Laddered bond ETFs provide diversified exposure to bonds with varying maturities, offering liquidity and professional management compared to traditional bond ladders, which involve purchasing individual bonds staggered across different maturity dates. Bond ladders allow investors to reinvest principal at regular intervals, managing interest rate risk and providing predictable income streams, while laddered bond ETFs trade like stocks and can offer cost efficiency through pooled investments. Explore the key differences and advantages of each strategy to determine the best fit for your fixed-income portfolio.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between Laddered Bond ETFs and Bond Ladders is crucial for optimizing fixed-income investment strategies and managing interest rate risk effectively. Laddered Bond ETFs offer diversification and liquidity with professionally managed portfolios of bonds staggered by maturity date. Bond Ladders involve directly purchasing individual bonds with varying maturities to generate predictable income and reduce reinvestment risk. Recognizing these distinctions helps investors tailor their approach to meet specific goals such as income stability or capital preservation.
Comparison Table
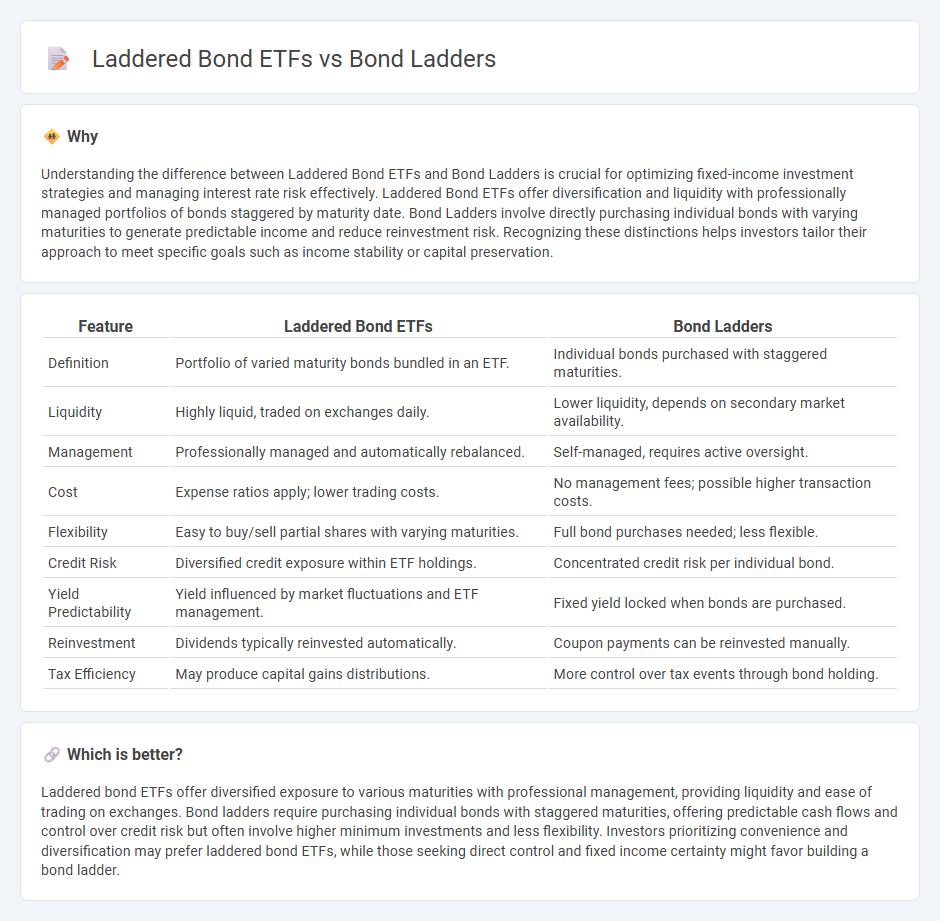
| Feature | Laddered Bond ETFs | Bond Ladders |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Portfolio of varied maturity bonds bundled in an ETF. | Individual bonds purchased with staggered maturities. |
| Liquidity | Highly liquid, traded on exchanges daily. | Lower liquidity, depends on secondary market availability. |
| Management | Professionally managed and automatically rebalanced. | Self-managed, requires active oversight. |
| Cost | Expense ratios apply; lower trading costs. | No management fees; possible higher transaction costs. |
| Flexibility | Easy to buy/sell partial shares with varying maturities. | Full bond purchases needed; less flexible. |
| Credit Risk | Diversified credit exposure within ETF holdings. | Concentrated credit risk per individual bond. |
| Yield Predictability | Yield influenced by market fluctuations and ETF management. | Fixed yield locked when bonds are purchased. |
| Reinvestment | Dividends typically reinvested automatically. | Coupon payments can be reinvested manually. |
| Tax Efficiency | May produce capital gains distributions. | More control over tax events through bond holding. |
Which is better?
Laddered bond ETFs offer diversified exposure to various maturities with professional management, providing liquidity and ease of trading on exchanges. Bond ladders require purchasing individual bonds with staggered maturities, offering predictable cash flows and control over credit risk but often involve higher minimum investments and less flexibility. Investors prioritizing convenience and diversification may prefer laddered bond ETFs, while those seeking direct control and fixed income certainty might favor building a bond ladder.
Connection
Laddered bond ETFs replicate the investment strategy of bond ladders by holding bonds with staggered maturities, providing consistent income and reducing interest rate risk. Both methods enhance portfolio diversification and liquidity by spreading reinvestment risk over time. Investors benefit from predictable cash flows and mitigated volatility through these structured fixed-income approaches.
Key Terms
Liquidity
Bond ladders offer direct ownership of individual bonds, providing predictable cash flows and maturity dates but limited liquidity as bonds must be sold in the secondary market, often at a discount. Laddered bond ETFs bundle diverse bonds with staggered maturities, delivering enhanced liquidity through daily tradability on exchanges and easier portfolio diversification with lower investment thresholds. Explore how these liquidity differences impact portfolio strategy and risk management.
Diversification
Bond ladders offer targeted diversification by staggering individual bond maturities, reducing interest rate risk and providing predictable cash flows. Laddered bond ETFs aggregate multiple bonds within a fund, enhancing diversification but adding management fees and less control over specific maturities. Explore the nuances of these strategies to optimize your bond investment diversification.
Maturity Structure
Bond ladders consist of individual bonds with staggered maturities, providing predictable cash flow and reducing interest rate risk through diversification across different time horizons. Laddered bond ETFs, however, offer a diversified portfolio of bonds managed by professionals, with continuous reinvestment and a more flexible maturity structure but less control over individual bond selection. Explore the differences in maturity structures to determine which strategy aligns best with your investment goals.
Source and External Links
How to build a bond ladder | Fidelity - A bond ladder involves buying bonds with staggered maturities to create a predictable income stream, manage interest rate risk, and maintain flexibility for reinvestment opportunities as market rates change.
Back in fashion: Bond ladders - Russell Investments - Bond ladders allow investors to own individual bonds to maturity, thereby preserving principal and locking in interest rates, differing from bond funds or ETFs where yields and value fluctuate with market rates.
Bond ladders vs. ETFs | Schwab Funds - A bond ladder strategy buys bonds with similar face values but staggered maturities to diversify risk, provide steady cash flow, and enable reinvestment in changing interest rate environments, offering advantages over single bonds and bond ETFs.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com