Convexity hedging involves managing the risk that arises from the curvature in the price-yield relationship of fixed-income securities, ensuring portfolio sensitivity to interest rate changes is controlled. Interest rate swaps are derivatives that allow counterparties to exchange fixed interest rate payments for floating rate payments, effectively customizing interest rate exposure. Explore the distinct strategies behind convexity hedging and interest rate swaps to optimize your financial risk management.
Why it is important
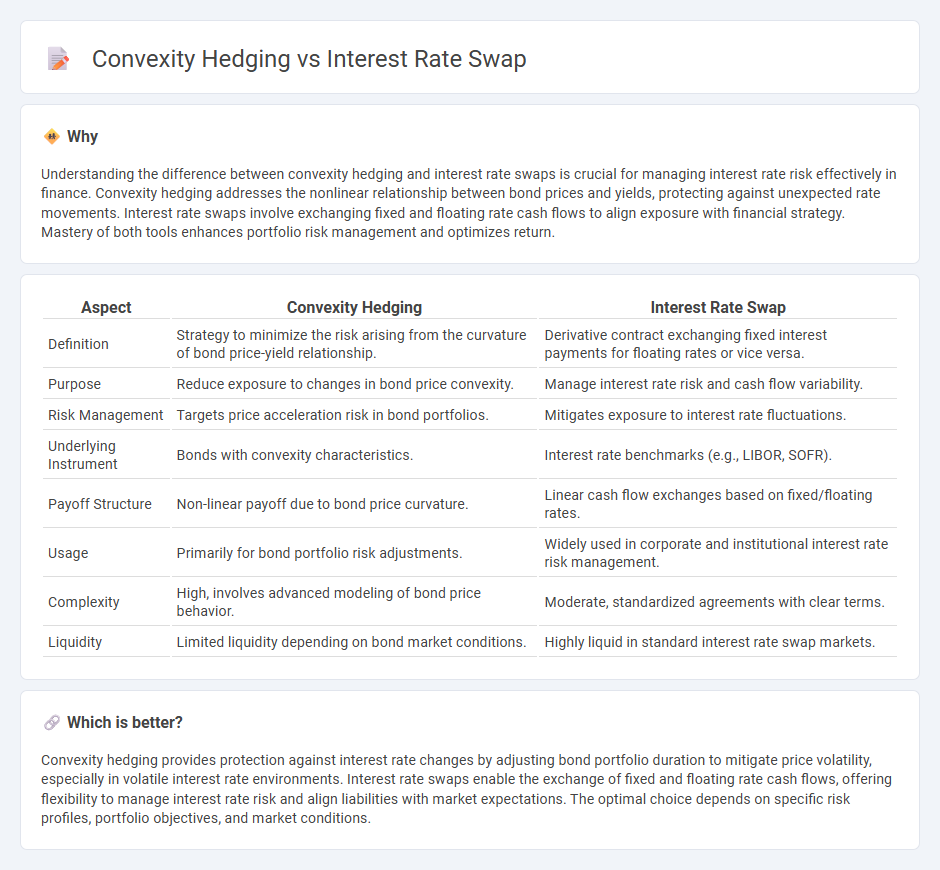
Understanding the difference between convexity hedging and interest rate swaps is crucial for managing interest rate risk effectively in finance. Convexity hedging addresses the nonlinear relationship between bond prices and yields, protecting against unexpected rate movements. Interest rate swaps involve exchanging fixed and floating rate cash flows to align exposure with financial strategy. Mastery of both tools enhances portfolio risk management and optimizes return.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Convexity Hedging | Interest Rate Swap |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Strategy to minimize the risk arising from the curvature of bond price-yield relationship. | Derivative contract exchanging fixed interest payments for floating rates or vice versa. |
| Purpose | Reduce exposure to changes in bond price convexity. | Manage interest rate risk and cash flow variability. |
| Risk Management | Targets price acceleration risk in bond portfolios. | Mitigates exposure to interest rate fluctuations. |
| Underlying Instrument | Bonds with convexity characteristics. | Interest rate benchmarks (e.g., LIBOR, SOFR). |
| Payoff Structure | Non-linear payoff due to bond price curvature. | Linear cash flow exchanges based on fixed/floating rates. |
| Usage | Primarily for bond portfolio risk adjustments. | Widely used in corporate and institutional interest rate risk management. |
| Complexity | High, involves advanced modeling of bond price behavior. | Moderate, standardized agreements with clear terms. |
| Liquidity | Limited liquidity depending on bond market conditions. | Highly liquid in standard interest rate swap markets. |
Which is better?
Convexity hedging provides protection against interest rate changes by adjusting bond portfolio duration to mitigate price volatility, especially in volatile interest rate environments. Interest rate swaps enable the exchange of fixed and floating rate cash flows, offering flexibility to manage interest rate risk and align liabilities with market expectations. The optimal choice depends on specific risk profiles, portfolio objectives, and market conditions.
Connection
Convexity hedging manages the risk of bond price fluctuations due to changes in interest rate volatility, while interest rate swaps exchange fixed and floating rate cash flows to stabilize borrowing costs. The connection lies in using interest rate swaps to mitigate convexity risk by adjusting duration and cash flow profiles. This strategy helps investors and institutions protect portfolios against adverse interest rate movements and optimize risk-return balance.
Key Terms
Fixed Rate
Interest rate swaps help manage fixed rate exposure by exchanging fixed interest payments for floating rate payments, reducing interest rate risk in portfolios with fixed-rate liabilities or assets. Convexity hedging adjusts for the non-linear relationship between bond prices and interest rates, stabilizing the fixed rate's value against interest rate volatility. Explore the mechanics and benefits of these strategies in depth for effective fixed rate risk management.
Floating Rate
Interest rate swaps involving floating rates allow counterparties to exchange fixed interest payments for floating ones, providing flexibility in managing exposure to interest rate fluctuations. Convexity hedging specifically addresses the non-linear relationship between bond prices and yields, particularly impacting floating-rate instruments by mitigating risks from rate volatility. Discover how combining interest rate swaps with convexity hedging can optimize risk management strategies for floating rate portfolios.
Duration
Interest rate swaps are financial derivatives used to exchange fixed and floating interest payments, effectively managing interest rate exposure and modifying portfolio duration. Convexity hedging, by contrast, aims to adjust the curvature of the price-yield relationship of bonds, reducing sensitivity to interest rate volatility beyond simple duration measures. Explore the nuances of duration management in these strategies to optimize your fixed income risk control.
Source and External Links
Video An Overview Of Interest Rate Swaps - PNC Bank - An interest rate swap is an agreement between two parties to exchange a floating interest rate for a fixed rate, helping borrowers manage interest rate risk and budget with greater confidence.
Interest Rate Swap: Meaning, Types, Examples and How Works? - An interest rate swap is a derivative contract where two parties exchange future interest payments, typically swapping fixed-rate payments for floating-rate payments to manage borrowing costs and stabilize cash flow.
Interest Rate Swap (IRS) - Corporate Finance Institute - Interest rate swaps involve exchanging interest payments where one party pays fixed rates and the other floating rates, with only the net interest difference being exchanged, not the principal.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com