Liquidity staking offers flexible asset management by allowing users to earn staking rewards while maintaining the ability to trade their staked tokens, enhancing capital efficiency in decentralized finance. Bond investing provides fixed income through periodic interest payments and principal return, making it a reliable choice for conservative portfolios seeking stable cash flow. Explore the advantages and risks of both to determine the best fit for your financial strategy.
Why it is important
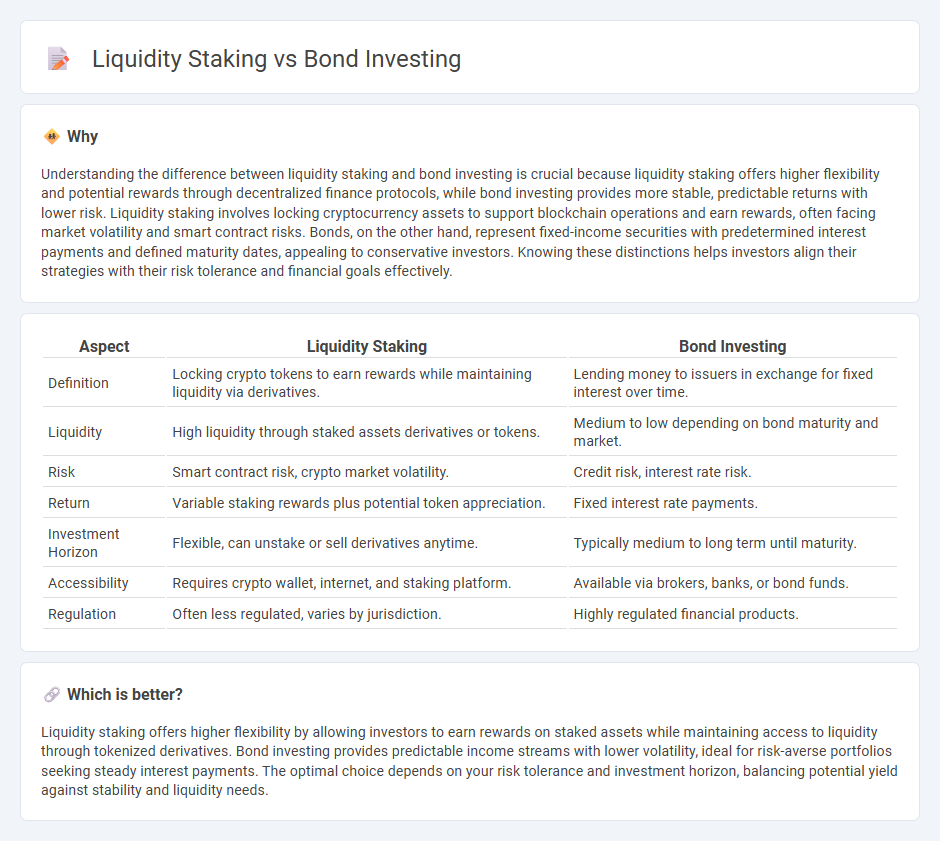
Understanding the difference between liquidity staking and bond investing is crucial because liquidity staking offers higher flexibility and potential rewards through decentralized finance protocols, while bond investing provides more stable, predictable returns with lower risk. Liquidity staking involves locking cryptocurrency assets to support blockchain operations and earn rewards, often facing market volatility and smart contract risks. Bonds, on the other hand, represent fixed-income securities with predetermined interest payments and defined maturity dates, appealing to conservative investors. Knowing these distinctions helps investors align their strategies with their risk tolerance and financial goals effectively.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Liquidity Staking | Bond Investing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Locking crypto tokens to earn rewards while maintaining liquidity via derivatives. | Lending money to issuers in exchange for fixed interest over time. |
| Liquidity | High liquidity through staked assets derivatives or tokens. | Medium to low depending on bond maturity and market. |
| Risk | Smart contract risk, crypto market volatility. | Credit risk, interest rate risk. |
| Return | Variable staking rewards plus potential token appreciation. | Fixed interest rate payments. |
| Investment Horizon | Flexible, can unstake or sell derivatives anytime. | Typically medium to long term until maturity. |
| Accessibility | Requires crypto wallet, internet, and staking platform. | Available via brokers, banks, or bond funds. |
| Regulation | Often less regulated, varies by jurisdiction. | Highly regulated financial products. |
Which is better?
Liquidity staking offers higher flexibility by allowing investors to earn rewards on staked assets while maintaining access to liquidity through tokenized derivatives. Bond investing provides predictable income streams with lower volatility, ideal for risk-averse portfolios seeking steady interest payments. The optimal choice depends on your risk tolerance and investment horizon, balancing potential yield against stability and liquidity needs.
Connection
Liquidity staking enhances bond investing by providing increased asset flexibility, enabling investors to earn staking rewards while maintaining access to liquid capital for bond purchases. This connection optimizes portfolio diversification and risk management by combining the predictable income streams of bond coupons with the dynamic yield generation of liquidity staking protocols. The integration of these strategies improves overall financial efficiency and capital allocation in modern investment landscapes.
Key Terms
**Bond Investing:**
Bond investing involves purchasing fixed-income securities that provide regular interest payments and return principal at maturity, offering predictable cash flow and lower risk compared to equities. Investors benefit from government bonds, corporate bonds, and municipal bonds, each with varying yields, maturities, and credit risk profiles to match different risk appetites and investment goals. Explore how strategic bond investing can balance your portfolio and provide steady income in diverse market conditions.
Yield
Bond investing typically offers fixed interest payments with moderate yield and lower risk, appealing to conservative investors seeking predictable income streams. Liquidity staking in decentralized finance platforms often provides higher yields through rewards or fees but with increased volatility and potential impermanent loss. Explore detailed comparisons to determine which strategy maximizes your investment yield effectively.
Maturity
Bond investing offers fixed maturity dates, providing predictable returns and principal repayment upon maturity, which aligns with long-term financial planning. Liquidity staking lacks a defined maturity, often subjecting staked assets to variable lock-up periods and withdrawal restrictions that affect access to funds. Explore further to understand how maturity impacts your choice between bond investing and liquidity staking strategies.
Source and External Links
Bonds 101: The What and Why of Bond Investing - Bonds are fixed income investments where you lend money to governments or companies, receiving periodic interest (coupons) and the principal back at maturity; they are issued to raise capital for projects or operational funding.
Bonds - Bonds function as debt securities where issuers promise to pay regular interest and return face value at maturity, offering investors a predictable income and capital preservation tool while helping diversify risk.
What is a Bond and How do they Work? - Vanguard - Bonds can be held to receive steady coupon payments until maturity or traded on secondary markets where prices fluctuate; key terms include coupon, yield, face value, and current price, all affecting bond investment decisions.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com