Carbon trading markets allow companies to buy and sell carbon credits to meet regulatory emission targets, creating financial incentives for reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Nature-based solutions financing focuses on investing in projects like reforestation, wetland restoration, and soil carbon sequestration to naturally absorb carbon while enhancing biodiversity and ecosystem health. Explore the benefits and challenges of both approaches to better understand their roles in sustainable finance.
Why it is important
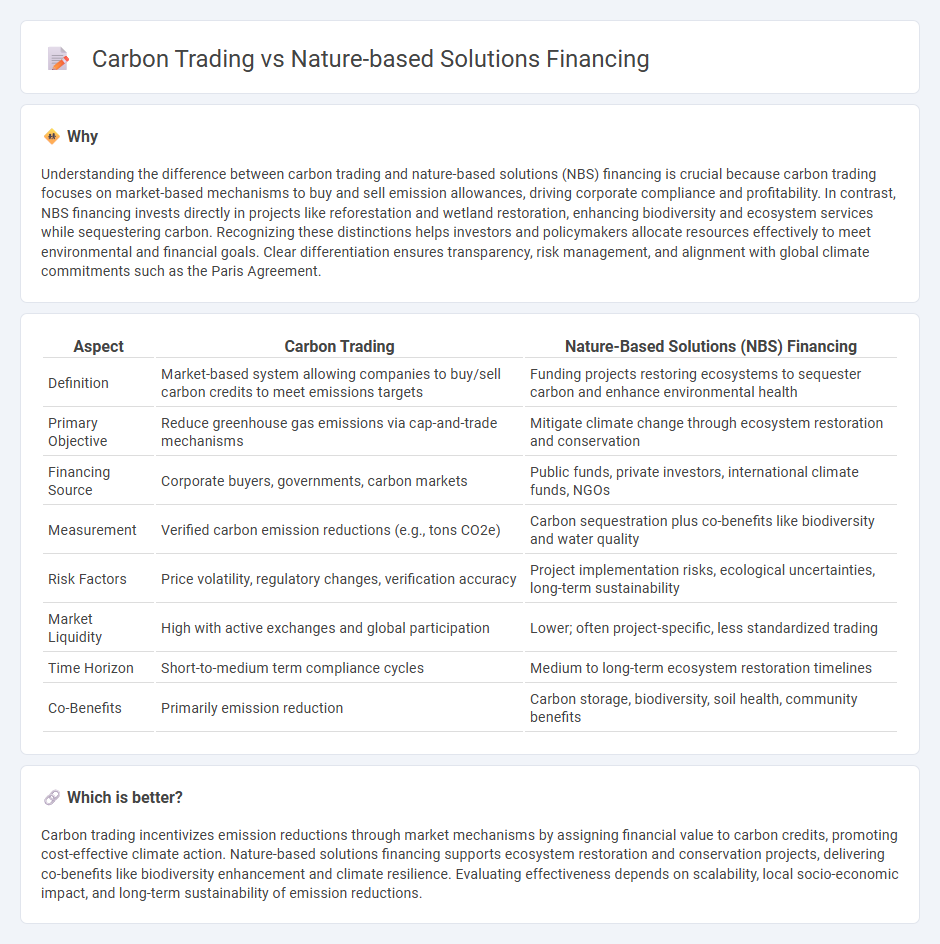
Understanding the difference between carbon trading and nature-based solutions (NBS) financing is crucial because carbon trading focuses on market-based mechanisms to buy and sell emission allowances, driving corporate compliance and profitability. In contrast, NBS financing invests directly in projects like reforestation and wetland restoration, enhancing biodiversity and ecosystem services while sequestering carbon. Recognizing these distinctions helps investors and policymakers allocate resources effectively to meet environmental and financial goals. Clear differentiation ensures transparency, risk management, and alignment with global climate commitments such as the Paris Agreement.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Carbon Trading | Nature-Based Solutions (NBS) Financing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Market-based system allowing companies to buy/sell carbon credits to meet emissions targets | Funding projects restoring ecosystems to sequester carbon and enhance environmental health |
| Primary Objective | Reduce greenhouse gas emissions via cap-and-trade mechanisms | Mitigate climate change through ecosystem restoration and conservation |
| Financing Source | Corporate buyers, governments, carbon markets | Public funds, private investors, international climate funds, NGOs |
| Measurement | Verified carbon emission reductions (e.g., tons CO2e) | Carbon sequestration plus co-benefits like biodiversity and water quality |
| Risk Factors | Price volatility, regulatory changes, verification accuracy | Project implementation risks, ecological uncertainties, long-term sustainability |
| Market Liquidity | High with active exchanges and global participation | Lower; often project-specific, less standardized trading |
| Time Horizon | Short-to-medium term compliance cycles | Medium to long-term ecosystem restoration timelines |
| Co-Benefits | Primarily emission reduction | Carbon storage, biodiversity, soil health, community benefits |
Which is better?
Carbon trading incentivizes emission reductions through market mechanisms by assigning financial value to carbon credits, promoting cost-effective climate action. Nature-based solutions financing supports ecosystem restoration and conservation projects, delivering co-benefits like biodiversity enhancement and climate resilience. Evaluating effectiveness depends on scalability, local socio-economic impact, and long-term sustainability of emission reductions.
Connection
Carbon trading drives investment in nature-based solutions by assigning monetary value to carbon sequestration, incentivizing projects like reforestation and wetland restoration. Financing mechanisms for nature-based solutions often depend on the revenue generated from carbon credits sold in voluntary or compliance markets. This integration enhances sustainable finance flow, aligning environmental benefits with economic incentives.
Key Terms
Ecosystem Services Valuation
Nature-based solutions financing emphasizes direct investment in ecosystems to enhance services like water purification, carbon sequestration, and biodiversity. Carbon trading, by contrast, monetizes emissions reductions through market mechanisms, creating tradable carbon credits primarily linked to carbon storage or avoidance. Explore how Ecosystem Services Valuation integrates these approaches to optimize environmental and economic outcomes.
Carbon Credits
Nature-based solutions financing involves funding projects that enhance ecosystems to sequester carbon, such as reforestation and wetland restoration, generating carbon credits through verified emission reductions. Carbon trading markets enable companies to buy and sell these credits to meet regulatory or voluntary emissions targets, creating a financial incentive for conservation and sustainable land management. Explore the mechanisms and benefits of carbon credits to understand their role in advancing climate goals through nature-based solutions.
Additionality
Nature-based solutions financing prioritizes additionality by ensuring that investments lead to genuine, measurable environmental benefits beyond business-as-usual scenarios, often supporting projects like reforestation and wetland restoration. Carbon trading markets rely on additionality to validate that emission reductions are new and would not have occurred without the offset project, maintaining the integrity of carbon credits. Discover how additionality shapes the effectiveness and credibility of nature-based solutions financing compared to carbon trading.
Source and External Links
Making blended finance work for nature-based solutions - This paper outlines innovative financial instruments and blended finance mechanisms designed to catalyze large-scale funding for nature-based solutions, addressing their urgent underfunding and linking biodiversity loss with the climate crisis.
Financing conservation and nature-based solutions - A practical guide explaining how entrepreneurs, conservation organizations, corporations, and municipalities can access finance and structure projects to boost investment in biodiversity, conservation, and nature-based climate adaptation, including support from the European Investment Bank's Natural Capital Financing Facility.
Toolbox on Financing Nature-Based Solutions - This report presents blended finance case studies that overcome investment barriers in NbS, emphasizing the unique challenges stemming from NbS's public-good nature and multisectoral scope, and highlighting the potential for NbS to provide significant climate mitigation if financed at scale.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com