Buy Now Pay Later (BNPL) services offer consumers flexible payment options by splitting purchases into interest-free installments, contrasting with credit cards that typically involve revolving credit lines accruing interest on unpaid balances. BNPL appeals to budget-conscious shoppers seeking short-term financial management without interest, while credit cards provide broader usage with rewards and credit-building benefits but may lead to debt if mismanaged. Explore the advantages and risks of each to make informed financial decisions tailored to your needs.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between Buy Now Pay Later (BNPL) and credit cards is crucial for managing personal finances effectively and avoiding unexpected debt. BNPL often offers interest-free short-term financing, whereas credit cards involve revolving credit with interest charges on unpaid balances. Misusing BNPL can lead to missed payments and credit score damage, while credit cards require careful tracking of spending and timely payments to prevent high interest costs. Knowing these differences empowers consumers to choose the best payment method that aligns with their financial goals and cash flow.
Comparison Table
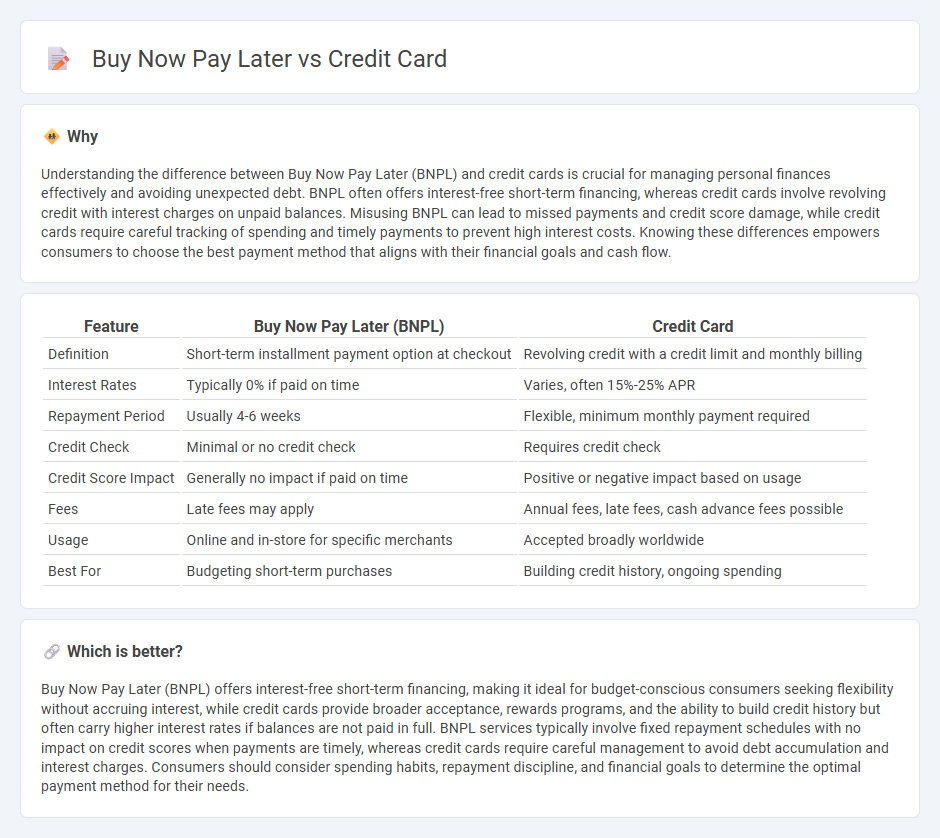
| Feature | Buy Now Pay Later (BNPL) | Credit Card |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Short-term installment payment option at checkout | Revolving credit with a credit limit and monthly billing |
| Interest Rates | Typically 0% if paid on time | Varies, often 15%-25% APR |
| Repayment Period | Usually 4-6 weeks | Flexible, minimum monthly payment required |
| Credit Check | Minimal or no credit check | Requires credit check |
| Credit Score Impact | Generally no impact if paid on time | Positive or negative impact based on usage |
| Fees | Late fees may apply | Annual fees, late fees, cash advance fees possible |
| Usage | Online and in-store for specific merchants | Accepted broadly worldwide |
| Best For | Budgeting short-term purchases | Building credit history, ongoing spending |
Which is better?
Buy Now Pay Later (BNPL) offers interest-free short-term financing, making it ideal for budget-conscious consumers seeking flexibility without accruing interest, while credit cards provide broader acceptance, rewards programs, and the ability to build credit history but often carry higher interest rates if balances are not paid in full. BNPL services typically involve fixed repayment schedules with no impact on credit scores when payments are timely, whereas credit cards require careful management to avoid debt accumulation and interest charges. Consumers should consider spending habits, repayment discipline, and financial goals to determine the optimal payment method for their needs.
Connection
Buy Now Pay Later (BNPL) and credit cards both offer consumers flexible payment options that enable purchases without immediate full payment, increasing purchasing power and cash flow management. Credit cards typically involve revolving credit with interest charges if balances are not paid in full, while BNPL services often provide interest-free installment plans for a fixed period. Both financial tools impact consumer credit scores and spending behavior, with BNPL gaining popularity among younger demographics seeking transparent, short-term financing alternatives.
Key Terms
Interest Rate
Credit cards typically feature interest rates ranging from 15% to 25% APR, which can significantly increase the total repayment amount if the balance is not paid in full monthly. Buy Now Pay Later (BNPL) services often provide interest-free periods, but exceeding those terms or missing payments can lead to high late fees and interest charges comparable to credit cards. Explore detailed comparisons to determine which payment option best suits your financial strategy.
Credit Limit
Credit card credit limits are typically set based on the individual's credit score, income, and credit history, allowing for flexible spending up to a predetermined ceiling. Buy Now Pay Later (BNPL) services often set smaller, transaction-specific limits that reset after each payment, providing controlled borrowing primarily for immediate purchases. Explore more key differences and benefits to determine which option best fits your financial needs.
Installment Plan
Credit cards typically offer revolving credit with minimum monthly payments, while Buy Now Pay Later (BNPL) services provide fixed installment plans that divide purchases into equal payments over a set period, often interest-free. Installment plans in BNPL programs simplify budgeting by locking in payment amounts and schedules, reducing the risk of accumulating interest and debt compared to credit card balances. Discover how installment options can impact your financial strategy and compare key features to make informed payment decisions.
Source and External Links
Credit card - Wikipedia - A credit card is a payment card, usually issued by a bank, that allows users to purchase goods or services or withdraw cash on credit, creating debt to be repaid later with interest, and is distinguished from charge and debit cards by its credit features.
Best Credit Cards | July 2025 - Lists various top credit card options including no annual fee, cash back, travel rewards, low interest, balance transfer, secured, and student credit cards tailored to different financial needs and lifestyles.
Apple Card - The Apple Card offers up to 3% daily cash back on purchases, no fees, real-time interest calculations encouraging lower interest payment, and allows cash back to be deposited or saved with interest.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com