Frequency | Periodic, often daily or weekly. | Continuous, based on trading volume. |
Which is better?
Altcoin staking offers predictable, passive income by locking coins in a blockchain network, often yielding annual returns between 5% and 15%, with lower risk compared to liquidity provision. Liquidity provision involves supplying assets to decentralized exchanges, earning fees and rewards but exposing investors to impermanent loss and higher market volatility. Investors prioritizing stable returns and reduced risk typically prefer staking, while those seeking higher yields and actively engaging in decentralized finance may favor liquidity provision.
Connection
Altcoin staking and liquidity provision both involve locking cryptocurrency to earn rewards, enhancing network security and market efficiency. Staking supports blockchain consensus mechanisms, while liquidity provision ensures trading platforms have sufficient asset availability, reducing price volatility. Both activities incentivize holders with yields, driving DeFi ecosystem growth and increasing capital efficiency.
Key Terms
Market Depth
Liquidity provision enhances market depth by enabling larger trades with minimal price impact, fostering stability in cryptocurrency exchanges. Altcoin staking, while rewarding holders, typically does not improve market depth directly as it locks assets rather than circulating them. Explore how these mechanisms differently influence market liquidity and trader opportunities for deeper insights.
Lock-up Period
Liquidity provision often requires locking assets in decentralized finance (DeFi) pools, with lock-up periods ranging from a few days to several months, influencing users' flexibility and risk exposure. Altcoin staking typically involves fixed lock-up durations determined by the blockchain protocol, impacting rewards and liquidity accessibility. Explore the nuances of lock-up periods in these investment strategies to optimize your crypto portfolio.
Yield
Liquidity provision often yields higher annual percentage rates (APRs) compared to altcoin staking, driven by fees generated from decentralized exchange trades and rewards from liquidity mining programs. Altcoin staking typically offers more predictable returns through fixed reward rates but may carry lower yield potential and greater exposure to token price volatility. Explore our detailed analysis to determine the best yield strategy for your crypto portfolio.
Source and External Links
Liquidity Provision: Strategy & Examples - Macroeconomics - Vaia - Liquidity provision is a strategy crucial for economic stability by ensuring financial institutions and markets have enough access to funds, balancing risk and return to keep assets liquid and the economy resilient during crises.
Liquidity Provision Strategies - DayTrading.com - It refers to various techniques such as market making, high-frequency trading, and central bank interventions that facilitate trading, reduce transaction costs, and sustain market stability.
Liquidity Provision by the Federal Reserve - Central banks provide liquidity to mitigate financial crises by ensuring institutions can meet payment demands, using tools like open market operations and direct credit lending, balancing liquidity needs against risks of underlying solvency issues.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com