Latency arbitrage exploits millisecond-level price discrepancies between markets using high-frequency trading algorithms, while ETF arbitrage focuses on capitalizing on value differences between an ETF's market price and its net asset value (NAV). Both strategies aim to generate risk-free profits by identifying and acting on price inefficiencies in financial markets. Explore deeper insights into how these arbitrage techniques impact trading strategies and market liquidity.
Why it is important
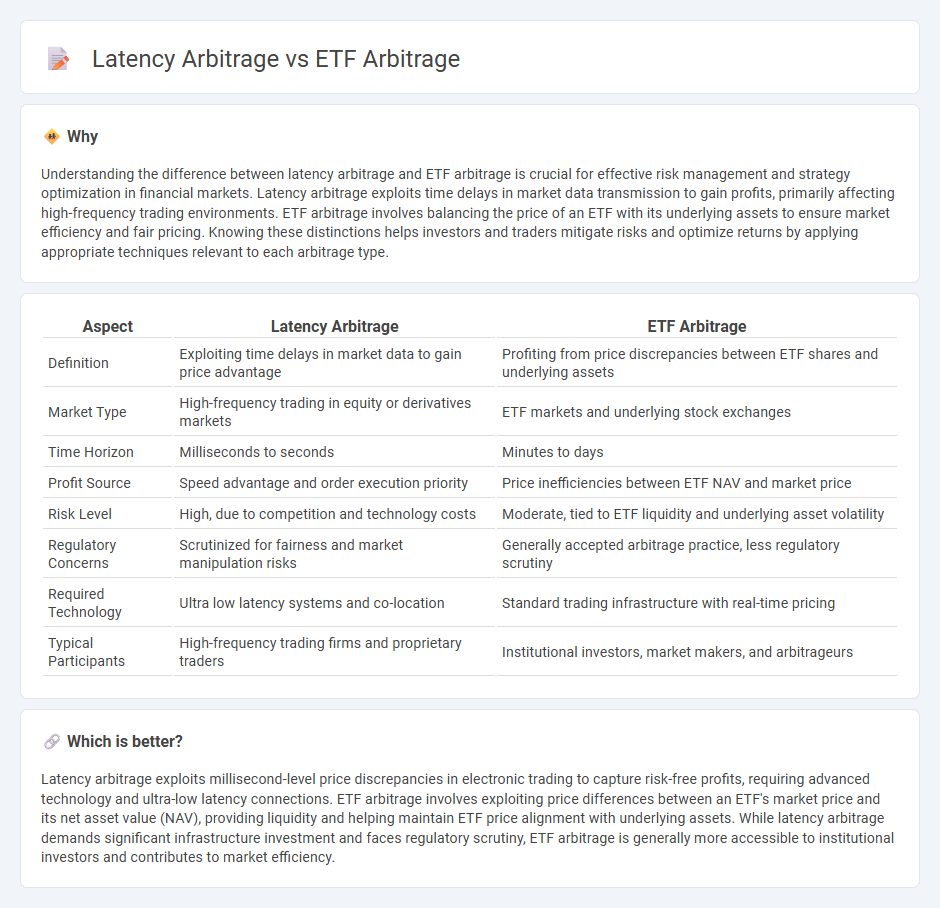
Understanding the difference between latency arbitrage and ETF arbitrage is crucial for effective risk management and strategy optimization in financial markets. Latency arbitrage exploits time delays in market data transmission to gain profits, primarily affecting high-frequency trading environments. ETF arbitrage involves balancing the price of an ETF with its underlying assets to ensure market efficiency and fair pricing. Knowing these distinctions helps investors and traders mitigate risks and optimize returns by applying appropriate techniques relevant to each arbitrage type.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Latency Arbitrage | ETF Arbitrage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Exploiting time delays in market data to gain price advantage | Profiting from price discrepancies between ETF shares and underlying assets |
| Market Type | High-frequency trading in equity or derivatives markets | ETF markets and underlying stock exchanges |
| Time Horizon | Milliseconds to seconds | Minutes to days |
| Profit Source | Speed advantage and order execution priority | Price inefficiencies between ETF NAV and market price |
| Risk Level | High, due to competition and technology costs | Moderate, tied to ETF liquidity and underlying asset volatility |
| Regulatory Concerns | Scrutinized for fairness and market manipulation risks | Generally accepted arbitrage practice, less regulatory scrutiny |
| Required Technology | Ultra low latency systems and co-location | Standard trading infrastructure with real-time pricing |
| Typical Participants | High-frequency trading firms and proprietary traders | Institutional investors, market makers, and arbitrageurs |
Which is better?
Latency arbitrage exploits millisecond-level price discrepancies in electronic trading to capture risk-free profits, requiring advanced technology and ultra-low latency connections. ETF arbitrage involves exploiting price differences between an ETF's market price and its net asset value (NAV), providing liquidity and helping maintain ETF price alignment with underlying assets. While latency arbitrage demands significant infrastructure investment and faces regulatory scrutiny, ETF arbitrage is generally more accessible to institutional investors and contributes to market efficiency.
Connection
Latency arbitrage exploits time delays in market data to gain price advantages, affecting ETF arbitrage by enabling faster traders to capitalize on discrepancies between an ETF's market price and its net asset value. This connection intensifies market efficiency pressures, as latency arbitrageurs continuously narrow ETF price misalignments. Consequently, the interplay between these arbitrage strategies influences liquidity, bid-ask spreads, and price discovery in financial markets.
Key Terms
Net Asset Value (NAV)
ETF arbitrage exploits discrepancies between an ETF's market price and its Net Asset Value (NAV), ensuring prices align through creation and redemption mechanisms. Latency arbitrage leverages millisecond delays in NAV dissemination to trade ahead of others, capitalizing on temporary price inefficiencies. Explore the detailed mechanisms and strategies behind these arbitrage types to deepen your understanding.
Price Discrepancy
ETF arbitrage exploits price discrepancies between an exchange-traded fund (ETF) and its underlying assets, allowing traders to profit by buying undervalued components or selling overvalued ETFs until prices realign. Latency arbitrage leverages speed advantages in accessing market data to capitalize on short-term price differences before competitors, often relying on high-frequency trading algorithms. Explore how these arbitrage strategies optimize market efficiency and impact liquidity dynamics.
Execution Speed
ETF arbitrage exploits price discrepancies between an ETF and its underlying assets, relying on timely execution to capitalize on market inefficiencies. Latency arbitrage depends on ultra-fast access to market data, using minimal execution delays to exploit small price differences before others react. Explore the differences in execution speed and the impact on profitability to understand these arbitrage strategies better.
Source and External Links
The anatomy of bond ETF arbitrage - ETF arbitrage involves authorized participants (APs) creating or redeeming shares using in-kind baskets to exploit price differences between the ETF market price and its underlying assets, keeping ETF prices aligned with NAV through primary and secondary market activity.
Exchange Traded Fund (ETF) Arbitrage - How Does It Work? - ETF arbitrage keeps ETF prices synchronized with their underlying assets by APs buying and selling ETF shares and exchanging them for underlying stocks to profit from price differences, often using automated trading systems.
Understanding ETF trading and liquidity: Arbitrage, premiums, and discounts - The ETF arbitrage mechanism allows APs to exploit price premiums or discounts relative to NAV by creating or redeeming ETF shares, thus maintaining price alignment and market liquidity.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com