Buy Now Pay Later (BNPL) services offer consumers the flexibility to split purchases into interest-free installments over time, enhancing budgeting ease without immediate financial strain. Charge cards require full payment by the due date, often providing rewards and no preset spending limit but can incur fees if balances are not settled promptly. Explore the pros and cons of BNPL versus charge cards to determine the best fit for your financial strategy.
Why it is important
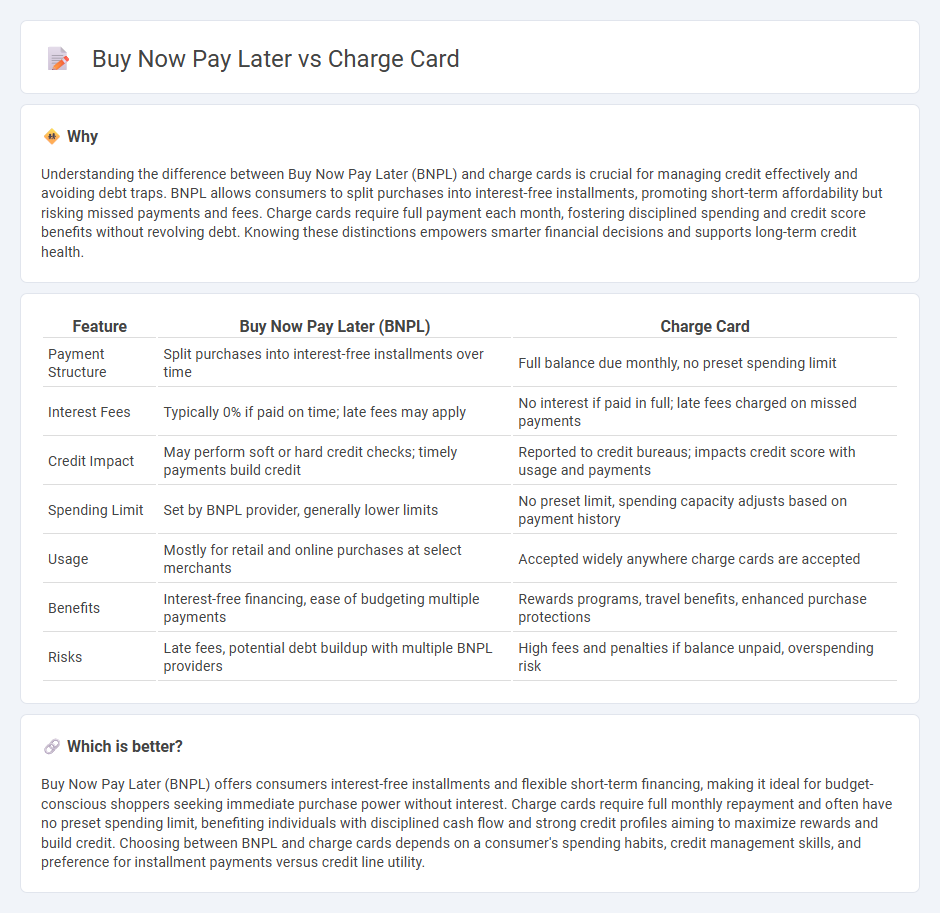
Understanding the difference between Buy Now Pay Later (BNPL) and charge cards is crucial for managing credit effectively and avoiding debt traps. BNPL allows consumers to split purchases into interest-free installments, promoting short-term affordability but risking missed payments and fees. Charge cards require full payment each month, fostering disciplined spending and credit score benefits without revolving debt. Knowing these distinctions empowers smarter financial decisions and supports long-term credit health.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Buy Now Pay Later (BNPL) | Charge Card |
|---|---|---|
| Payment Structure | Split purchases into interest-free installments over time | Full balance due monthly, no preset spending limit |
| Interest Fees | Typically 0% if paid on time; late fees may apply | No interest if paid in full; late fees charged on missed payments |
| Credit Impact | May perform soft or hard credit checks; timely payments build credit | Reported to credit bureaus; impacts credit score with usage and payments |
| Spending Limit | Set by BNPL provider, generally lower limits | No preset limit, spending capacity adjusts based on payment history |
| Usage | Mostly for retail and online purchases at select merchants | Accepted widely anywhere charge cards are accepted |
| Benefits | Interest-free financing, ease of budgeting multiple payments | Rewards programs, travel benefits, enhanced purchase protections |
| Risks | Late fees, potential debt buildup with multiple BNPL providers | High fees and penalties if balance unpaid, overspending risk |
Which is better?
Buy Now Pay Later (BNPL) offers consumers interest-free installments and flexible short-term financing, making it ideal for budget-conscious shoppers seeking immediate purchase power without interest. Charge cards require full monthly repayment and often have no preset spending limit, benefiting individuals with disciplined cash flow and strong credit profiles aiming to maximize rewards and build credit. Choosing between BNPL and charge cards depends on a consumer's spending habits, credit management skills, and preference for installment payments versus credit line utility.
Connection
Buy Now Pay Later (BNPL) services and charge cards both offer alternative payment options that enhance consumer purchasing power by allowing deferred payments. BNPL allows consumers to split purchases into interest-free installments over time, while charge cards require full balance payment every billing cycle, avoiding interest but encouraging disciplined budget management. Both payment methods generate valuable transactional data for financial institutions, helping to assess consumer credit behavior and tailor personalized financial products.
Key Terms
Credit Limit
Charge cards require full payment of the balance each billing cycle and typically have no preset spending limit, offering flexibility based on your payment history and creditworthiness. Buy Now Pay Later (BNPL) services set specific credit limits or installment amounts per purchase, limiting your borrowing capacity to a predetermined threshold. Explore how these credit options impact your purchasing power and financial management to make informed decisions.
Deferred Payment
Charge cards require full payment each billing cycle without interest but offer flexible spending limits, while Buy Now Pay Later (BNPL) services allow deferred payment over time, often interest-free if paid within promotional periods. Deferred payment plans in BNPL increase purchasing power by splitting costs into manageable installments, appealing to budget-conscious consumers seeking immediate ownership without upfront full payment. Explore our detailed comparison to understand which payment option suits your financial strategy best.
Interest-Free Period
Charge cards offer an interest-free period that typically requires full payment by the due date, avoiding interest charges if the balance is cleared on time. Buy Now Pay Later (BNPL) services provide a set interest-free repayment schedule, usually spanning several weeks or months, allowing consumers to spread out payments without accruing interest. Explore how these interest-free options impact your spending habits and financial planning to choose the best fit for your needs.
Source and External Links
What Is a Charge Card? | Capital One - A charge card requires full payment of the balance each billing cycle, typically has no preset spending limit, and usually does not charge interest but may have high fees for late payment and annual use.
What Is A Charge Card? | American Express Australia - Charge cards have flexible spending power without a preset limit and require the full balance to be paid each month, generally not charging interest but imposing fees if the balance is not fully paid.
Charge card - Wikipedia - A charge card enables purchases paid by the issuer with no interest charged if paid in full monthly, often has no preset spending limit whose amount varies based on usage and credit history, with some allowing partial payment for certain purchases over time.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com