Convexity hedging focuses on managing interest rate risk by adjusting bond portfolio duration to minimize price volatility during rate fluctuations. The barbell strategy involves balancing short-term and long-term bonds, optimizing yield while maintaining liquidity and reducing exposure to intermediate maturities. Explore the nuances of these approaches to enhance portfolio risk management and performance.
Why it is important
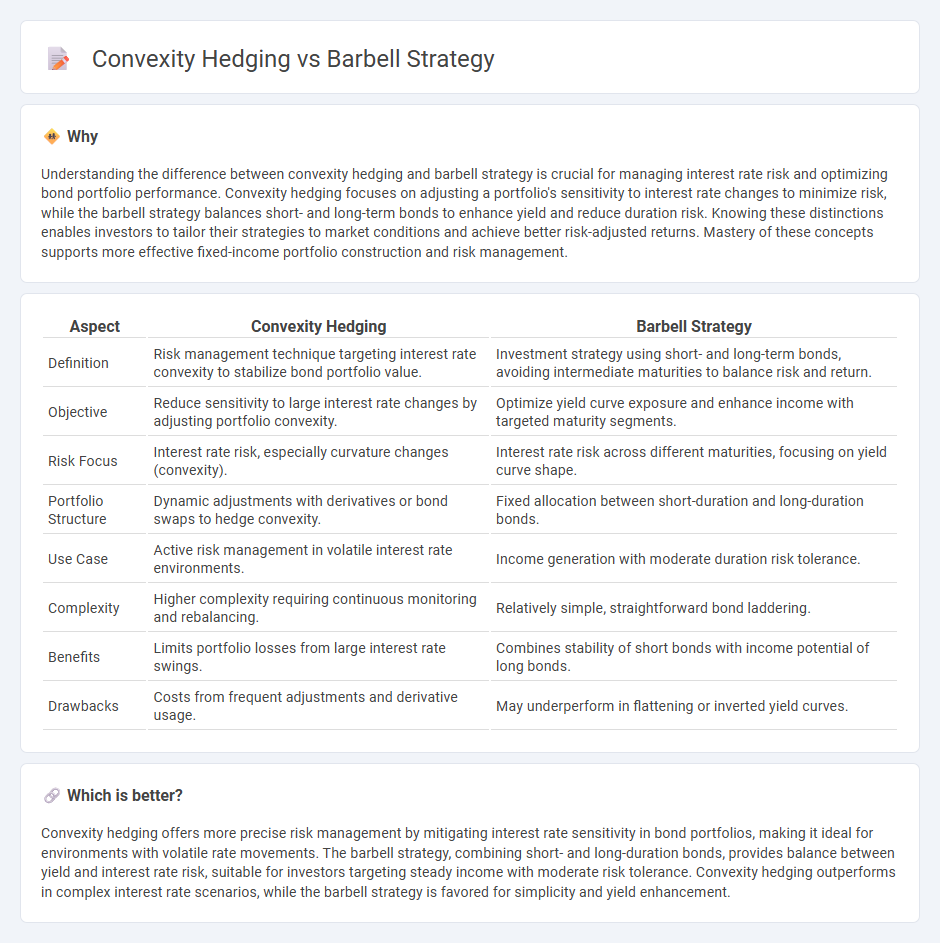
Understanding the difference between convexity hedging and barbell strategy is crucial for managing interest rate risk and optimizing bond portfolio performance. Convexity hedging focuses on adjusting a portfolio's sensitivity to interest rate changes to minimize risk, while the barbell strategy balances short- and long-term bonds to enhance yield and reduce duration risk. Knowing these distinctions enables investors to tailor their strategies to market conditions and achieve better risk-adjusted returns. Mastery of these concepts supports more effective fixed-income portfolio construction and risk management.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Convexity Hedging | Barbell Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Risk management technique targeting interest rate convexity to stabilize bond portfolio value. | Investment strategy using short- and long-term bonds, avoiding intermediate maturities to balance risk and return. |
| Objective | Reduce sensitivity to large interest rate changes by adjusting portfolio convexity. | Optimize yield curve exposure and enhance income with targeted maturity segments. |
| Risk Focus | Interest rate risk, especially curvature changes (convexity). | Interest rate risk across different maturities, focusing on yield curve shape. |
| Portfolio Structure | Dynamic adjustments with derivatives or bond swaps to hedge convexity. | Fixed allocation between short-duration and long-duration bonds. |
| Use Case | Active risk management in volatile interest rate environments. | Income generation with moderate duration risk tolerance. |
| Complexity | Higher complexity requiring continuous monitoring and rebalancing. | Relatively simple, straightforward bond laddering. |
| Benefits | Limits portfolio losses from large interest rate swings. | Combines stability of short bonds with income potential of long bonds. |
| Drawbacks | Costs from frequent adjustments and derivative usage. | May underperform in flattening or inverted yield curves. |
Which is better?
Convexity hedging offers more precise risk management by mitigating interest rate sensitivity in bond portfolios, making it ideal for environments with volatile rate movements. The barbell strategy, combining short- and long-duration bonds, provides balance between yield and interest rate risk, suitable for investors targeting steady income with moderate risk tolerance. Convexity hedging outperforms in complex interest rate scenarios, while the barbell strategy is favored for simplicity and yield enhancement.
Connection
Convexity hedging involves managing the curvature risk of bond prices to protect against interest rate volatility, while the barbell strategy allocates investments between short- and long-term bonds to optimize yield and duration. Both techniques aim to balance interest rate sensitivity by adjusting portfolio convexity, enhancing risk-adjusted returns in fixed income management. Implementing convexity hedging within a barbell strategy helps investors mitigate price fluctuations and take advantage of shifting yield curves effectively.
Key Terms
Yield Curve
The barbell strategy involves investing in short-term and long-term bonds to balance risk and return along the yield curve, enhancing portfolio flexibility amid interest rate fluctuations. Convexity hedging focuses on managing bond portfolio sensitivity to interest rate changes by adjusting exposure to convexity, minimizing price volatility. Explore further to understand which approach aligns best with your yield curve investment objectives.
Duration
The barbell strategy balances portfolio duration by investing in short- and long-term bonds, enhancing returns while maintaining interest rate risk exposure, whereas convexity hedging aims to mitigate the portfolio's sensitivity to interest rate changes by adjusting duration to manage price volatility. Barbell strategies optimize duration positioning for yield curve shifts, while convexity hedging fine-tunes duration to reduce nonlinear risks from interest rate movements. Explore detailed comparisons to optimize your fixed income portfolio's duration management.
Interest Rate Risk
The barbell strategy involves investing in short- and long-term bonds to balance interest rate risk and achieve higher yields with moderate duration exposure, while convexity hedging focuses on adjusting portfolio convexity to mitigate adverse effects of interest rate volatility on bond prices. Barbell strategy offers predictable cash flows from short-term bonds combined with capital appreciation potential from long-term bonds, whereas convexity hedging uses derivatives or bond options to protect against nonlinear price changes due to interest rate movements. Explore how each approach can optimize interest rate risk management in different market environments.
Source and External Links
What's The Barbell Strategy? - Definition, Examples, and More - The barbell strategy is an approach to managing risk by investing in two extremes, such as 90% in safe cash and 10% in highly speculative assets like Bitcoin, to cap downside loss while maintaining high upside potential.
Barbell strategy - Wikipedia - In finance, the barbell strategy involves investing exclusively in short- and long-duration bonds, avoiding intermediate maturities, to benefit from higher yields on long bonds while reducing risk and allowing quick turnover of the short-term investments.
Barbell, Bullet, and Bond Ladder Strategy | Charles Schwab - The barbell bond strategy focuses on short- and long-term bonds to capture rising interest rates, with short-term bonds freeing cash for reinvestment and long-term bonds offering higher yields, making it tactical for a rising-rate environment.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com