Sovereign debt restructuring involves renegotiating the terms of a country's outstanding debt to improve its financial stability and prevent default. Bridge financing provides short-term capital to cover immediate funding gaps until long-term financing is secured or economic conditions improve. Explore the differences and strategic uses of these financial tools to better understand their impact on sovereign economic management.
Why it is important
Understanding sovereign debt restructuring is crucial for assessing long-term debt sustainability and the impact on national credit ratings, whereas bridge financing provides short-term liquidity to manage immediate budget gaps or crises. Accurate knowledge of each helps policymakers and investors make informed decisions about risk, repayment terms, and fiscal stability. Sovereign debt restructuring often involves negotiating with creditors to extend maturities or reduce principal, significantly affecting a country's economic recovery. Bridge financing, in contrast, is temporary and designed to support ongoing government operations without altering existing debt structures.
Comparison Table
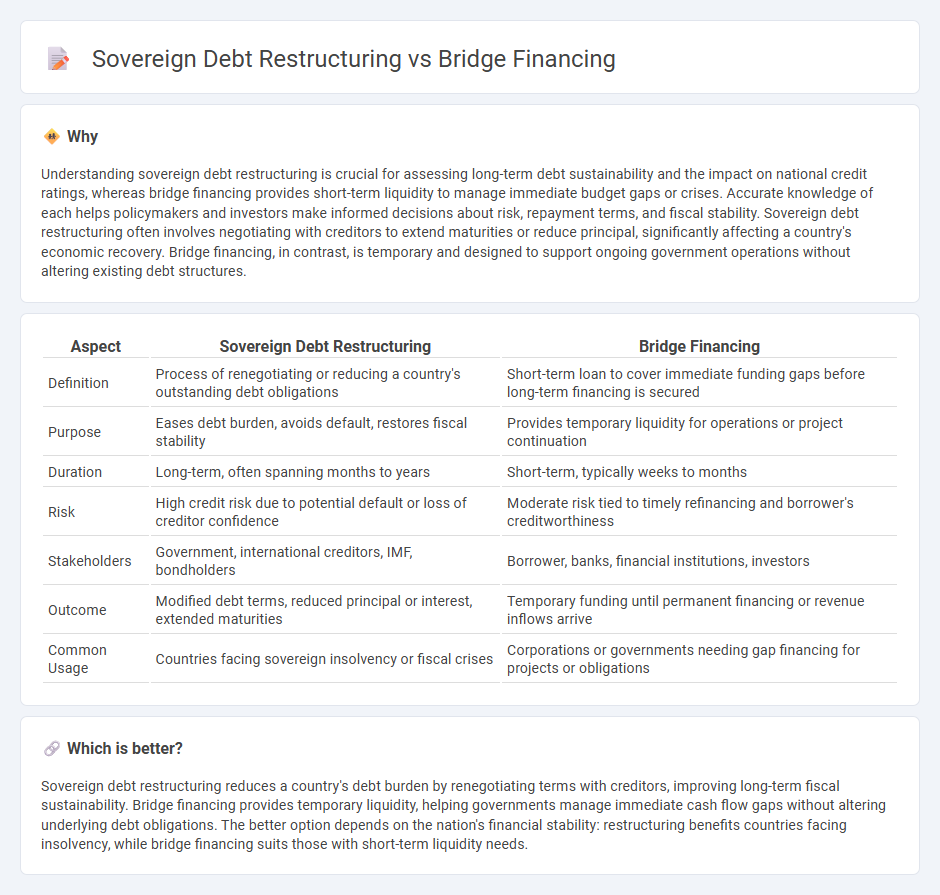
| Aspect | Sovereign Debt Restructuring | Bridge Financing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process of renegotiating or reducing a country's outstanding debt obligations | Short-term loan to cover immediate funding gaps before long-term financing is secured |
| Purpose | Eases debt burden, avoids default, restores fiscal stability | Provides temporary liquidity for operations or project continuation |
| Duration | Long-term, often spanning months to years | Short-term, typically weeks to months |
| Risk | High credit risk due to potential default or loss of creditor confidence | Moderate risk tied to timely refinancing and borrower's creditworthiness |
| Stakeholders | Government, international creditors, IMF, bondholders | Borrower, banks, financial institutions, investors |
| Outcome | Modified debt terms, reduced principal or interest, extended maturities | Temporary funding until permanent financing or revenue inflows arrive |
| Common Usage | Countries facing sovereign insolvency or fiscal crises | Corporations or governments needing gap financing for projects or obligations |
Which is better?
Sovereign debt restructuring reduces a country's debt burden by renegotiating terms with creditors, improving long-term fiscal sustainability. Bridge financing provides temporary liquidity, helping governments manage immediate cash flow gaps without altering underlying debt obligations. The better option depends on the nation's financial stability: restructuring benefits countries facing insolvency, while bridge financing suits those with short-term liquidity needs.
Connection
Sovereign debt restructuring often requires bridge financing to provide immediate liquidity while long-term debt agreements are renegotiated or restructured. Bridge financing serves as a temporary financial solution that helps governments meet urgent fiscal obligations and maintain public services during periods of financial instability. Efficient coordination between sovereign debt restructuring plans and bridge financing arrangements is critical to restore investor confidence and ensure sustainable fiscal management.
Key Terms
Source and External Links
Bridge Financing - Definition, How it Works, Example - Bridge financing is a temporary funding method used to cover a company's short-term costs until long-term financing is secured, acting as a financial "bridge" often used in IPOs or urgent capital needs, but typically with high interest rates.
What is Bridge Financing - Capchase - Bridge financing is critical for startups and businesses to handle immediate funding needs and maintain operations while awaiting permanent financing, serving as a stopgap solution to cover short-term expenses and enable growth.
Bridge loan - Wikipedia - A bridge loan is a short-term loan lasting from weeks to a few years, often used by developers or buyers to cover costs until longer-term financing or sales proceeds become available, usually carrying higher interest rates due to their temporary and risky nature.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com